Jaguar moved
| Jaguar [1] Panthera onca Temporal range: Early to Middle Pleistocene – Recent
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Genus: | 'Panthera' |
| Species: | ''P. onca'' |
| Binomial name | |
| Panthera onca | |
| |
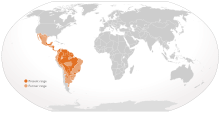
| Jaguar range | |
The jaguar (/ˈdʒæɡjuːər, ˈdʒæɡjʊər, ˈdʒæɡjuːɑːr/ or /ˈdʒæɡwɑːr/;[3] Template:IPA-pt, Spanish:
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI), Panthera onca, is a big cat, a feline in the Panthera genus, and is the only Panthera species native to the Americas. The jaguar is the third-largest feline after the tiger and the lion, and the largest in the Western Hemisphere. The jaguar's present range extends from Southwestern United States and Mexico across much of Central America and south to Paraguay and northern Argentina. Apart from a known and possibly breeding population in Arizona (southeast of Tucson), the cat has largely been extirpated from the United States since the early 20th century.
This spotted cat most closely resembles the leopard physically, although it is usually larger and of sturdier build and its behavioral and habitat characteristics are closer to those of the tiger. While dense rainforest is its preferred habitat, the jaguar will range across a variety of forested and open terrains. It is strongly associated with the presence of water and is notable, along with the tiger, as a feline that enjoys swimming. The jaguar is largely a solitary, opportunistic, stalk-and-ambush predator at the top of the food chain (an apex predator). It is a keystone species, playing an important role in stabilizing ecosystems and regulating the populations of the animals it hunts. The jaguar has an exceptionally powerful bite, even relative to the other big cats.[4] This allows it to pierce the shells of armored reptiles[5] and to employ an unusual killing method: it bites directly through the skull of prey between the ears to deliver a fatal bite to the brain.[6]
The jaguar is a near threatened species and its numbers are declining. Threats include loss and fragmentation of habitat. While international trade in jaguars or their parts is prohibited, the cat is still frequently killed by humans, particularly in conflicts with ranchers and farmers in South America. Although reduced, its range remains large. Given its historical distribution, the jaguar has featured prominently in the mythology of numerous indigenous American cultures, including those of the Maya and Aztec.
Etymology
[edit]The word 'jaguar' comes to English from one of the Tupi–Guarani languages, presumably the Amazonian trade language Tupinambá, via Portuguese jaguar.[7] The Tupian word, yaguara "beast", is sometimes translated as "dog".[8][9] The specific word for jaguar is yaguareté, with the suffix -eté meaning "real" or "true".[7][10]
The first component of its taxonomic designation, Panthera, is Latin, from the Greek word for leopard, πάνθηρ, the type species for the genus. This has been said to derive from the παν- "all" and θήρ from θηρευτής "predator", meaning "predator of all" (animals), though this may be a folk etymology[11]—it may instead be ultimately of Sanskrit origin, from pundarikam, the Sanskrit word for "tiger".[12]
Onca is the Portuguese onça, with the cedilla dropped for typographical reasons, found in English as ounce for the snow leopard, Panthera uncia. It derives from the Latin lyncea lynx, with the letter L confused with the definite article (Italian lonza, Old French l'once).[13]
Taxonomy and evolution
[edit]The jaguar, Panthera onca, is the only extant New World member of the Panthera genus. DNA evidence shows the lion, tiger, leopard, jaguar, snow leopard, and clouded leopard share a common ancestor, and that this group is between six and ten million years old; the fossil record points to the emergence of Panthera just two to 3.8 million years ago.[14][15] Phylogenetic studies generally have shown the clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) is basal to this group.[14][16][17][18] The position of the remaining species varies between studies and is effectively unresolved.
Based on morphological evidence, British zoologist Reginald Pocock concluded the jaguar is most closely related to the leopard.[18] However, DNA evidence is inconclusive and the position of the jaguar relative to the other species varies between studies.[14][16][17][18] Fossils of extinct Panthera species, such as the European jaguar (Panthera gombaszoegensis) and the American lion (Panthera atrox), show characteristics of both the lion and the jaguar.[18] Analysis of jaguar mitochondrial DNA has dated the species' lineage to between 280,000 and 510,000 years ago, later than suggested by fossil records.[19]
Asian ancestry
[edit]While jaguars now live only in the Americas, they are descended from Old World cats. Two million years ago, scientists believe, the jaguar and its closest relative, the similarly spotted leopard, shared a common ancestor in Asia.[20] In the early Pleistocene, the forerunners of modern jaguars crossed Beringia, the land bridge that once spanned the Bering Strait and connected Asia and North America. These jaguar ancestors then moved south into Central and South America, feeding on the deer and other grazing animals that once covered the landscape in huge herds.[20]
Geographical variation
[edit]
The last taxonomic delineation of the jaguar subspecies was performed by Pocock in 1939. Based on geographic origins and skull morphology, he recognized eight subspecies. However, he did not have access to sufficient specimens to critically evaluate all subspecies, and he expressed doubt about the status of several. Later consideration of his work suggested only three subspecies should be recognized.[21]
Recent studies have also failed to find evidence for well-defined subspecies, which are no longer recognized.[22] Larson (1997) studied the morphological variation in the jaguar and showed there is clinal north–south variation, but also the differentiation within the supposed subspecies is larger than that between them, and thus does not warrant subspecies subdivision.[23] A genetic study by Eizirik and coworkers in 2001 confirmed the absence of a clear geographical subspecies structure, although they found that major geographical barriers, such as the Amazon River, limited the exchange of genes between the different populations.[19] A subsequent, more detailed study confirmed the predicted population structure within the Colombian jaguars.[24]
Pocock's subspecies divisions are still regularly listed in general descriptions of the cat.[25] Seymour grouped these in three subspecies.[21]
- Panthera onca onca: Venezuela through the Amazon, including
- P. o. peruviana (Peruvian jaguar): Coastal Peru
- P. o. hernandesii (Mexican jaguar'): Western Mexico – including
- P. o. centralis (Central American jaguar): El Salvador to Colombia
- P. o. arizonensis (Arizonan jaguar): Southern Arizona to Sonora, Mexico
- P. o. veraecrucis: Central Texas to southeastern Mexico

- P. o. goldmani (Goldman's jaguar): Yucatán Peninsula to Belize and Guatemala
- P. o. palustris (the largest subspecies, weighing more than 135 kg or 300 lb):[26] The Pantanal regions of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, along the Paraguay River into Paraguay and northeastern Argentina.
The Mammal Species of the World continues to recognize nine subspecies, the eight subspecies above and additionally P. o. paraguensis.[1]
Biology and behavior
[edit]Physical characteristics
[edit]
The jaguar, a compact and well-muscled animal, is the largest cat in the New World and the largest carnivorous mammal in Central and South America.[27] Size and weight vary considerably: weights are normally in the range of 56–96 kg (124–211 lb). Larger males have been recorded to weigh as much as 158 kg (348 lb)[28][22] (roughly matching a tigress or lioness), and the smallest females have low weights of 36 kg (79 lb).[22] Females are typically 10–20% smaller than males. The length, from the nose to the base of the tail, of the cats varies from 1.12 to 1.85 m (3.7 to 6.1 ft). Their tails are the shortest of any big cat, at 45 to 75 cm (18 to 30 in) in length.[22][29] Their legs are also short, considerably shorter when compared to a small tiger or lion in a similar weight range, but are thick and powerful. The jaguar stands 63 to 76 cm (25 to 30 in) tall at the shoulders.[30] Compared to the similarly colored Old World leopard, this cat is bigger, heavier and relatively stocky in build.[21]
Further variations in size have been observed across regions and habitats, with size tending to increase from the north to south. A study of the jaguar in the Chamela-Cuixmala Biosphere Reserve on the Mexican Pacific coast, showed ranges of just about 50 kg (110 lb), about the size of a female cougar.[31] Jaguars in Venezuela or Brazil are much larger with average weights of about 95 kg (220 lb) in males and of about 56 kilograms (123 lb) to 78 kilograms (172 lb) in females.[21] In the Brazilian Pantanal, weights of 136 kilograms (300 lb) or more are not uncommon in old males,[32] with the highest recorded weight being 148 kilograms (326 lb).[33] Forest jaguars are frequently darker and considerably smaller than those found in open areas (the Pantanal is an open wetland basin), possibly due to the smaller numbers of large, herbivorous prey in forest areas.[34]
A short and stocky limb structure makes the jaguar adept at climbing, crawling, and swimming.[30] The head is robust and the jaw extremely powerful, it has the third highest bite force of all felids, after lion and tiger. A 100 kg (220 lb) jaguar can bite with a force of 503.57 kgf (1110 lbf) at canine teeth and 705.79 kgf (1556 lbf) at carnassial notch.[35] This strength adaptation allows the jaguar to pierce turtle shells.[5] A comparative study of bite force adjusted for body size ranked it as the top felid, alongside the clouded leopard and ahead of the lion and tiger.[36] It has been reported that "an individual jaguar can drag an 800 lb (360 kg) bull 25 ft (7.6 m) in its jaws and pulverize the heaviest bones".[37] The jaguar hunts wild animals weighing up to 300 kg (660 lb) in dense jungle, and its short and sturdy physique is thus an adaptation to its prey and environment. The base coat of the jaguar is generally a tawny yellow, but can range to reddish-brown and black, for most of the body. However, the ventral areas are white.[30] The cat is covered in rosettes for camouflage in the dappled light of its forest habitat. The spots vary over individual coats and between individual jaguars: rosettes may include one or several dots, and the shapes of the dots vary. The spots on the head and neck are generally solid, as are those on the tail, where they may merge to form a band.[21]
While the jaguar closely resembles the leopard, it is sturdier and heavier, and the two animals can be distinguished by their rosettes: the rosettes on a jaguar's coat are larger, fewer in number, usually darker, and have thicker lines and small spots in the middle that the leopard lacks. Jaguars also have rounder heads and shorter, stockier limbs compared to leopards.[38]
Color morphism
[edit]
Color morphism occurs in the species. A near-black melanistic form occurs regularly. Jaguars with melanism appear entirely black, although their spots are still visible on close examination.
The black morph is less common than the spotted form but, at about six percent of the population,[39] it is several orders of magnitude above the rate of mutation. Hence, it is being supported by selection. Some evidence indicates the melanism allele is dominant.[40] The black form may be an example of heterozygote advantage; breeding in captivity is not yet conclusive on this.
Melanistic jaguars are informally known as black panthers, but (as with all forms of polymorphism) they do not form a separate species.
Extremely rare albino individuals, sometimes called white panthers, also occur among jaguars, as with the other big cats.[34] As usual with albinos in the wild, selection keeps the frequency close to the rate of mutation.
Reproduction and life cycle
[edit]
Jaguar females reach sexual maturity at about two years of age, and males at three or four. The cat is believed to mate throughout the year in the wild, although births may increase when prey is plentiful.[41] Research on captive male jaguars supports the year-round mating hypothesis, with no seasonal variation in semen traits and ejaculatory quality; low reproductive success has also been observed in captivity.[42] Female estrus is 6–17 days out of a full 37-day cycle, and females will advertise fertility with urinary scent marks and increased vocalization.[41] Both sexes will range more widely than usual during courtship.
Pairs separate after mating, and females provide all parenting. The gestation period lasts 93–105 days; females give birth to up to four cubs, and most commonly to two. The mother will not tolerate the presence of males after the birth of cubs, given a risk of infanticide; this behavior is also found in the tiger.[43]
The young are born blind, gaining sight after two weeks. Cubs are weaned at three months, but remain in the birth den for six months before leaving to accompany their mother on hunts.[44] They will continue in their mother's company for one to two years before leaving to establish a territory for themselves. Young males are at first nomadic, jostling with their older counterparts until they succeed in claiming a territory. Typical lifespan in the wild is estimated at around 12–15 years; in captivity, the jaguar lives up to 23 years, placing it among the longest-lived cats.[32]
Social activity
[edit]
Like most cats, the jaguar is solitary outside mother–cub groups. Adults generally meet only to court and mate (though limited noncourting socialization has been observed anecdotally[43]) and carve out large territories for themselves. Female territories, which range from 25 to 40 km2 in size, may overlap, but the animals generally avoid one another. Male ranges cover roughly twice as much area, varying in size with the availability of game and space, and do not overlap.[43][45] The jaguar uses scrape marks, urine, and feces to mark its territory.[46][47]
Like the other big cats, the jaguar is capable of roaring[48][49] and does so to warn territorial and mating competitors away; intensive bouts of counter-calling between individuals have been observed in the wild.[50] Their roar often resembles a repetitive cough, and they may also vocalize mews and grunts.[32] Mating fights between males occur, but are rare, and aggression avoidance behavior has been observed in the wild.[46] When it occurs, conflict is typically over territory: a male's range may encompass that of two or three females, and he will not tolerate intrusions by other adult males.[43]
The jaguar is often described as nocturnal, but is more specifically crepuscular (peak activity around dawn and dusk). Both sexes hunt, but males travel farther each day than females, befitting their larger territories. The jaguar may hunt during the day if game is available and is a relatively energetic feline, spending as much as 50–60% of its time active.[34] The jaguar's elusive nature and the inaccessibility of much of its preferred habitat make it a difficult animal to sight, let alone study.
Hunting and diet
[edit]
Like all cats, the jaguar is an obligate carnivore, feeding only on meat. It is an opportunistic hunter and its diet encompasses at least 87 species.[34] The jaguar can take virtually any terrestrial or riparian vertebrate found in Central or South America, with a preference for large prey. The jaguar is more of a dietary generalist than its Old World cousins: the American tropics have a high diversity of small animals but relatively low populations and diversity of the large ungulates which this genus favors.[51] They regularly take adult caimans,[52] deer, capybaras, tapirs, peccaries, dogs, zorros, and sometimes even anacondas.[21] However, the cat will eat any small species that can be caught, including frogs, mice, birds (mainly ground-based species such as cracids), fish, sloths, monkeys, and turtles; a study conducted in Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary in Belize, for example, revealed that the diets of jaguars there consisted primarily of armadillos and pacas.[46] Some jaguars will also take domestic livestock, including adult cattle and horses.[53]
There is evidence that jaguars in the wild consume the roots of Banisteriopsis caapi.[54]
While the jaguar often employs the deep throat-bite and suffocation technique typical among Panthera, it sometimes uses a killing method unique amongst cats: it pierces directly through the temporal bones of the skull between the ears of prey (especially the capybara) with its canine teeth, piercing the brain.[55] This may be an adaptation to "cracking open" turtle shells; following the late Pleistocene extinctions, armored reptiles such as turtles would have formed an abundant prey base for the jaguar.[34][50] The skull bite is employed with mammals in particular; with reptiles such as the caiman, the jaguar may leap onto the back of the prey and sever the cervical vertebrae, immobilizing the target. While capable of cracking turtle shells, the jaguar may simply smash into the shell with its paw and scoop out the flesh.[43] When attacking sea turtles, including the huge Leatherback sea turtle which weighs about 385 kg (849 lb) on average, as they try to nest on beaches, the jaguar will bite at the head, often beheading the prey, before dragging it off to eat.[56] Reportedly, while hunting horses, a jaguar may leap onto their back, place one paw on the muzzle and another on the nape and then twist, dislocating the neck. Local people have anecdotally reported that when hunting a pair of horses bound together, the jaguar will kill one horse and then drag it while the other horse, still living, is dragged in their wake.[57] With prey such as smaller dogs, a paw swipe to the skull may be sufficient to kill it.

The jaguar is a stalk-and-ambush rather than a chase predator. The cat will walk slowly down forest paths, listening for and stalking prey before rushing or ambushing. The jaguar attacks from cover and usually from a target's blind spot with a quick pounce; the species' ambushing abilities are considered nearly peerless in the animal kingdom by both indigenous people and field researchers, and are probably a product of its role as an apex predator in several different environments. The ambush may include leaping into water after prey, as a jaguar is quite capable of carrying a large kill while swimming; its strength is such that carcasses as large as a heifer can be hauled up a tree to avoid flood levels.[43]
On killing prey, the jaguar will drag the carcass to a thicket or other secluded spot. It begins eating at the neck and chest, rather than the midsection. The heart and lungs are consumed, followed by the shoulders.[43] The daily food requirement of a 34 kg (75 lb) animal, at the extreme low end of the species' weight range, has been estimated at 1.4 kg (3.1 lb).[58] For captive animals in the 50–60 kg (110–130 lb) range, more than 2 kg (4.4 lb) of meat daily are recommended.[59] In the wild, consumption is naturally more erratic; wild cats expend considerable energy in the capture and kill of prey, and they may consume up to 25 kg (55 lb) of meat at one feeding, followed by periods of famine.[60] Unlike all other Panthera species, jaguars very rarely attack humans. In most of the few cases where a jaguar has turned to taking a human, the animal was either old with damaged teeth or wounded.[61] Sometimes, if scared or threatened, jaguars in captivity may lash out at zookeepers.[62]
Ecology
[edit]Distribution and habitat
[edit]The jaguar has been an American cat since crossing the Bering Land Bridge during the Pleistocene epoch; the immediate ancestor of modern animals is Panthera onca augusta, which was larger than the contemporary cat.[24] Its present range extends from Mexico, through Central America and into South America, including much of Amazonian Brazil.[63] The countries included in this range are Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica (particularly on the Osa Peninsula), Ecuador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, the United States and Venezuela. The jaguar is now extinct in El Salvador and Uruguay.[2] It occurs in the 400 km² Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary in Belize, the 5,300 km² Sian Ka'an Biosphere Reserve in Mexico, the approximately 15,000 km2 Manú National Park in Peru, the approximately 26,000 km2 Xingu National Park in Brazil, and numerous other reserves throughout its range.

The inclusion of the United States in the list is based on occasional sightings in the southwest, particularly in Arizona, New Mexico and Texas. In the early 20th century, the jaguar's range extended as far north as the Grand Canyon, and as far west as Southern California.[58] The jaguar is a protected species in the United States under the Endangered Species Act, which has stopped the shooting of the animal for its pelt. In 1996 and from 2004 on, wildlife officials in Arizona photographed and documented jaguars in the southern part of the state. Between 2004 and 2007, two or three jaguars have been reported by researchers around Buenos Aires National Wildlife Refuge in southern Arizona. One of them, called 'Macho B', had been previously photographed in 1996 in the area.[64] For any permanent population in the USA to thrive, protection from killing, an adequate prey base, and connectivity with Mexican populations are essential.[65] In February 2009, a 53.5 kg (118 lb) jaguar was caught, radio-collared and released in an area southwest of Tucson, Arizona; this is farther north than had previously been expected and represents a sign there may be a permanent breeding population of jaguars within southern Arizona. The animal was later confirmed to be indeed the same male individual ('Macho B') that was photographed in 2004.[66] On 2 March 2009, Macho B was recaptured and euthanized after he was found to be suffering from kidney failure; the animal was thought to be 16 years old, older than any known wild jaguar.[67]
Completion of the United States–Mexico barrier as currently proposed will reduce the viability of any population currently residing in the United States, by reducing gene flow with Mexican populations, and prevent any further northward expansion for the species.[68]
The historic range of the species included much of the southern half of the United States, and in the south extended much farther to cover most of the South American continent. In total, its northern range has receded 1,000 km (621 mi) southward and its southern range 2,000 km (1243 mi) northward. Ice age fossils of the jaguar, dated between 40,000 and 11,500 years ago, have been discovered in the United States, including some at an important site as far north as Missouri. Fossil evidence shows jaguars of up to 190 kg (420 lb), much larger than the contemporary average for the animal.[69]
The habitat of the cat includes the rain forests of South and Central America, open, seasonally flooded wetlands, and dry grassland terrain. Of these habitats, the jaguar much prefers dense forest;[34] the cat has lost range most rapidly in regions of drier habitat, such as the Argentinian pampas, the arid grasslands of Mexico, and the southwestern United States.[2] The cat will range across tropical, subtropical, and dry deciduous forests (including, historically, oak forests in the United States). The jaguar is strongly associated with water, and it often prefers to live by rivers, swamps, and in dense rainforest with thick cover for stalking prey. Jaguars have been found at elevations as high as 3,800 m, but they typically avoid montane forest and are not found in the high plateau of central Mexico or in the Andes.[34]
Substantial evidence exists for a colony of nonnative, melanistic leopards or jaguars inhabiting the rainforests around Sydney, Australia. A local report compiled statements from over 450 individuals recounting their stories of sighting large black cats in the area, and confidential NSW Government documents regarding the matter proved wildlife authorities were so concerned about the big cats and the danger to humans, they commissioned an expert to catch one. The three-day hunt later failed, but ecologist Johannes J. Bauer warned: "Difficult as it seems to accept, the most likely explanation is the presence of a large, feline predator. In this area, [it is] most likely a leopard, less likely a jaguar."[70]
Ecological role
[edit]The adult jaguar is an apex predator, meaning it exists at the top of its food chain and is not preyed on in the wild. The jaguar has also been termed a keystone species, as it is assumed, through controlling the population levels of prey such as herbivorous and granivorous mammals, apex felids maintain the structural integrity of forest systems.[31][71] However, accurately determining what effect species like the jaguar have on ecosystems is difficult, because data must be compared from regions where the species is absent as well as its current habitats, while controlling for the effects of human activity. It is accepted that mid-sized prey species undergo population increases in the absence of the keystone predators, and this has been hypothesized to have cascading negative effects.[72] However, field work has shown this may be natural variability and the population increases may not be sustained. Thus, the keystone predator hypothesis is not accepted by all scientists.[73]
The jaguar also has an effect on other predators. The jaguar and the cougar, the next-largest feline of the Americas, are often sympatric (related species sharing overlapping territory) and have often been studied in conjunction. Where sympatric with the jaguar, the cougar is smaller than normal and is smaller than the local jaguars. The jaguar tends to take larger prey, usually over 22 kg (49 lb) and the cougar smaller, usually between 2 and 22 kg (4.4 and 48.5 lb), reducing the latter's size.[51][74] This situation may be advantageous to the cougar. Its broader prey niche, including its ability to take smaller prey, may give it an advantage over the jaguar in human-altered landscapes;[31] while both are classified as near-threatened species, the cougar has a significantly larger current distribution.
Conservation status
[edit]
Jaguar populations are rapidly declining. The animal is considered Near Threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN),[2] meaning it may be threatened with extinction in the near future. The loss of parts of its range, including its virtual elimination from its historic northern areas and the increasing fragmentation of the remaining range, have contributed to this status. The 1960s had particularly significant declines, with more than 15,000 jaguar skins brought out of the Brazilian Amazon yearly; the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of 1973 brought about a sharp decline in the pelt trade.[75] Detailed work performed under the auspices of the Wildlife Conservation Society revealed the animal has lost 37% of its historic range, with its status unknown in an additional 18%. More encouragingly, the probability of long-term survival was considered high in 70% of its remaining range, particularly in the Amazon basin and the adjoining Gran Chaco and Pantanal.[63] In 1990 Belize created the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary as the world's first wilderness reserve for jaguar protection and study.
The major risks to the jaguar include deforestation across its habitat, increasing competition for food with human beings,[2] poaching, hurricanes in northern parts of its range, and the behavior of ranchers who will often kill the cat where it preys on livestock. When adapted to the prey, the jaguar has been shown to take cattle as a large portion of its diet; while land clearance for grazing is a problem for the species, the jaguar population may have increased when cattle were first introduced to South America, as the animals took advantage of the new prey base. This willingness to take livestock has induced ranch owners to hire full-time jaguar hunters, and the cat is often shot on sight.[32]

The jaguar is regulated as an Appendix I species under CITES: all international trade in jaguars or their parts is prohibited. All hunting of jaguars is prohibited in Argentina, Belize, Colombia, French Guiana, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Suriname, the United States (where it is listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Act), Uruguay and Venezuela. Hunting of jaguars is restricted to "problem animals" in Brazil, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Mexico and Peru, while trophy hunting is still permitted in Bolivia. The species has no legal protection in Ecuador or Guyana.[25]
Current conservation efforts often focus on educating ranch owners and promoting ecotourism.[76] The jaguar is generally defined as an umbrella species – its home range and habitat requirements are sufficiently broad that, if protected, numerous other species of smaller range will also be protected.[77] Umbrella species serve as "mobile links" at the landscape scale, in the jaguar's case through predation. Conservation organizations may thus focus on providing viable, connected habitat for the jaguar, with the knowledge other species will also benefit.[76]
Given the inaccessibility of much of the species' range, particularly the central Amazon, estimating jaguar numbers is difficult. Researchers typically focus on particular bioregions, thus species-wide analysis is scant. In 1991, 600–1,000 (the highest total) were estimated to be living in Belize. A year earlier, 125–180 jaguars were estimated to be living in Mexico's 4,000-km2 (2400-mi2) Calakmul Biosphere Reserve, with another 350 in the state of Chiapas. The adjoining Maya Biosphere Reserve in Guatemala, with an area measuring 15,000 km2 (9,000 mi2), may have 465–550 animals.[78] Work employing GPS telemetry in 2003 and 2004 found densities of only six to seven jaguars per 100 km2 in the critical Pantanal region, compared with 10 to 11 using traditional methods; this suggests the widely used sampling methods may inflate the actual numbers of cats.[79]
In the past, conservation of jaguars sometimes occurred through the protection of jaguar "hotspots". These hotspots, described as jaguar conservation units, were large areas populated by about 50 jaguars. However, some researchers recently determined, to maintain a robust sharing of the jaguar gene pool necessary for maintaining the species, it is important that the jaguars are interconnected. To facilitate this, a new project, the Paseo del Jaguar, has been established to connect several jaguar hotspots.[80]
Jaguars in the United States
[edit]
The only extant cat native to North America that roars,[81] the jaguar was recorded as an animal of the Americas by Thomas Jefferson in 1799.[82] There are multiple zoological reports of jaguar in California, two as far north as Monterey in 1814 (Langsdorff) and 1826 (Beechey).[83] The coastal Diegueño (Kumeyaay people) of San Diego and Cahuilla Indians of Palm Springs had words for jaguar and the cats persisted there until about 1860.[84] The only recorded description of an active jaguar den with breeding adults and kittens in the U.S. was in the Tehachapi Mountains of California prior to 1860.[83] In 1843, Rufus Sage, an explorer and experienced observer recorded jaguar present on the headwaters of the North Platte River 30–50 miles north of Long's Peak in Colorado. Cabot's 1544 map has a drawing of jaguar ranging over the Pennsylvania and Ohio valleys. Historically, the jaguar was recorded in far eastern Texas, and the northern parts of Arizona and New Mexico. However, since the 1940s, the jaguar has been limited to the southern parts of these states. Although less reliable than zoological records, native American artefacts with possible jaguar motifs range from the Pacific Northwest to Pennsylvania and Florida.[85]
Jaguars were rapidly eliminated in the United States. The last female jaguar in the United States was shot by a hunter in Arizona's White Mountains in 1963. Arizona outlawed jaguar hunting in 1969, but by then no females remained and over the next 25 years only two male jaguars were found (and killed) in Arizona. Then in 1996, Warner Glenn, a rancher and hunting guide from Douglas, Arizona, came across a jaguar in the Peloncillo Mountains and became a jaguar researcher, placing webcams which recorded four more Arizona jaguars.[86] None of the other four male jaguars sighted in Arizona in the last 15 years have been seen since 2006.[87] Then, in 2009, a male jaguar named Macho B, died shortly after being radio-collared by Arizona Game and Fish Department (AGFD) officials in 2009. In the Macho B incident, a former AGFD subcontractor pleaded guilty to violating the endangered species act for trapping the cat and a Game and Fish employee was fired for lying to federal investigators.[81] In 2011, a 200-pound male jaguar was photographed near Cochise in southern Arizona by a hunter after being treed by his dogs (the animal left the scene unharmed). A second 2011 sighting of an Arizona jaguar was reported by a Homeland Security border pilot in June 2011, and conservation researchers sighted two jaguars within 30 miles of the Mexico/U.S. border in 2010.[81] In September 2012, a jaguar was photographed in the Santa Rita Mountains of Arizona, the second such sighting in this region in two years.[88] Apparently this jaguar has been photographed numerous times over the past nine months through June 2013.[89]
Legal action by the Center for Biological Diversity led to federal listing of the cat on the endangered species list in 1997. However, on January 7, 2008, George W. Bush appointee H. Dale Hall, Director of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS), signed a recommendation to abandon jaguar recovery as a federal goal under the Endangered Species Act. Critics, including the Center of Biological Diversity and New Mexico Department of Game and Fish, were concerned the jaguar was being sacrificed for the government's new border fence, which is to be built along many of the cat's typical crossings between the United States and Mexico.[90] In 2010, the Obama Administration reversed the Bush Administration policy and pledged to protect "critical habitat" and draft a recovery plan for the species. The USFWS was ultimately ordered by the court to develop a jaguar recovery plan and designate critical habitat for the cats.[81] On August 20, 2012, the USFWS proposed setting aside 838,232 acres in Arizona and New Mexico—an area larger than Rhode Island—as critical jaguar habitat.[91] On March 4, 2014 Federal wildlife officials set aside nearly 1,200 square miles along the U.S.-Mexico border as habitat essential for the conservation of the jaguar. The reservation includes parts of Pima, Santa Cruz and Cochise counties in Arizona and Hidalgo County in New Mexico.[92]
In mythology and culture
[edit]Pre-Columbian Americas
[edit]

In pre-Columbian Central and South America, the jaguar was a symbol of power and strength. Among the Andean cultures, a jaguar cult disseminated by the early Chavín culture became accepted over most of what is today Peru by 900 BC. The later Moche culture of northern Peru used the jaguar as a symbol of power in many of their ceramics.[93][94][95]
In Mesoamerica, the Olmec—an early and influential culture of the Gulf Coast region roughly contemporaneous with the Chavín—developed a distinct "were-jaguar" motif of sculptures and figurines showing stylised jaguars or humans with jaguar characteristics. In the later Maya civilization, the jaguar was believed to facilitate communication between the living and the dead and to protect the royal household. The Maya saw these powerful felines as their companions in the spiritual world, and a number of Maya rulers bore names that incorporated the Mayan word for jaguar (b'alam in many of the Mayan languages). The Aztec civilization shared this image of the jaguar as the representative of the ruler and as a warrior. The Aztecs formed an elite warrior class known as the Jaguar Knights. In Aztec mythology, the jaguar was considered to be the totem animal of the powerful deity Tezcatlipoca.[43][96]
Contemporary culture
[edit]The jaguar and its name are widely used as a symbol in contemporary culture. It is the national animal of Guyana, and is featured in its coat of arms.[97] The flag of the Department of Amazonas, a Colombian department, features a black jaguar silhouette pouncing towards a hunter.[98] The jaguar also appears in banknotes of Brazilian real. The jaguar is also a common fixture in the mythology of many contemporary native cultures in South America,[99] usually being portrayed as the creature which gave humans the power over fire.
Jaguar is widely used as a product name, most prominently for a British luxury car brand. The name has been adopted by sports franchises, including the NFL's Jacksonville Jaguars and the Mexican soccer club Chiapas F.C. The crest of Argentina's national federation in rugby union features a jaguar; however, because of a historic accident, the country's national team is nicknamed Los Pumas.[100] In the spirit of the ancient Mayan culture, the 1968 Olympics in Mexico City adopted a red jaguar as the first official Olympic mascot.[101]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Template:MSW3 Wozencraft
- ^ a b c d e Template:IUCN Database entry includes justification for why this species is near threatened.
- ^ The pronunciation /ˈdʒæɡwɑːr/ is North American.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ a b Hamdig, Paul. "Sympatric Jaguar and Puma". Ecology Online Sweden via archive.org. Archived from the original on 1 February 2008. Retrieved 19 March 2009.
- ^ de la Rosa, Carlos Leonardo and Nocke, Claudia C. (2000). A guide to the carnivores of Central America: natural history, ecology, and conservation. University of Texas Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-292-71604-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Jaguar". Online Etymology Dictionary. Douglas Harper. Retrieved 6 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help) - ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Díaz, Eduardo Acevedo (1890). "Notas". Nativas (in Spanish). Retrieved 29 September 2006.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ "panther", Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition
- ^ "Panther". Online Etymology Dictionary. Douglas Harper. Retrieved 26 October 2006.
- ^ "ounce" 2, Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition
- ^ a b c Johnson, W. E., Eizirik, E., Pecon-Slattery, J., Murphy, W. J., Antunes, A., Teeling, E. and O'Brien, S. J. (2006). "The Late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: A genetic assessment". Science. 311 (5757): 73–7. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. PMID 16400146.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Turner, A. (1987). "New fossil carnivore remains from the Sterkfontein hominid site (Mammalia: Carnivora)". Annals of the Transvaal Museum. 34: 319–347. ISSN 0041-1752.
- ^ a b Yu, L. Zhang, Y. P. (2005). "Phylogenetic studies of pantherine cats (Felidae) based on multiple genes, with novel application of nuclear beta-fibrinogen intron 7 to carnivores". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 35 (2): 483–95. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.01.017. PMID 15804417.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Johnson, W. E. and Obrien, S. J. (1997). "Phylogenetic reconstruction of the Felidae using 16S rRNA and NADH-5 mitochondrial genes". Journal of Molecular Evolution. 44: S98–116. doi:10.1007/PL00000060. PMID 9071018.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d Janczewski, Dianne N.; Modi, William S.; Stephens, J. Claiborne and O'Brien, Stephen J. (1996). "Molecular Evolution of Mitochondrial 12S RNA and Cytochrome b Sequences in the Pantherine Lineage of Felidae". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 12 (4): 690–707. PMID 7544865. Retrieved 6 August 2006.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Eizirik E.; Kim, J. H., Menotti-Raymond M., Crawshaw P. G., Jr; O'Brien, S. J., Johnson, W. E. (2001). "Phylogeography, population history and conservation genetics of jaguars (Panthera onca, Mammalia, Felidae)". Molecular Ecology. 10 (1): 65–79. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2001.01144.x. PMID 11251788.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Spirits of the Jaguar". PBS online – Nature. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f Seymour, K.L. (1989). "Panthera onca" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 340 (340): 1–9. doi:10.2307/3504096. JSTOR 3504096. Retrieved 27 December 2009.
- ^ a b c d Nowak, Ronald M (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Vol. 2. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 831. ISBN 0-8018-5789-9.
- ^ Larson, Shawn E. (1997). "Taxonomic re-evaluation of the jaguar". Zoo Biology. 16 (2): 107. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2361(1997)16:2<107::AID-ZOO2>3.0.CO;2-E.
- ^ a b Ruiz-Garcia, M.; Payan, E; Murillo, A. and Alvarez, D. (2006). "DNA microsatellite characterization of the jaguar (Panthera onca) in Colombia" (PDF). Genes & Genetic Systems. 81 (2): 115–127. doi:10.1266/ggs.81.115. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Baker, Taxonomy, pp. 5–7.
- ^ "Brazil nature tours, Pantanal nature tours, Brazil tours, Pantanal birding tours, Amazon tours, Iguazu Falls tours, all Brazil tours". Focustours.com. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 28 February 2007.
- ^ Anton, Mauricio (1997). The Big Cats and Their Fossil Relatives. Columbia University Press. p. 63. ISBN 978-0-231-10228-5.
- ^ Burnien, David and Wilson, Don E. (2001). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. New York City: Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 0-7894-7764-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Boitani, Luigi (1984). Simon and Schuster's Guide to Mammals. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-43727-5.
- ^ a b c "All about Jaguars: Ecology". Wildlife Conservation Society. Archived from the original on 29 May 2009. Retrieved 11 August 2006.
- ^ a b c Rodrigo Nuanaez, Brian Miller, and Fred Lindzey (2000). "Food habits of jaguars and pumas in Jalisco, Mexico". Journal of Zoology. 252 (3): 373. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb00632.x. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d "Jaguar Fact Sheet". Jaguar Species Survival Plan. American Zoo and Aquarium Association. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
- ^ http://img17.imageshack.us/img17/5272/heaviestjaguar148kg.jpg
- ^ a b c d e f g Nowell, K. and Jackson, P., ed. (1996). "Panthera Onca". Wild Cats. Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan (PDF). Gland, Switzerland: IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group. IUCN. pp. 118–122. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ar.22518/full
- ^ "Search for the Jaguar". National Geographic Specials. Kentucky Educational Television. 2003. Retrieved 19 March 2012.
- ^ McGrath, Susan (August 2004). "Top Cat". National Audubon Society. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Jaguar (panthera onca)". Our animals. Akron Zoo. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 11 August 2006.
- ^ Dinets, Vladmir. "First documentation of melanism in the jaguar (Panthera onca) from northern Mexico". Retrieved 29 September 2006.
- ^ Meyer, John R. (1994). "Black jaguars in Belize?: A survey of melanism in the jaguar, Panthera onca". Belize Explorer Group. biological-diversity.info.
- ^ a b Baker, Reproduction, pp. 28–38.
- ^ Morato, R. G.; Vaz Guimaraes, M; A; B.; Ferriera, F.; Nascimento Verreschi, I. T. and Renato Campanarut Barnabe (1999). "Reproductive characteristics of captive male jaguars". Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Research and Animal Science. 36 (5). Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g h Baker, Natural History and Behavior, pp. 8–16.
- ^ <Please add first missing authors to populate metadata.> (Spring 2006). "Jaguars: Magnificence in the Southwest" (PDF). Newsletter. Southwest Wildlife Rehabilitation & Educational Foundation. Retrieved 6 December 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Schaller, George B. and Crawshaw, Peter Gransden, Jr. (1980). "Movement Patterns of Jaguar". Biotropica. 12 (3): 161–168. doi:10.2307/2387967. JSTOR 2387967.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Rabinowitz, A. R., Nottingham, B. G., Jr (1986). "Ecology and behaviour of the Jaguar (Panthera onca) in Belize, Central America". Journal of Zoology. 210 (1): 149. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1986.tb03627.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Overlapping male ranges are observed in this study in Belize. Note the overall size of ranges is about half of normal. - ^ An Error Occurred Setting Your User Cookie
- ^ Weissengruber, G. E.; Forstenpointner, G.; Peters, G.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Fitch, W. T. (2002). "Hyoid apparatus and pharynx in the lion (Panthera leo), jaguar (Panthera onca), tiger (Panthera tigris), cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) and domestic cat (Felis silvestris f. catus)". Journal of Anatomy. 201 (3): 195–209. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00088.x. PMC 1570911. PMID 12363272.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hast, M. H. (1989). "The larynx of roaring and non-roaring cats". Journal of Anatomy. 163: 117–121. PMC 1256521. PMID 2606766.
- ^ a b Emmons, Louise H. (1987). "Comparative feeding ecology of felids in a neotropical rainforest". Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 20 (4): 271. doi:10.1007/BF00292180.
- ^ a b Brakefield, T. (1993). Big Cats: Kingdom of Might. ISBN 0-89658-329-5.
- ^ Otfinoski, Steven (2010). Jaguars. Marshall Cavendish. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-7614-4839-6. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Jaguar". Kids' Planet. Defenders of Wildlife. Retrieved 23 September 2006.
- ^ Robin Rood (2011). "Reassessing the Cultural and Psychopharmacological Significance of Banisteriopsis caapi: Preparation, Classification and Use Among the Piaroa of Southern Venezuela". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 40 (3): 301–307. doi:10.1080/02791072.2008.10400645.
- ^ Schaller, G. B. and Vasconselos, J. M. C. (1978). "Jaguar predation on capybara" (PDF). Z. Saugetierk. 43: 296–301. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Travellers' Wildlife Guide to Costa Rica by Les Beletsky. Interlink Publishing Group (2004), ISBN 1566565294
- ^ The animal kingdom: based upon the writings of the eminent naturalists Audubon, Wallace, Brehm, Wood, and Others, edited by Hugh Craig. Trinity College (1897), New York.
- ^ a b "Determination That Designation of Critical Habitat Is Not Prudent for the Jaguar". Federal Register Environmental Documents. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 30 August 2006.
- ^ Baker, Hand-rearing, pp. 62–75 (table 5).
- ^ Baker, Nutrition, pp. 55–61.
- ^ "Jaguar". Catsurvivaltrust.org. 9 March 2002. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ "Jaguar: The Western Hemisphere's Top Cat". Planeta. February 2008. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ a b Sanderson, E. W.; Redford, K. H.; Chetkiewicz, C-L. B.; Medellín, R. A.; Rabinowitz, A. R.: Robinson, J. G. and Taber, A. B. (2002). "Planning to Save a Species: the Jaguar as a Model" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 16 (1): 58. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2002.00352.x. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Detailed analysis of present range and terrain types provided here. - ^ Mccain, Emil B. and Childs, Jack L. (2008). "Evidence of resident Jaguars (Panthera onca) in the Southwestern United States and the Implications for Conservation" (PDF). Journal of Mammalogy. 89 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1644/07-MAMM-F-268.1. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Jaguar Management". Arizona Game and Fish Department. 2009. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
- ^ "Arizona Game and Fish collars first wild jaguar in United States". Readitnews.com. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ Hock, Heather (2 March 2009). "Illness forced vets to euthuanize recaptured jaguar". Azcentral.com. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ "Addressing the Impacts of Border Security Activities On Wildlife and Habitat in Southern Arizona: Stakeholder Recommendations" (PDF). Wildlands Project. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 July 2007. Retrieved 3 November 2008.
- ^ "Jaguars". The Midwestern United States 16,000 years ago. Illinois State Museum. Retrieved 20 August 2006.
- ^ "On the hunt for the big cat that refuses to die". Sydney Morning Herald. 20 June 2010. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Jaguar (Panthera Onca)" (PDF). Phoenix Zoo. Retrieved 30 August 2006.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Iriarte, J. A.; Franklin, W. L.; Johnson, W. E. and Redford, K. H. (1990). "Biogeographic variation of food habits and body size of the America puma". Oecologia. 85 (2): 185. doi:10.1007/BF00319400.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Weber, William; Rabinowitz, Alan (August 1996). "A Global Perspective on Large Carnivore Conservation" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 10 (4): 1046–1054. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10041046.x. Retrieved 17 December 2009.
- ^ a b Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Baker, Protection and Population Status, p. 4.
- ^ Soisalo, M. K. and Cavalcanti, S. M. C. (2006). "Estimating the density of a jaguar population in the Brazilian Pantanal using camera-traps and capture–recapture sampling in combination with GPS radio-telemetry" (PDF). Biological Conservation. 129 (4): 487. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2005.11.023. Retrieved 8 August 2006.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Path of the jaguars project". Ngm.nationalgeographic.com. March 2009. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ^ a b c d Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Full text of "The writings of Thomas Jefferson"
- ^ a b Merriam, C. Hart (1919). "Is the Jaguar Entitled to a Place in the California Fauna?". Journal of Mammalogy. 1: 38–40.
- ^ Pavlik, Steve (2003). "Rohonas and Spotted Lions: The Historical and Cultural Occurrence of the Jaguar, Panthera onca, among the Native Tribes of the American Southwest". Wicazo Sa Review. 18 (1): 157–175. doi:10.1353/wic.2003.0006. JSTOR 1409436.
- ^ Daggett, Pierre M. and Henning, Dale R. (1974). "The Jaguar in North America". American Antiquity. 39 (3): 465–469. doi:10.2307/279437. JSTOR 279437.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Will Rizzo (December 2005). "Return of the Jaguar?". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 23 November 2011.
- ^ Davis, Tony and Steller, Tim (22 November 2011). "Jaguar seen in area of Cochise". Arizona Daily Star. Retrieved 23 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Davis, Tony (25 November 2012). "Jaguar photo taken near Rosemont". azstarnet.com. Arizona Daily Star. Retrieved 1 December 2012.
- ^ Tony Davis (28 June 2013). "Jaguar roves near Rosemount mine site". Arizona Daily Star. Retrieved 29 June 2013.
- ^ Matlock, Staci (17 January 2008). "Jaguar recovery efforts lack support from federal agency" (PDF). The New Mexican. Retrieved 28 November 2011.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Museo Arqueologico Rafael Larco Herrera (1997). Berrin, Katherine (ed.). The Spirit of Ancient Peru: Treasures from the Museo Arqueologico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York City: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-01802-2.
- ^ Bulliet, Richard W.; et al. (2010). The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History. Cengage Learning. pp. 75–. ISBN 978-1-4390-8476-2. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Lockard, Craig A. (2010). Societies, Networks, and Transitions, Volume I: To 1500: A Global History. Cengage Learning. pp. 215–. ISBN 978-1-4390-8535-6. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
- ^ Christenson, Allen J. (2007). Popol Vuh: The Sacred Book of the Maya. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 196. ISBN 978-0-8061-3839-8. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
- ^ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ^ Gutterman, D. (26 July 2008). "Amazonas Department (Colombia)". Fotw.net. Retrieved 2 April 2010.
- ^ Levi-Strauss, Claude (2004) [1964]. O Cru e o Cozido. São Paulo: Cosac & Naify. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ Davies, Sean (26 July 2007). "Puma power: Argentinian rugby". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 8 October 2007.
- ^ Welch, Paula. Cute Little Creatures: Mascots Lend a Smile to the Games (PDF). Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
Bibliography
[edit]- Baker, W. K., Jr.; et al. Law, Christopher (ed.). Guidelines for Captive Management of Jaguars (PDF). Jaguar Species Survival Plan. American Zoo and Aquarium Association. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
[edit]- Brown, David, and Carlos A. López González (2001). Borderland Jaguars. University of Utah Press. ISBN 978-0-87480-696-0.
External links
[edit]Template:Side box Template:Wikispecies
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- Sound of a jaguar roar at Vivanatura.org
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- People and Jaguars a Guide for Coexistence
- Felidae Conservation Fund
- Template:Cite Americana

Template:Brazil symbols Check API scriptCheck API scriptCheck API scriptCheck API scriptCheck API scriptCheck API scriptCheck API script
- Pages using the JsonConfig extension
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list
- CS1 errors: markup
- CS1 Spanish-language sources (es)
- CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list
- CS1 errors: missing periodical
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from January 2014
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- CS1 errors: explicit use of et al.
- CS1 errors: periodical ignored
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Use dmy dates from June 2011
- Wikipedia pages with incorrect protection templates
- IUCN Red List near threatened species
- Articles with 'species' microformats
- Taxoboxes with the error color
- Taxobox articles possibly missing a taxonbar
- Spoken articles
- Articles with hAudio microformats
- Featured articles
- Animals described in 1758
- Apex predators
- Fauna of the Southwestern United States
- Mammals of Belize
- Mammals of Costa Rica
- Mammals of Guatemala
- Mammals of Honduras
- Mammals of Mexico
- Mammals of North America
- Mammals of South America
- Mammals of the United States
- Mammals of Venezuela
- Megafauna of North America
- Megafauna of South America
- National symbols of Guyana
- Near threatened fauna of the United States
- Near threatened animals
- Panthera

