Denmark
Coordinates: 56°N 10°E / 56°N 10°E
Template:Infobox political division
Denmark (Danish: [Danmark] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), Template:IPA-da) is a Nordic constituent country in Northern Europe. It is the metropolitan part of and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,[N 1] a constitutionally unitary state that includes the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland in the North Atlantic Ocean.[1] Metropolitan Denmark[N 2] is the southernmost of the Scandinavian countries, lying south-west and south (Bornholm and Ertholmene) of Sweden, south of Norway,[N 3] and north of Germany, with which it shares a short and only land border.
As of 2013, the Kingdom of Denmark, including the Faroe Islands and Greenland, has a total of 1,419 islands above 100 square metres (1,100 sq ft); 443 of which have been named and of which 78 are inhabited.[2] Spanning a total area of 42,943 km2 (16,580 sq mi),[3] metropolitan Denmark consists of the northern part of the Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands.[4] Of these, the most populated island is Zealand, on which the capital Copenhagen is situated, followed by Funen, the North Jutlandic Island, and Amager.[5] Denmark's geography is characterised by flat, arable land, sandy coasts, low elevation, and a temperate climate. It had a population of 5.935 million (1 February 2023), of which 800,000 (2 million in the wider area) live in the capital and largest city, Copenhagen.[6] Denmark exercises hegemonic influence in the Danish Realm, devolving powers to handle internal affairs. Home rule was established in the Faroe Islands in 1948 and in Greenland in 1979; the latter obtained further autonomy in 2009.
The unified Kingdom of Denmark emerged in the eighth century as a proficient maritime power amid the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea.[7] In 1397, it joined Norway and Sweden to form the Kalmar Union, which persisted until the latter's secession in 1523. The remaining Kingdom of Denmark–Norway endured a series of wars in the 17th century that resulted in further territorial cessions to the Swedish Empire. Following the Napoleonic Wars, Norway was absorbed into Sweden, leaving Denmark with the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland. A surge of nationalist movements in the 19th century were defeated in the First Schleswig War of 1848, though the Second Schleswig War of 1864 resulted in further territorial losses to Prussia. The period saw the adoption of the Constitution of Denmark on 5 June 1849, ending the absolute monarchy that was established in 1660 and introducing the current parliamentary system.
An industrialised exporter of agricultural produce in the second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social and labour-market reforms in the early 20th century, which formed the basis for the present welfare state model and advanced mixed economy. Denmark remained neutral during World War I but regained the northern half of Schleswig in 1920. Danish neutrality was violated in World War II following a swift German invasion in April 1940. During occupation, a resistance movement emerged in 1943 while Iceland declared independence in 1944; Denmark was liberated in May 1945. Soviet forces left Bornholm 5 April 1946. In 1973, Denmark, together with Greenland but not the Faroes, became a member of what is now the European Union, but negotiated certain opt-outs, such as retaining its own currency, the krone.
Denmark is a developed country with a high standard of living. Denmark is a founding member of NATO, the Nordic Council, the OECD, OSCE, and the United Nations; it is also part of the Schengen Area. Denmark maintains close political, cultural, and linguistic ties with its Scandinavian neighbours, with the Danish language being partially mutually intelligible with both Norwegian and Swedish.
Etymology
[edit]The etymology of the name "Denmark", the relationship between "Danes" and "Denmark", and the emergence of Denmark as a unified kingdom are topics of continuous scholarly debate.[8][9] This is centred primarily on the prefix "Dan" and whether it refers to the Dani or a historical person Dan and the exact meaning of the -"mark" ending.
Most etymological dictionaries and handbooks derive "Dan" from a word meaning "flat land",[10] related to German Tenne "threshing floor", English den "cave".[10] The element mark is believed to mean woodland or borderland (see marches), with probable references to the border forests in south Schleswig.[11]
The first recorded use of the word Danmark within Denmark itself is found on the two Jelling stones, which are runestones believed to have been erected by Gorm the Old (c. 955) and Harald Bluetooth (c. 965). The larger of the two stones is popularly cited as the "baptismal certificate" (dåbsattest) of Denmark,[12] though both use the word "Denmark", in the accusative Template:Runic tanmaurk (
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI) on the large stone, and the genitive Template:Runic "tanmarkar" (pronounced
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI) on the small stone, while the dative form tąnmarku (pronounced
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI) is found on the contemporaneous Skivum stone. The inhabitants of Denmark are there called tani (
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI), or "Danes", in the accusative.
History
[edit]Prehistory
[edit]
The earliest archaeological finds in Denmark date back to the Eem interglacial period from 130,000 to 110,000 BC.[13] Denmark has been inhabited since around 12,500 BC and agriculture has been evident since 3900 BC.[14] The Nordic Bronze Age (1800–600 BC) in Denmark was marked by burial mounds, which left an abundance of findings including lurs and the Sun Chariot.
During the Pre-Roman Iron Age (500 BC – AD 1), native groups began migrating south, and the first tribal Danes came to the country between the Pre-Roman and the Germanic Iron Age,[15] in the Roman Iron Age (AD 1–400).[14] The Roman provinces maintained trade routes and relations with native tribes in Denmark, and Roman coins have been found in Denmark. Evidence of strong Celtic cultural influence dates from this period in Denmark and much of North-West Europe and is among other things reflected in the finding of the Gundestrup cauldron.
The tribal Danes came from the east Danish islands (Zealand) and Scania and spoke an early form of North Germanic. Historians believe that before their arrival, most of Jutland and the nearest islands were settled by tribal Jutes. The Jutes migrated to Great Britain eventually, some as mercenaries of Brythonic King Vortigern, and were granted the south-eastern territories of Kent, the Isle of Wight and other areas, where they settled. They were later absorbed or ethnically cleansed by the invading Angles and Saxons, who formed the Anglo-Saxons. The remaining Jutish population in Jutland assimilated in with the settling Danes.
A short note about the Dani in Getica by the historian Jordanes is believed to be an early mention of the Danes, one of the ethnic groups from whom modern Danes are descended.[16][17] The Danevirke defence structures were built in phases from the 3rd century forward and the sheer size of the construction efforts in AD 737 are attributed to the emergence of a Danish king.[18] A new runic alphabet was first used around the same time and Ribe, the oldest town of Denmark, was founded about AD 700.
Viking and Middle Ages
[edit]
From the 8th to the 10th century the wider Scandinavian region was the source of Vikings. They colonised, raided, and traded in all parts of Europe. The Danish Vikings were most active in the eastern and southern British Isles and Western Europe. They settled in parts of England (known as the Danelaw) under King Sweyn Forkbeard in 1013, and in France where Danes and Norwegians were allowed to settle in what would become Normandy in exchange of allegiance to Robert I of France with Rollo as first ruler. Some Anglo-Saxon pence of this period have been found in Denmark.[19]

Denmark was largely consolidated by the late 8th century and its rulers are consistently referred to in Frankish sources as kings (reges). Under the reign of Gudfred in 804 the Danish kingdom may have included all the lands of Jutland, Scania and the Danish islands, excluding Bornholm.[20]
The extant Danish monarchy traces its roots back to Gorm the Old, who established his reign in the early 10th century.[7] As attested by the Jelling stones, the Danes were Christianised around 965 by Harald Bluetooth, the son of Gorm. It is believed that Denmark became Christian for political reasons so as not to get invaded by the Holy Roman Empire. A rising Christian power in Europe, the Holy Roman Empire was an important trading partner for the Danes. As a deterrent against this threat, Harald built six fortresses around Denmark called Trelleborg and built a further Danevirke. In the early 11th century, Canute the Great won and united Denmark, England, and Norway for almost 30 years with a Scandinavian army.[19]
Throughout the High and Late Middle Ages, Denmark also included Skåneland (the areas of Scania, Halland, and Blekinge in present-day south Sweden) and Danish kings ruled Danish Estonia, as well as the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. Most of the latter two now form the state of Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany.
In 1397, Denmark entered into a personal union with Norway and Sweden, united under Queen Margaret I.[21] The three countries were to be treated as equals in the union. However, even from the start, Margaret may not have been so idealistic—treating Denmark as the clear "senior" partner of the union.[22] Thus, much of the next 125 years of Scandinavian history revolves around this union, with Sweden breaking off and being re-conquered repeatedly. The issue was for practical purposes resolved on 17 June 1523, as Swedish King Gustav Vasa conquered the city of Stockholm. The Protestant Reformation spread to Scandinavia in the 1530s, and following the Count's Feud civil war, Denmark converted to Lutheranism in 1536. Later that year, Denmark entered into a union with Norway.
Early modern history (1536–1849)
[edit]
After Sweden permanently broke away from the personal union, Denmark tried on several occasions to reassert control over its neighbour. King Christian IV attacked Sweden in the 1611–1613 Kalmar War but failed to accomplish his main objective of forcing it to return to the union. The war led to no territorial changes, but Sweden was forced to pay a war indemnity of 1 million silver riksdaler to Denmark, an amount known as the Älvsborg ransom.[23] King Christian used this money to found several towns and fortresses, most notably Glückstadt (founded as a rival to Hamburg) and Christiania. Inspired by the Dutch East India Company, he founded a similar Danish company and planned to claim Ceylon as a colony, but the company only managed to acquire Tranquebar on India's Coromandel Coast. Denmark's large colonial aspirations included a few key trading posts in Africa and India. While Denmark's trading posts in India were of little note, it played an important role in the highly lucrative Atlantic slave trade, through its trading outposts in Fort Christiansborg in Osu, Ghana through which 1.5 million slaves were traded.[24] While the Danish colonial empire was sustained by trade with other major powers, and plantations – ultimately a lack of resources led to its stagnation.[25]
In the Thirty Years' War, Christian tried to become the leader of the Lutheran states in Germany but suffered a crushing defeat at the Battle of Lutter.[26] The result was that the Catholic army under Albrecht von Wallenstein was able to invade, occupy, and pillage Jutland, forcing Denmark to withdraw from the war.[27] Denmark managed to avoid territorial concessions, but King Gustavus Adolphus' intervention in Germany was seen as a sign that the military power of Sweden was on the rise while Denmark's influence in the region was declining. Swedish armies invaded Jutland in 1643 and claimed Scania in 1644. In the 1645 Treaty of Brømsebro, Denmark surrendered Halland, Gotland, the last parts of Danish Estonia, and several provinces in Norway.

Seeing an opportunity to tear up the Treaty of Brømsebro, King Frederick III of Denmark, in 1657, declared war on Sweden, the latter being deeply involved in the Second Northern War (1655–1660), and marched on Bremen-Verden. This led to a massive Danish defeat as the armies of King Charles X Gustav of Sweden conquered Jutland and, following the Swedish March across the frozen Danish straits, occupied Funen and much of Zealand before signing the Peace of Roskilde in February 1658, which gave Sweden control of Scania, Blekinge, Bohuslän, Trøndelag, and the island of Bornholm. Charles X Gustav quickly regretted not having ruined Denmark and in August 1658, he launched a second attack on Denmark, conquered most of the Danish islands, and began a two-year-long siege of Copenhagen. King Frederick III actively led the defence of the city, rallying its citizens to take up arms, and repelled the Swedish attacks.[28][29] The siege ended following the death of Charles X Gustav in 1660.[30] In the ensuing peace settlement, Denmark managed to maintain its independence and regain control of Trøndelag and Bornholm.[31] Attaining great popularity following the war, Frederick III used this to disband the elective monarchy in favour of absolute monarchy, which lasted until 1848 in Denmark.[32]
Denmark tried but failed to regain control of Scania in the Scanian War (1675–1679). After the Great Northern War (1700–21), Denmark managed to regain control of the parts of Schleswig and Holstein ruled by the house of Holstein-Gottorp in the 1720 Treaty of Frederiksborg and the 1773 Treaty of Tsarskoye Selo, respectively. Denmark prospered greatly in the last decades of the 18th century due to its neutral status allowing it to trade with both sides in the many contemporary wars. In the Napoleonic Wars, Denmark traded with both France and the United Kingdom and joined the League of Armed Neutrality with Russia, Sweden, and Prussia.[33] The British considered this a hostile act and attacked Copenhagen in 1801 and 1807, in one case carrying off the Danish fleet, in the other, burning large parts of the Danish capital. This led to the so-called Danish-British Gunboat War. British control of the waterways between Denmark and Norway proved disastrous to the union's economy and in 1813 Denmark–Norway went bankrupt.
The union was dissolved by the Treaty of Kiel in 1814; the Danish monarchy "irrevocably and forever" renounced claims to the Kingdom of Norway in favour of the Swedish king.[34] Denmark kept the possessions of Iceland (which retained the Danish monarchy until 1944), the Faroe Islands and Greenland, all of which had been governed by Norway for centuries.[35] Apart from the Nordic colonies, Denmark continued to rule over Danish India from 1620 to 1869, the Danish Gold Coast (Ghana) from 1658 to 1850, and the Danish West Indies from 1671 to 1917.
Constitutional monarchy (1849–present)
[edit]
Liberal movement and cession of Schleswig and Holstein
[edit]A nascent Danish liberal and national movement gained momentum in the 1830s; after the European Revolutions of 1848, Denmark peacefully became a constitutional monarchy on 5 June 1849. A new constitution established a two-chamber parliament. Denmark faced war against both Prussia and Austrian Empire in what became known as the Second Schleswig War, lasting from February to October 1864. Denmark was defeated and obliged to cede Schleswig and Holstein to Prussia. This loss came as the latest in the long series of defeats and territorial losses that had begun in the 17th century. After these events, Denmark pursued a policy of neutrality in Europe.
Industrialization
[edit]Industrialisation came to Denmark in the second half of the 19th century.[36] The nation's first railways were constructed in the 1850s, and improved communications and overseas trade allowed industry to develop in spite of Denmark's lack of natural resources. Trade unions developed, starting in the 1870s. There was a considerable migration of people from the countryside to the cities, and Danish agriculture became centred on the export of dairy and meat products.
Denmark in World War I
[edit]Denmark maintained its neutral stance during World War I. After the defeat of Germany, the Versailles powers offered to return the region of Schleswig-Holstein to Denmark. Fearing German irredentism, Denmark refused to consider the return of the area without a plebiscite; the two Schleswig Plebiscites took place on 10 February and 14 March 1920, respectively. On 10 July 1920, Northern Schleswig was recovered by Denmark, thereby adding some 163,600 inhabitants and 3,984 square kilometres (1,538 sq mi). The country's first social democratic government took office in 1924.[37]
German non-aggression pact and invasion
[edit]In 1939 Denmark signed a 10-year non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany but Germany invaded Denmark on 9 April 1940 and the Danish government quickly surrendered. World War II in Denmark was characterised by economic co-operation with Germany until 1943, when the Danish government refused further co-operation and its navy scuttled most of its ships and sent many of its officers to Sweden, which was neutral. The Danish resistance performed a rescue operation that managed to evacuate several thousand Jews and their families to safety in Sweden before the Germans could send them to death camps. Some Danes supported Nazism by joining the Danish Nazi Party or volunteering to fight with Germany as part of the Frikorps Danmark.[38] Iceland severed ties with Denmark and became an independent republic in 1944; Germany surrendered in May 1945. In 1948, the Faroe Islands gained home rule. In 1949, Denmark became a founding member of NATO.

Denmark was a founding member of European Free Trade Association (EFTA). During the 1960s, the EFTA countries were often referred to as the Outer Seven, as opposed to the Inner Six of what was then the European Economic Community (EEC).[39] In 1973, along with Britain and Ireland, Denmark joined the European Economic Community (now the European Union) after a public referendum. The Maastricht Treaty, which involved further European integration, was rejected by the Danish people in 1992; it was only accepted after a second referendum in 1993, which provided for four opt-outs from policies. The Danes rejected the euro as the national currency in a referendum in 2000. Greenland gained home rule in 1979 and was awarded self-determination in 2009. Neither the Faroe Islands nor Greenland are members of the European Union, the Faroese having declined membership of the EEC in 1973 and Greenland in 1986, in both cases because of fisheries policies.
Constitutional change in 1953 led to a single-chamber parliament elected by proportional representation, female accession to the Danish throne, and Greenland becoming an integral part of Denmark. The centre-left Social Democrats led a string of coalition governments for most of the second half of the 20th century, introducing the Nordic welfare model. The Liberal Party and the Conservative People's Party have also led centre-right governments.
Geography
[edit]
Located in Northern Europe, Denmark[N 2] consists of the northern part of the Jutland peninsula and an archipelago of 406 islands.[4] Of these, the largest island is Zealand, on which the capital Copenhagen is situated, followed by the North Jutlandic Island, Funen, and Lolland.[41] The island of Bornholm is located east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea. Many of the larger islands are connected by bridges; a bridge-tunnel across the Øresund connects Zealand with Sweden; the Great Belt Fixed Link connects Funen with Zealand; and the Little Belt Bridge connects Jutland with Funen. Ferries or small aircraft connect to the smaller islands. The four cities with populations over 100,000 are the capital Copenhagen on Zealand; Aarhus and Aalborg in Jutland; and Odense on Funen.
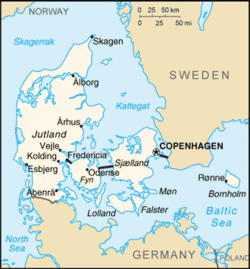
The country occupies a total area of 42,943.9 square kilometres (16,581 sq mi).[3] The area of inland water is 700 km2 (270 sq mi), variously stated as from 500 to 700 km2 (193–270 sq mi).[citation needed] Lake Arresø northwest of Copenhagen is the largest lake. The size of the land area cannot be stated exactly since the ocean constantly erodes and adds material to the coastline, and because of human land reclamation projects (to counter erosion). Post-glacial rebound raises the land by a bit less than 1 cm (0.4 in) per year in the north and east, extending the coast. A circle enclosing the same area as Denmark would be 234 kilometres (145 miles) in diameter with a circumference of 736 km (457 mi) (land area only:232.33 km (144.36 mi) and 730 km (454 mi) respectively). It shares a border of 68 kilometres (42 mi) with Germany to the south and is otherwise surrounded by 8,750 km (5,437 mi) of tidal shoreline (including small bays and inlets).[42] No location in Denmark is farther from the coast than 52 km (32 mi). On the south-west coast of Jutland, the tide is between 1 and 2 m (3.28 and 6.56 ft), and the tideline moves outward and inward on a 10 km (6.2 mi) stretch.[43] Denmark's territorial waters total 105,000 square kilometres (40,541 square miles).
Denmark's northernmost point is Skagen point (the north beach of the Skaw) at 57° 45' 7" northern latitude; the southernmost is Gedser point (the southern tip of Falster) at 54° 33' 35" northern latitude; the westernmost point is Blåvandshuk at 8° 4' 22" eastern longitude; and the easternmost point is Østerskær at 15° 11' 55" eastern longitude. This is in the small Ertholmene archipelago 18 kilometres (11 mi) north-east of Bornholm. The distance from east to west is 452 kilometres (281 mi), from north to south 368 kilometres (229 mi).

The country is flat with little elevation, having an average height above sea level of 31 metres (102 ft). The highest natural point is Møllehøj, at 170.86 metres (560.56 ft).[44] Although this is by far the lowest high point in the Nordic countries and also less than half of the highest point in Southern Sweden, Denmark's general elevation in its interior is generally at a safe level from rising sea levels. A sizeable portion of Denmark's terrain consists of rolling plains whilst the coastline is sandy, with large dunes in northern Jutland. Although once extensively forested, today Denmark largely consists of arable land. It is drained by a dozen or so rivers, and the most significant include the Gudenå, Odense, Skjern, Suså and Vidå—a river that flows along its southern border with Germany.
The Kingdom of Denmark includes two overseas territories, both well to the west of Denmark: Greenland, the world's largest island, and the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic Ocean. These territories are self-governing under their own parliaments (the Løgting and Inatsisartut) and form, together with continental Denmark, part of the Danish Realm.
Climate
[edit]Denmark has a temperate climate, characterised by mild winters, with mean temperatures in January of 1.5 °C (34.7 °F), and cool summers, with a mean temperature in August of 17.2 °C (63.0 °F).[45] The most extreme temperatures recorded in Denmark, since 1874 when recordings began, was 36.4 °C (97.5 °F) in 1975 and −31.2 °C (−24.2 °F) in 1982.[46] Denmark has an average of 179 days per year with precipitation, on average receiving a total of 765 millimetres (30 in) per year; autumn is the wettest season and spring the driest.[45] The position between a continent and an ocean means that the weather is often unstable.[47]
Because of Denmark's northern location, there are large seasonal variations in daylight. There are short days during the winter with sunrise coming around 8:45 am and sunset 3:45 pm (standard time), as well as long summer days with sunrise at 4:30 am and sunset at 10 pm (daylight saving time).[48]
Ecology
[edit]
Denmark belongs to the Boreal Kingdom and can be subdivided into two ecoregions: the Atlantic mixed forests and Baltic mixed forests.[49][50] Almost all of Denmark's primeval temperate forests have been destroyed or fragmented, chiefly for agricultural purposes during the last millennia.[51] The deforestation has created large swaths of heathland and devastating sand drifts.[51] In spite of this, there are several larger second growth woodlands in the country and, in total, 12.9% of the land is now forested.[52] Norway spruce is the most widespread tree (2017); an important tree in the Christmas tree production. Denmark holds a Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 0.5/10, ranking it 171st globally out of 172 countries—behind only San Marino.[53]Template:Explain
Roe deer occupy the countryside in growing numbers, and large-antlered red deer can be found in the sparse woodlands of Jutland. Denmark is also home to smaller mammals, such as polecats, hares and hedgehogs.[54] Approximately 400 bird species inhabit Denmark and about 160 of those breed in the country.[55] Large marine mammals include healthy populations of Harbour porpoise, growing numbers of pinnipeds and occasional visits of large whales, including blue whales and orcas. Cod, herring and plaice are abundant culinary fish in Danish waters and form the basis for a large fishing industry.[56]
Environment
[edit]
Denmark stopped issuing new licences for oil and gas extraction in December 2020.[57]
Land and water pollution are two of Denmark's most significant environmental issues, although much of the country's household and industrial waste is now increasingly filtered and sometimes recycled. The country has historically taken a progressive stance on environmental preservation; in 1971 Denmark established a Ministry of Environment and was the first country in the world to implement an environmental law in 1973.[58] To mitigate environmental degradation and global warming the Danish Government has signed the Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol.[59] However, the national ecological footprint is 8.26 global hectares per person, which is very high compared to a world average of 1.7 in 2010.[60] Contributing factors to this value are an exceptional high value for cropland but also a relatively high value for grazing land,[61] which may be explained by the substantially high meat production in Denmark (115.8 kilograms (255 lb) meat annually per capita) and the large economic role of the meat and dairy industries.[62] In December 2014, the Climate Change Performance Index for 2015 placed Denmark at the top of the table, explaining that although emissions are still quite high, the country was able to implement effective climate protection policies.[63] In 2020, Denmark was placed first in the index again.[64] In 2021 Denmark, with Costa Rica, launched the "Beyond Oil and Gas alliance" for stopping use fossil fuels.[65]
Denmark's territories, Greenland and the Faroe Islands, catch approximately 650 whales per year.[66][67] Greenland's quotas for the catch of whales are determined according to the advice of the International Whaling Commission (IWC), having quota decision-making powers.[68]
Government and politics
[edit]Politics in Denmark operate under a framework laid out in the Constitution of Denmark.[N 4] First written in 1849, it establishes a sovereign state in the form of a constitutional monarchy, with a representative parliamentary system. The monarch officially retains executive power and presides over the Council of State (privy council).[70][71] In practice, the duties of the monarch are strictly representative and ceremonial,[N 5][72] such as the formal appointment and dismissal of the Prime Minister and other Government ministers. The Monarch is not answerable for his or her actions, and their person is sacrosanct.[73] Hereditary monarch Queen Margrethe II has been head of state since 14 January 1972.
Government
[edit]
The Danish parliament is unicameral and called the Folketing (Danish: [Folketinget] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). It is the legislature of the Kingdom of Denmark, passing acts that apply in Denmark and, variably, Greenland and the Faroe Islands. The Folketing is also responsible for adopting the state's budgets, approving the state's accounts, appointing and exercising control of the Government, and taking part in international co-operation. Bills may be initiated by the Government or by members of parliament. All bills passed must be presented before the Council of State to receive Royal Assent within thirty days in order to become law.[74]

Denmark is a representative democracy with universal suffrage.[N 6] Membership of the Folketing is based on proportional representation of political parties,[76] with a 2% electoral threshold. Denmark elects 175 members to the Folketing, with Greenland and the Faroe Islands electing an additional two members each—179 members in total.[77] Parliamentary elections are held at least every four years, but it is within the powers of the prime minister to ask the monarch to call for an election before the term has elapsed. On a vote of no confidence, the Folketing may force a single minister or an entire government to resign.[78]
The Government of Denmark operates as a cabinet government, where executive authority is exercised—formally, on behalf of the monarch—by the prime minister and other cabinet ministers, who head ministries. As the executive branch, the Cabinet is responsible for proposing bills and a budget, executing the laws, and guiding the foreign and internal policies of Denmark. The position of prime minister belongs to the person most likely to command the confidence of a majority in the Folketing; this is often the current leader of the largest political party or, more effectively, through a coalition of parties. A single party generally does not have sufficient political power in terms of the number of seats to form a cabinet on its own; Denmark has often been ruled by coalition governments, themselves usually minority governments dependent on non-government parties.[79]
Following a general election defeat in June 2015, Helle Thorning-Schmidt, leader of the Social Democrats (Socialdemokraterne), resigned as prime minister.[80] She was succeeded by Lars Løkke Rasmussen, the leader of the Liberal Party (Venstre). Rasmussen became the leader of a cabinet that, unusually, consisted entirely of ministers from his own party.[81] In November 2016, Liberal Alliance and the Conservatives joined the government.[82] Liberal Prime Minister, Lars Løkke Rasmussen held the office from 2009 to 2011, and again from 2015 to 2019, with backing from the Danish People's Party (DF). Following the 2019 general election, the Social Democrats, led by leader Mette Frederiksen, formed a single-party government with support from the left-wing coalition.[83] Frederiksen became prime minister on 27 June 2019.[84] In the November 2022 snap general election, Prime Minister Frederiksen's Social Democrats remained the majority party, adding two more seats to gain its best result in two decades.[85] The second largest was the Venstre, led by Jakob Ellemann-Jensen. The recently formed Moderates party, led by former prime minister Rasmussen, became the third largest party in Denmark.[86] In December 2022, Frederiksen formed a new coalition government with the top three largest political parties. Ellemann-Jensen became deputy prime minister and defence minister, and Rasmussen was appointed foreign minister.[87]
Law and judicial system
[edit]
Denmark has a civil law system with some references to Germanic law. Denmark resembles Norway and Sweden in never having developed a case-law like that of England and the United States nor comprehensive codes like those of France and Germany. Much of its law is customary.[88]
The judicial system of Denmark is divided between courts with regular civil and criminal jurisdiction and administrative courts with jurisdiction over litigation between individuals and the public administration. Articles sixty-two and sixty-four of the Constitution ensure judicial independence from government and Parliament by providing that judges shall only be guided by the law, including acts, statutes and practice.[89] The Kingdom of Denmark does not have a single unified judicial system – Denmark has one system, Greenland another, and the Faroe Islands a third.[90] However, decisions by the highest courts in Greenland and the Faroe Islands may be appealed to the Danish High Courts. The Danish Supreme Court is the highest civil and criminal court responsible for the administration of justice in the Kingdom.
Danish Realm
[edit]
The Kingdom of Denmark is a unitary state that comprises, in addition to metropolitan Denmark, two autonomous territories[1] in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. They have been integrated parts of the Danish Realm since the 18th century; however, due to their separate historical and cultural identities, these parts of the Realm have extensive political powers and have assumed legislative and administrative responsibility in a substantial number of fields.[91] Home rule was granted to the Faroe Islands in 1948 and to Greenland in 1979, each having previously had the status of counties.[92]
The Faroe Islands and Greenland have their own home governments and parliaments and are effectively self-governing in regards to domestic affairs apart from the judicial system and monetary policy.[92] High Commissioners (Rigsombudsmand) act as representatives of the Danish government in the Faroese Løgting and in the Greenlandic Parliament, but they cannot vote.[92] The Faroese home government is defined to be an equal partner with the Danish national government,[93] while the Greenlandic people are defined as a separate people with the right to self-determination.[94]
| Autonomous territory | Population (2020) | Total area | Capital | Local parliament | Premier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52,110[95] | 1,399 km2 (540.16 sq mi) | Løgting | Bárður á Steig Nielsen | ||
| Template:Country data Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaat) | 56,081[96] | 2,166,086 km2 (836,330 sq mi) | Inatsisartut | Múte Bourup Egede |
Administrative divisions
[edit]Denmark, with a total area of 43,094 square kilometres (16,639 sq mi), is divided into five administrative regions (Danish: [regioner] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The regions are further subdivided into 98 municipalities (kommuner). The easternmost land in Denmark, the Ertholmene archipelago, with an area of 39 hectares (0.16 sq mi), is neither part of a municipality nor a region but belongs to the Ministry of Defence.[97] The provinces of Denmark are statistical divisions of Denmark, positioned between the administrative regions and municipalities. They are not administrative divisions, nor subject for any kind of political elections, but are mainly for statistical use.
The regions were created on 1 January 2007 to replace the 16 former counties. At the same time, smaller municipalities were merged into larger units, reducing the number from 270. Most municipalities have a population of at least 20,000 to give them financial and professional sustainability, although a few exceptions were made to this rule.[98] The administrative divisions are led by directly elected councils, elected proportionally every four years; the most recent Danish local elections were held on 16 November 2021. Other regional structures use the municipal boundaries as a layout, including the police districts, the court districts and the electoral wards.
Regions
[edit]The governing bodies of the regions are the regional councils, each with forty-one councillors elected for four-year terms. The councils are headed by regional district chairmen (regionsrådsformand), who are elected by the council.[99] The areas of responsibility for the regional councils are the national health service, social services and regional development.[99][100] Unlike the counties they replaced, the regions are not allowed to levy taxes and the health service is partly financed by a national health care contribution until 2018 (sundhedsbidrag), partly by funds from both government and municipalities.[101] From 1 January 2019 this contribution will be abolished, as it is being replaced by higher income tax instead.
The area and populations of the regions vary widely; for example, the Capital Region, which encompasses the Copenhagen metropolitan area with the exception of the subtracted province East Zealand but includes the Baltic Sea island of Bornholm, has a population three times larger than that of North Denmark Region, which covers the more sparsely populated area of northern Jutland. Under the county system certain densely populated municipalities, such as Copenhagen Municipality and Frederiksberg, had been given a status equivalent to that of counties, making them first-level administrative divisions. These sui generis municipalities were incorporated into the new regions under the 2007 reforms.
| Danish name | English name | Admin. centre | Largest city (populous) |
Population (April 2021) |
Total area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hovedstaden | Capital Region of Denmark | Hillerød | Copenhagen | 1,856,061 | 2,568.29 |
| Midtjylland | Central Denmark Region | Viborg | Aarhus | 1,333,245 | 13,095.80 |
| Nordjylland | North Denmark Region | Aalborg | Aalborg | 590,322 | 7,907.09 |
| Sjælland | Region Zealand | Sorø | Roskilde | 839,619 | 7,268.75 |
| Syddanmark | Region of Southern Denmark | Vejle | Odense | 1,224,100 | 12,132.21 |
| Source: Regional and municipal key figures | |||||
Foreign relations
[edit]
Denmark wields considerable influence in Northern Europe and is a middle power in international affairs.[102] In recent years, Greenland and the Faroe Islands have been guaranteed a say in foreign policy issues such as fishing, whaling, and geopolitical concerns. The foreign policy of Denmark is substantially influenced by its membership of the European Union (EU); Denmark including Greenland joined the European Economic Community (EEC), the EU's predecessor, in 1973.[N 7] Denmark held the Presidency of the Council of the European Union on seven occasions, most recently from January to June 2012.[103] Following World War II, Denmark ended its two-hundred-year-long policy of neutrality. It has been a founding member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) since 1949, and membership remains highly popular.[104]
As a member of Development Assistance Committee (DAC), Denmark has for a long time been among the countries of the world contributing the largest percentage of gross national income to development aid. In 2015, Denmark contributed 0.85% of its gross national income (GNI) to foreign aid and was one of only six countries meeting the longstanding UN target of 0.7% of GNI.[N 8][105] The country participates in both bilateral and multilateral aid, with the aid usually administered by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The organisational name of Danish International Development Agency (DANIDA) is often used, in particular when operating bilateral aid.
Military
[edit]
Denmark's armed forces are known as the Danish Defence (Danish: [Forsvaret] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). The Minister of Defence is commander-in-chief of the Danish Defence, and serves as chief diplomatic official abroad. During peacetime, the Ministry of Defence employs around 33,000 in total. The main military branches employ almost 27,000: 15,460 in the Royal Danish Army, 5,300 in the Royal Danish Navy and 6,050 in the Royal Danish Air Force (all including conscripts).[citation needed] The Danish Emergency Management Agency employs 2,000 (including conscripts), and about 4,000 are in non-branch-specific services like the Danish Defence Command and the Danish Defence Intelligence Service. Furthermore, around 44,500 serve as volunteers in the Danish Home Guard.[106]
Denmark is a long-time supporter of international peacekeeping, but since the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia in 1999 and the War in Afghanistan in 2001, Denmark has also found a new role as a warring nation, participating actively in several wars and invasions. This relatively new situation has stirred some internal critique, but the Danish population has generally been very supportive, in particular of the War in Afghanistan.[107][108] The Danish Defence has around 1,400[109] staff in international missions, not including standing contributions to NATO SNMCMG1. Danish forces were heavily engaged in the former Yugoslavia in the UN Protection Force (UNPROFOR), with IFOR,[110] and now SFOR.[111] Between 2003 and 2007, there were approximately 450 Danish soldiers in Iraq.[112] Denmark also strongly supported American operations in Afghanistan and has contributed both monetarily and materially to the ISAF.[113] These initiatives are often described by the authorities as part of a new "active foreign policy" of Denmark.
Economy
[edit]

Denmark has a developed mixed economy that is classed as a high-income economy by the World Bank.[114] In 2017, it ranked 16th in the world in terms of gross national income (PPP) per capita and 10th in nominal GNI per capita.[115] Denmark's economy stands out as one of the most free in the Index of Economic Freedom and the Economic Freedom of the World.[116][117] It is the 10th most competitive economy in the world, and 6th in Europe, according to the World Economic Forum in its Global Competitiveness Report 2018.[118]
Denmark has the fourth highest ratio of tertiary degree holders in the world.[119] The country ranks highest in the world for workers' rights.[120] GDP per hour worked was the 13th highest in 2009. The country has a market income inequality close to the OECD average,[121][122] but after taxes and public cash transfers the income inequality is considerably lower. According to Eurostat, Denmark's Gini coefficient for disposable income was the 7th-lowest among EU countries in 2017.[123] According to the International Monetary Fund, Denmark has the world's highest minimum wage.[124] As Denmark has no minimum wage legislation, the high wage floor has been attributed to the power of trade unions. For example, as the result of a collective bargaining agreement between the 3F trade union and the employers group Horesta, workers at McDonald's and other fast food chains make the equivalent of US$20 an hour, which is more than double what their counterparts earn in the United States, and have access to five weeks' paid vacation, parental leave and a pension plan.[125] Union density in 2015 was 68%.[126]
Once a predominantly agricultural country on account of its arable landscape, since 1945 Denmark has greatly expanded its industrial base and service sector. By 2017 services contributed circa 75% of GDP, manufacturing about 15% and agriculture less than 2%.[127] Major industries include wind turbines, pharmaceuticals, medical equipment, machinery and transportation equipment, food processing, and construction.[128] Circa 60% of the total export value is due to export of goods, and the remaining 40% is from service exports, mainly sea transport. The country's main export goods are: wind turbines, pharmaceuticals, machinery and instruments, meat and meat products, dairy products, fish, furniture and design.[128] Denmark is a net exporter of food and energy and has for a number of years had a balance of payments surplus which has transformed the country from a net debitor to a net creditor country. By 1 July 2018, the net international investment position (or net foreign assets) of Denmark was equal to 64.6% of GDP.[129]

A liberalisation of import tariffs in 1797 marked the end of mercantilism and further liberalisation in the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century established the Danish liberal tradition in international trade that was only to be broken by the 1930s.[130] Even when other countries, such as Germany and France, raised protection for their agricultural sector because of increased American competition resulting in much lower agricultural prices after 1870, Denmark retained its free trade policies, as the country profited from the cheap imports of cereals (used as feedstuffs for their cattle and pigs) and could increase their exports of butter and meat of which the prices were more stable.[131] Today, Denmark is part of the European Union's internal market, which represents more than 508 million consumers. Several domestic commercial policies are determined by agreements among European Union (EU) members and by EU legislation. Support for free trade is high among the Danish public; in a 2016 poll 57% responded saw globalisation as an opportunity whereas 18% viewed it as a threat.[132] 70% of trade flows are inside the European Union. As of 2017[update], Denmark's largest export partners are Germany, Sweden, the United Kingdom and the United States.[59]
Denmark's currency, the krone (DKK), is pegged at approximately 7.46 kroner per euro through the ERM II. Although a September 2000 referendum rejected adopting the euro,[133] the country follows the policies set forth in the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union (EMU) and meets the economic convergence criteria needed to adopt the euro. The majority of the political parties in the Folketing support joining the EMU, but since 2010 opinion polls have consistently shown a clear majority against adopting the euro. In May 2018, 29% of respondents from Denmark in a Eurobarometer opinion poll stated that they were in favour of the EMU and the euro, whereas 65% were against it.[134]
Ranked by turnover in Denmark, the largest Danish companies are: A.P. Møller-Mærsk (international shipping), Novo Nordisk (pharmaceuticals), ISS A/S (facility services), Vestas (wind turbines), Arla Foods (dairy), DSV (transport), Carlsberg Group (beer), Salling Group (retail), Ørsted A/S (power), Danske Bank.[135]
The Danish government focused into methods to increase taxes on energy dealers in 2023.[136]
Public policy
[edit]Danes enjoy a high standard of living and the Danish economy is characterised by extensive government welfare provisions. Denmark has a corporate tax rate of 22% and a special time-limited tax regime for expatriates.[137] The Danish taxation system is broad based, with a 25% value-added tax, in addition to excise taxes, income taxes and other fees. The overall level of taxation (sum of all taxes, as a percentage of GDP) was 46% in 2017.[138] The tax structure of Denmark (the relative weight of different taxes) differs from the OECD average, as the Danish tax system in 2015 was characterised by substantially higher revenues from taxes on personal income and a lower proportion of revenues from taxes on corporate income and gains and property taxes than in OECD generally, whereas no revenues at all derive from social security contributions. The proportion deriving from payroll taxes, VAT, and other taxes on goods and services correspond to the OECD average[139]
As of 2014[update], 6% of the population was reported to live below the poverty line, when adjusted for taxes and transfers. Denmark has the 2nd lowest relative poverty rate in the OECD, below the 11.3% OECD average.[140] The share of the population reporting that they feel that they cannot afford to buy sufficient food in Denmark is less than half of the OECD average.[140]
Labour market
[edit]Like other Nordic countries, Denmark has adopted the Nordic Model, which combines free market capitalism with a comprehensive welfare state and strong worker protection.[141] As a result of its acclaimed "flexicurity" model, Denmark has the freest labour market in Europe, according to the World Bank. Employers can hire and fire whenever they want (flexibility), and between jobs, unemployment compensation is relatively high (security). According to OECD, initial as well as long-term net replacement rates for unemployed persons were 65% of previous net income in 2016, against an OECD average of 53%.[142] Establishing a business can be done in a matter of hours and at very low costs.[143] No restrictions apply regarding overtime work, which allows companies to operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.[144] With an employment rate in 2017 of 74.2% for people aged 15–64-years, Denmark ranks 9th highest among the OECD countries, and above the OECD average of 67.8%.[145] The unemployment rate was 5.7% in 2017,[146] which is considered close to or below its structural level.[147]
The level of unemployment benefits is dependent on former employment and normally on membership of an unemployment fund, which is usually closely connected to a trade union, and previous payment of contributions. Circa 65% of the financing comes from earmarked member contributions, whereas the remaining third originates from the central government and hence ultimately from general taxation.[148]
Science and technology
[edit]
Denmark has a long tradition of scientific and technological invention and engagement, and has been involved internationally from the very start of the scientific revolution. In current times, Denmark is participating in many high-profile international science and technology projects, including CERN, ITER, ESA, ISS and E-ELT. Denmark was ranked 10th in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, down from 6th in 2020 and from 7th in 2019.[150][151][152]
In the 20th century, Danes have also been innovative in several fields of the technology sector. Danish companies have been influential in the shipping industry with the design of the largest and most energy efficient container ships in the world, the Maersk Triple E class, and Danish engineers have contributed to the design of MAN Diesel engines. In the software and electronic field, Denmark contributed to design and manufacturing of Nordic Mobile Telephones, and the now-defunct Danish company DanCall was among the first to develop GSM mobile phones.
Life science is a key sector with extensive research and development activities. Danish engineers are world-leading in providing diabetes care equipment and medication products from Novo Nordisk and, since 2000, the Danish biotech company Novozymes, the world market leader in enzymes for first generation starch-based bioethanol, has pioneered development of enzymes for converting waste to cellulosic ethanol.[153] Medicon Valley, spanning the Øresund Region between Zealand and Sweden, is one of Europe's largest life science clusters, containing a large number of life science companies and research institutions located within a very small geographical area.
Danish-born computer scientists and software engineers have taken leading roles in some of the world's programming languages: Anders Hejlsberg (Turbo Pascal, Delphi, C#); Rasmus Lerdorf (PHP); Bjarne Stroustrup (C++); David Heinemeier Hansson (Ruby on Rails); Lars Bak, a pioneer in virtual machines (V8, Java VM, Dart). Physicist Lene Vestergaard Hau is the first person to stop light, leading to advances in quantum computing, nanoscale engineering, and linear optics.
Energy
[edit]
Denmark has considerably large deposits of oil and natural gas in the North Sea and ranks as number 32 in the world among net exporters of crude oil[154] and was producing 259,980 barrels of crude oil a day in 2009.[155] Denmark is a long-time leader in wind power: In 2015 wind turbines provided 42.1% of the total electricity consumption.[156] In May 2011[update][[Category:Articles containing potentially dated statements from Expression error: Unexpected < operator.]] Denmark derived 3.1% of its gross domestic product from renewable (clean) energy technology and energy efficiency, or around €6.5 billion ($9.4 billion).[157] Denmark is connected by electric transmission lines to other European countries.
Denmark's electricity sector has integrated energy sources such as wind power into the national grid. Denmark now aims to focus on intelligent battery systems (V2G) and plug-in vehicles in the transport sector.[158] The country is a member nation of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).[159]
Denmark exported roughly 460 million GJ of energy in 2018.[160]
Transport
[edit]

Significant investment has been made in building road and rail links between regions in Denmark, most notably the Great Belt Fixed Link, which connects Zealand and Funen. It is now possible to drive from Frederikshavn in northern Jutland to Copenhagen on eastern Zealand without leaving the motorway. The main railway operator is DSB for passenger services and DB Cargo for freight trains. The railway tracks are maintained by Banedanmark. The North Sea and the Baltic Sea are intertwined by various, international ferry links. Construction of the Fehmarn Belt Fixed Link, connecting Denmark and Germany with a second link, Started in 2021.[162] Copenhagen has a rapid transit system, the Copenhagen Metro, and an extensive electrified suburban railway network, the S-train. In the four largest cities – Copenhagen, Aarhus, Odense, Aalborg – light rail systems are planned to be in operation around 2020.[163]
Cycling in Denmark is a very common form of transport, particularly for the young and for city dwellers. With a network of bicycle routes extending more than 12,000 km[164] and an estimated 7,000 km[165] of segregated dedicated bicycle paths and lanes, Denmark has a solid bicycle infrastructure.
Private vehicles are increasingly used as a means of transport. Because of the high registration tax (150%), VAT (25%), and one of the world's highest income tax rates, new cars are very expensive. The purpose of the tax is to discourage car ownership. In 2007, an attempt was made by the government to favour environmentally friendly cars by slightly reducing taxes on high mileage vehicles. However, this has had little effect, and in 2008 Denmark experienced an increase in the import of fuel inefficient old cars,[166] as the cost for older cars—including taxes—keeps them within the budget of many Danes. As of 2011[update], the average car age is 9.2 years.[167]
With Norway and Sweden, Denmark is part of the Scandinavian Airlines flag carrier. Copenhagen Airport is Scandinavia's busiest passenger airport, handling over 25 million passengers in 2014.[161] Other notable airports are Billund Airport, Aalborg Airport, and Aarhus Airport.
Demographics
[edit]Population by ancestry (Q2 2020):[6]
Population
[edit]The population of Denmark, as registered by Statistics Denmark, was 5.825 million in April 2020.[6] Denmark has one of the oldest populations in the world, with the average age of 41.9 years,[168] with 0.97 males per female. Despite a low birth rate, the population is growing at an average annual rate of 0.59%[128] because of net immigration and increasing longevity. The World Happiness Report frequently ranks Denmark's population as the happiest in the world.[169][170][171] This has been attributed to the country's highly regarded education and health care systems,[172] and its low level of income inequality.[173]
Denmark is a historically homogeneous nation.[174] However, as with its Scandinavian neighbours, Denmark has recently transformed from a nation of net emigration, up until World War II, to a nation of net immigration. Today, residence permits are issued mostly to immigrants from other EU countries (54% of all non-Scandinavian immigrants in 2017). Another 31% of residence permits were study- or work-related, 4% were issued to asylum seekers and 10% to persons who arrive as family dependants.[175] Overall, the net migration rate in 2017 was 2.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population, somewhat lower than the United Kingdom and the other Nordic countries.[128][176][177]
There are no official statistics on ethnic groups, but according to 2020 figures from Statistics Denmark, 86.11% of the population in Denmark was of Danish descent (including Faroese and Greenlandic), defined as having at least one parent who was born in the Kingdom of Denmark and holds Danish Nationality.[6][N 9] The remaining 13.89% were of foreign background, defined as immigrants or descendants of recent immigrants. With the same definition, the most common countries of origin were Turkey, Poland, Syria, Germany, Iraq, Romania, Lebanon, Pakistan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Somalia.[6]
The Inuit are indigenous to Greenland in the Kingdom and have traditionally inhabited Greenland and the northern parts of Canada and Alaska in the Arctic. From the 18th century up to the 1970s, the Danish government (Dano-Norwegian until 1814) have through time tried to assimilate the Greenlandic Inuit, encouraging them to adopt the majority language, culture and religion. Because of this "Danization process", several persons of Inuit ancestry now identify their mother tongue as Danish.
Template:Largest cities of Denmark
Languages
[edit]Template:See also Danish is the de facto national language of Denmark.[178] Faroese and Greenlandic are the official languages of the Faroe Islands and Greenland respectively.[178] German is a recognised minority language in the area of the former South Jutland County (now part of the Region of Southern Denmark), which was part of the German Empire prior to the Treaty of Versailles.[178] Danish and Faroese belong to the North Germanic (Nordic) branch of the Indo-European languages, along with Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish.[179] There is a limited degree of mutual intelligibility between Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. Danish is more distantly related to German, which is a West Germanic language. Greenlandic or "Kalaallisut" is an Inuit language, and is entirely unrelated to Danish.[179]
A large majority (86%) of Danes speak English as a second language,[180] generally with a high level of proficiency. German is the second-most spoken foreign language, with 47% reporting a conversational level of proficiency.[178] Denmark had 25,900 native speakers of German in 2007 (mostly in the South Jutland area).[178]
Religion
[edit]Christianity is the dominant religion in Denmark. In January 2020, 74.3%[181] of the population of Denmark were members of the Church of Denmark (Den Danske Folkekirke), the officially established church, which is Protestant in classification and Lutheran in orientation.[182][N 10] The membership percentage have been in steadily decline since the 1970s, mainly as fewer newborns are being baptised into it.[183] Only 3% of the population regularly attend Sunday services[184][185] and only 19% of Danes consider religion to be an important part of their life.[186]

The Constitution states that the sovereign must have the Lutheran faith, though the rest of the population is free to adhere to other faiths.[187][188][189] In 1682 the state granted limited recognition to three religious groups dissenting from the Established Church: Roman Catholicism, the Reformed Church and Judaism,[189] although conversion to these groups from the Church of Denmark remained illegal initially. Until the 1970s, the state formally recognised "religious societies" by royal decree. Today, religious groups do not need official government recognition, they can be granted the right to perform weddings and other ceremonies without this recognition.[189] Denmark's Muslims make up approximately 4.4% of the population[190] and form the country's second largest religious community and largest minority religion.[191] The Danish Foreign Ministry estimates that other religious groups comprise less than 1% of the population individually and approximately 2% when taken all together.[192]
According to a 2010 Eurobarometer Poll,[193] 28% of Danish nationals polled responded that they "believe there is a God", 47% responded that they "believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 24% responded that they "do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God or life force". Another poll, carried out in 2009, found that 25% of Danes believe Jesus is the son of God, and 18% believe he is the saviour of the world.[194]
Education
[edit]
All educational programmes in Denmark are regulated by the Ministry of Education and administered by local municipalities. Folkeskole covers the entire period of compulsory education, encompassing primary and lower secondary education.[195] Most children attend folkeskole for 10 years, from the ages of 6 to 16. There are no final examinations, but pupils can choose to sit an exam when finishing ninth grade (14–15 years old). The test is obligatory if further education is to be attended. Alternatively pupils can attend an independent school (friskole), or a private school (privatskole), such as Christian schools or Waldorf schools.
Following graduation from compulsory education, there are several continuing educational opportunities; the Gymnasium (STX) attaches importance in teaching a mix of humanities and science, Higher Technical Examination Programme (HTX) focuses on scientific subjects and the Higher Commercial Examination Programme emphasises on subjects in economics. Higher Preparatory Examination (HF) is similar to Gymnasium (STX), but is one year shorter. For specific professions, there is vocational education, training young people for work in specific trades by a combination of teaching and apprenticeship.
The government records upper secondary school completion rates of 95% and tertiary enrollment and completion rates of 60%.[196] All university and college (tertiary) education in Denmark is free of charges; there are no tuition fees to enrol in courses. Students aged 18 or above may apply for state educational support grants, known as Statens Uddannelsesstøtte (SU), which provides fixed financial support, disbursed monthly.[197] Danish universities offer international students a range of opportunities for obtaining an internationally recognised qualification in Denmark. Many programmes may be taught in the English language, the academic lingua franca, in bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, doctorates and student exchange programmes.[198]
Health
[edit]
As of 2015[update], Denmark has a life expectancy of 80.6 years at birth (78.6 for men, 82.5 for women), up from 76.9 years in 2000.[200] This ranks it 27th among 193 nations, behind the other Nordic countries. The National Institute of Public Health of the University of Southern Denmark has calculated 19 major risk factors among Danes that contribute to a lowering of the life expectancy; this includes smoking, alcohol, drug abuse and physical inactivity.[201] Although the obesity rate is lower than in North America and most other European countries,[202] the large number of Danes becoming overweight is an increasing problem and results in an annual additional consumption in the health care system of DKK 1,625 million.[201] In a 2012 study, Denmark had the highest cancer rate of all countries listed by the World Cancer Research Fund International; researchers suggest the reasons are better reporting, but also lifestyle factors like heavy alcohol consumption, smoking and physical inactivity.[203][204]
Denmark has a universal health care system, characterised by being publicly financed through taxes and, for most of the services, run directly by the regional authorities. One of the sources of income is a national health care contribution (sundhedsbidrag) (2007–11:8%; '12:7%; '13:6%; '14:5%; '15:4%; '16:3%; '17:2%; '18:1%; '19:0%) but it is being phased out and will be gone from January 2019, with the income taxes in the lower brackets being raised gradually each year instead.[101] Another source comes from the municipalities that had their income taxes raised by 3 percentage points from 1 January 2007, a contribution confiscated from the former county tax to be used from 1 January 2007 for health purposes by the municipalities instead. This means that most health care provision is free at the point of delivery for all residents. Additionally, roughly two in five have complementary private insurance to cover services not fully covered by the state, such as physiotherapy.[205] As of 2012[update], Denmark spends 11.2% of its GDP on health care; this is up from 9.8% in 2007 (US$3,512 per capita).[205] This places Denmark above the OECD average and above the other Nordic countries.[205][206]
Ghettos
[edit]
Denmark is the only country to have officially used the word 'ghetto' in the 21st century to denote certain residential areas.[207] From 2010 to 2021, the Danish Ministry of Transport, Building and Housing published ghettolisten (List of ghettos) which in 2018 consisted of 25 areas.[207][208] As a result, the term is widely used in the media and common parlance.[209] The legal designation is applied to areas based on the residents' income levels, employment status, education levels, criminal convictions and non-Western ethnic background.[208][209][210] In 2017, 8.7% of Denmark's population consisted of non-Western immigrants or their descendants. The population proportion of 'ghetto residents' with non-Western background was 66.5%.[211]
In 2018, the government has proposed measures to solve the issue of integration and to rid the country of parallel societies and ghettos by 2030.[210][211][212][213] The measures focus on physical redevelopment, control over who is allowed to live in these areas, crime abatement and education.[208] These policies have been criticised for undercutting 'equality before law' and for portraying immigrants, especially Muslim immigrants, in a bad light.[208][214] While some proposals like restricting 'ghetto children' to their homes after 8 p.m. have been rejected for being too radical, most of the 22 proposals have been agreed upon by a parliamentary majority.[207][209]
In 2021, the term ghetto was dropped and replaced by parallel society and vulnerable region.[215]
Culture
[edit]Denmark shares strong cultural and historic ties with its Scandinavian neighbours Sweden and Norway. It has historically been one of the most socially progressive cultures in the world. In 1969, Denmark was the first country to legalise pornography,[216] and in 2012, Denmark replaced its "registered partnership" laws, which it had been the first country to introduce in 1989,[217][218] with gender-neutral marriage, and allowed same-sex marriages to be performed in the Church of Denmark.[219][220] Modesty and social equality are important parts of Danish culture.[221] In a 2016 study comparing empathy scores of 63 countries, Denmark ranked 4th world-wide having the highest empathy among surveyed European countries.[222]


The astronomical discoveries of Tycho Brahe (1546–1601), Ludwig A. Colding's (1815–1888) neglected articulation of the principle of conservation of energy, and the contributions to atomic physics of Niels Bohr (1885–1962) indicate the range of Danish scientific achievement. The fairy tales of Hans Christian Andersen (1805–1875), the philosophical essays of Søren Kierkegaard (1813–1855), the short stories of Karen Blixen (penname Isak Dinesen), (1885–1962), the plays of Ludvig Holberg (1684–1754), and the dense, aphoristic poetry of Piet Hein (1905–1996), have earned international recognition, as have the symphonies of Carl Nielsen (1865–1931). From the mid-1990s, Danish films have attracted international attention, especially those associated with Dogme 95 like those of Lars von Trier.
A major feature of Danish culture is Jul (Danish Christmas). The holiday is celebrated throughout December, starting either at the beginning of Advent or on 1 December with a variety of traditions, culminating with the Christmas Eve meal.
There are seven heritage sites inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage list in Northern Europe: Christiansfeld, a Moravian Church Settlement, the Jelling Mounds (Runic Stones and Church), Kronborg Castle, Roskilde Cathedral, and The par force hunting landscape in North Zealand and 3 in the World Heritage list in North America: Ilulissat Icefjord, Aasivissuit — Nipisat, Kujataa within the Kingdom of Denmark.[224]
Human rights
[edit]Denmark has been considered a progressive country, which has adopted legislation and policies to support women's rights, minority rights, and LGBT rights. Human rights in Denmark are protected by the state's Constitution of the Realm (Danmarks Riges Grundlov); applying equally in Denmark proper, Greenland and the Faroe Islands, and through the ratification of international human rights treaties.[225] Denmark has held a significant role in the adoption of both the European Convention on Human Rights and in the establishment of the European Court of Human Rights (ECHR). In 1987, the Kingdom Parliament (Folketinget) established a national human rights institution, the Danish Centre of Human Rights, now the Danish Institute for Human Rights.[225]
In 2009, a referendum on changing the Danish Act of Succession were held to grant absolute primogeniture to the Danish throne, meaning that the eldest child, regardless of gender, takes precedence in the line of succession. As it was not retroactive, the current successor to the throne is the eldest son of the King, rather than his eldest child. The Danish constitution Article 2 states that "The monarchy is inherited by men and women".[226]
The Inuit have for decades been the subject of discrimination and abuse by the dominant colonisers from Europe, those countries claiming possession of Inuit lands. The Inuit have never been a single community in a single region of Inuit.[227] From the 18th century up to the 1970s, the Danish government (Dano-Norwegian until 1814) have through time tried to assimilate the indigenous people of Greenland, the Greenlandic Inuit, encouraging them to adopt the majority language, culture and religion. Denmark has been greatly criticised by the Greenlandic community for the politics of Danization (50's and 60's) of and discrimination against the indigenous population of the country. Critical treatment paying non-Inuit workers higher wages than the local people, the relocation of entire families from their traditional lands into settlements, and separating children from their parents and sending them away to Denmark for schooling has been practised.[228][better source needed][229] Nevertheless, Denmark ratified, in 1996, to recognise the ILO-convention 169 on indigenous people recommended by the UN.
In regard to LGBT rights, Denmark was the first country in the world to grant legal recognition to same-sex unions in the form of registered partnerships in 1989. On 7 June 2012, the law was replaced by a new same-sex marriage law, which came into effect on 15 June 2012.[230] Greenland and the Faroe Islands legalised same-sex marriage in April 2016,[231] and in July 2017 respectively.[232] In January 2016, a resolution was implemented by the Danish parliament which prevented transgender identity being classified as a mental health condition.[211] In doing so, Denmark became the first country in Europe to go against the World Health Organisation (WHO) standards, which classified transgender identity as being a mental health issue until June 2018.[233][234]
Media
[edit]Danish mass media date back to the 1540s, when handwritten fly sheets reported on the news. In 1666, Anders Bording, the father of Danish journalism, began a state paper. In 1834, the first liberal, factual newspaper appeared, and the 1849 Constitution established lasting freedom of the press in Denmark. Newspapers flourished in the second half of the 19th century, usually tied to one or another political party or trade union. Modernisation, bringing in new features and mechanical techniques, appeared after 1900. The total circulation was 500,000 daily in 1901, more than doubling to 1.2 million in 1925.[235] The German occupation during World War II brought informal censorship; some offending newspaper buildings were simply blown up by the Nazis. During the war, the underground produced 550 newspapers—small, surreptitiously printed sheets that encouraged sabotage and resistance.[235]

Danish cinema dates back to 1897 and since the 1980s has maintained a steady stream of productions due largely to funding by the state-supported Danish Film Institute. There have been three big internationally important waves of Danish cinema: erotic melodrama of the silent era; the increasingly explicit sex films of the 1960s and 1970s; and lastly, the Dogme 95 movement of the late 1990s, where directors often used hand-held cameras to dynamic effect in a conscious reaction against big-budget studios. Danish films have been noted for their realism, religious and moral themes, sexual frankness and technical innovation. The Danish filmmaker Carl Th. Dreyer (1889–1968) is considered one of the greatest directors of early cinema.[236][237]
Other Danish filmmakers of note include Erik Balling, the creator of the popular Olsen-banden films; Gabriel Axel, an Oscar-winner for Babette's Feast in 1987; and Bille August, the Oscar-, Palme d'Or- and Golden Globe-winner for Pelle the Conqueror in 1988. In the modern era, notable filmmakers in Denmark include Lars von Trier, who co-created the Dogme movement, and multiple award-winners Susanne Bier and Nicolas Winding Refn. Mads Mikkelsen is a world-renowned Danish actor, having starred in films such as King Arthur, Casino Royale, the Danish film The Hunt, and the American TV series Hannibal. Another renowned Danish actor Nikolaj Coster-Waldau is internationally known for playing the role of Jaime Lannister in the HBO series Game of Thrones.
Danish mass media and news programming are dominated by a few large corporations. In printed media JP/Politikens Hus and Berlingske Media, between them, control the largest newspapers Politiken, Berlingske Tidende and Jyllands-Posten and major tabloids B.T. and Ekstra Bladet. In television, publicly owned stations DR and TV 2 have large shares of the viewers.[238] DR in particular is famous for its high quality TV-series often sold to foreign broadcasters and often with leading female characters like internationally known actresses Sidse Babett Knudsen and Sofie Gråbøl. In radio, DR has a near monopoly, currently broadcasting on all four nationally available FM channels, competing only with local stations.[239]
Music
[edit]Denmark and its multiple outlying islands have a wide range of folk traditions. The country's most famous classical composer is Carl Nielsen (1865–1931), especially remembered for his six symphonies and his Wind Quintet, while the Royal Danish Ballet specialises in the work of the Danish choreographer August Bournonville. The Royal Danish Orchestra is among the world's oldest orchestras.[240] Danes have distinguished themselves as jazz musicians, and the Copenhagen Jazz Festival has acquired international recognition.
The modern pop and rock scene has produced a few names of international fame, including Aqua, Alphabeat, D-A-D, King Diamond, Kashmir, Lukas Graham, Mew, Michael Learns to Rock, MØ, Oh Land, The Raveonettes and Volbeat, among others. Lars Ulrich, the drummer of the band Metallica, has become the first Danish musician to be inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame.
Roskilde Festival near Copenhagen is the largest music festival in Northern Europe since 1971 and Denmark has many recurring music festivals of all genres throughout, including Aarhus International Jazz Festival, Skanderborg Festival, The Blue Festival in Aalborg, Esbjerg International Chamber Music Festival and Skagen Festival among many others.[241][242]
Denmark has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest since 1957 and has won the contest three times, in 1963, 2000 and 2013.
Architecture and design
[edit]
Denmark's architecture became firmly established in the Middle Ages when first Romanesque, then Gothic churches and cathedrals sprang up throughout the country. From the 16th century, Dutch and Flemish designers were brought to Denmark, initially to improve the country's fortifications, but increasingly to build magnificent royal castles and palaces in the Renaissance style. During the 17th century, many impressive buildings were built in the Baroque style, both in the capital and the provinces. Neoclassicism from France was slowly adopted by native Danish architects who increasingly participated in defining architectural style. A productive period of Historicism ultimately merged into the 19th-century National Romantic style.[243]
The 20th century brought along new architectural styles; including expressionism, best exemplified by the designs of architect Peder Vilhelm Jensen-Klint, which relied heavily on Scandinavian brick Gothic traditions; and Nordic Classicism, which enjoyed brief popularity in the early decades of the century. It was in the 1960s that Danish architects such as Arne Jacobsen entered the world scene with their highly successful Functionalist architecture. This, in turn, has evolved into more recent world-class masterpieces including Jørn Utzon's Sydney Opera House and Johan Otto von Spreckelsen's Grande Arche de la Défense in Paris, paving the way for a number of contemporary Danish designers such as Bjarke Ingels to be rewarded for excellence both at home and abroad.[244]
Danish design is a term often used to describe a style of functionalistic design and architecture that was developed in the mid-20th century, originating in Denmark. Danish design is typically applied to industrial design, furniture and household objects, which have won many international awards. The Royal Porcelain Factory is famous for the quality of its ceramics and export products worldwide. Danish design is also a well-known brand, often associated with world-famous, 20th-century designers and architects such as Børge Mogensen, Finn Juhl, Hans Wegner, Arne Jacobsen, Poul Henningsen and Verner Panton.[245] Other designers of note include Kristian Solmer Vedel (1923–2003) in the area of industrial design, Jens Quistgaard (1919–2008) for kitchen furniture and implements and Ole Wanscher (1903–1985) who had a classical approach to furniture design.
Literature and philosophy
[edit]
The first known Danish literature is myths and folklore from the 10th and 11th century. Saxo Grammaticus, normally considered the first Danish writer, worked for bishop Absalon on a chronicle of Danish history (Gesta Danorum). Very little is known of other Danish literature from the Middle Ages. With the Age of Enlightenment came Ludvig Holberg whose comedy plays are still being performed.
In the late 19th century, literature was seen as a way to influence society. Known as the Modern Breakthrough, this movement was championed by Georg Brandes, Henrik Pontoppidan (awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature) and J. P. Jacobsen. Romanticism influenced the renowned writer and poet Hans Christian Andersen, known for his stories and fairy tales, e.g. The Ugly Duckling, The Little Mermaid and The Snow Queen. In recent history Johannes Vilhelm Jensen was also awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature. Karen Blixen is famous for her novels and short stories. Other Danish writers of importance are Herman Bang, Gustav Wied, William Heinesen, Martin Andersen Nexø, Piet Hein, Hans Scherfig, Klaus Rifbjerg, Dan Turèll, Tove Ditlevsen, Inger Christensen and Peter Høeg.
Danish philosophy has a long tradition as part of Western philosophy. Perhaps the most influential Danish philosopher was Søren Kierkegaard, the creator of Christian existentialism. Kierkegaard had a few Danish followers, including Harald Høffding, who later in his life moved on to join the movement of positivism. Among Kierkegaard's other followers include Jean-Paul Sartre who was impressed with Kierkegaard's views on the individual, and Rollo May, who helped create humanistic psychology. Another Danish philosopher of note is Grundtvig, whose philosophy gave rise to a new form of non-aggressive nationalism in Denmark, and who is also influential for his theological and historical works.
Painting and photography
[edit]
While Danish art was influenced over the centuries by trends in Germany and the Netherlands, the 15th and 16th century church frescos, which can be seen in many of the country's older churches, are of particular interest as they were painted in a style typical of native Danish painters.[246]
The Danish Golden Age, which began in the first half of the 19th century, was inspired by a new feeling of nationalism and romanticism, typified in the later previous century by history painter Nicolai Abildgaard. Christoffer Wilhelm Eckersberg was not only a productive artist in his own right but taught at the Royal Danish Academy of Fine Arts where his students included notable painters such as Wilhelm Bendz, Christen Købke, Martinus Rørbye, Constantin Hansen, and Wilhelm Marstrand.
In 1871, Holger Drachmann and Karl Madsen visited Skagen in the far north of Jutland where they quickly built up one of Scandinavia's most successful artists' colonies specialising in Naturalism and Realism rather than in the traditional approach favoured by the academy. Hosted by Michael and his wife Anna, they were soon joined by P.S. Krøyer, Carl Locher and Laurits Tuxen. All participated in painting the natural surroundings and local people.[247] Similar trends developed on Funen with the Fynboerne who included Johannes Larsen, Fritz Syberg and Peter Hansen,[248] and on the island of Bornholm with the Bornholm school of painters including Niels Lergaard, Kræsten Iversen and Oluf Høst.[249]
Painting has continued to be a prominent form of artistic expression in Danish culture, inspired by and also influencing major international trends in this area. These include impressionism and the modernist styles of expressionism, abstract painting and surrealism. While international co-operation and activity has almost always been essential to the Danish artistic community, influential art collectives with a firm Danish base includes De Tretten (1909–1912), Linien (1930s and 1940s), COBRA (1948–1951), Fluxus (1960s and 1970s), De Unge Vilde (1980s) and more recently Superflex (founded in 1993). Most Danish painters of modern times have also been very active with other forms of artistic expressions, such as sculpting, ceramics, art installations, activism, film and experimental architecture. Notable Danish painters from modern times representing various art movements include Theodor Philipsen (1840–1920, impressionism and naturalism), Anna Klindt Sørensen (1899–1985, expressionism), Franciska Clausen (1899–1986, Neue Sachlichkeit, cubism, surrealism and others), Henry Heerup (1907–1993, naivism), Robert Jacobsen (1912–1993, abstract painting), Carl Henning Pedersen (1913–2007, abstract painting), Asger Jorn (1914–1973, Situationist, abstract painting), Bjørn Wiinblad (1918–2006, art deco, orientalism), Per Kirkeby (b. 1938, neo-expressionism, abstract painting), Per Arnoldi (b. 1941, pop art), Michael Kvium (b. 1955, neo-surrealism) and Simone Aaberg Kærn (b. 1969, superrealism).
Danish photography has developed from strong participation and interest in the very beginnings of the art of photography in 1839 to the success of a considerable number of Danes in the world of photography today. Pioneers such as Mads Alstrup and Georg Emil Hansen paved the way for a rapidly growing profession during the last half of the 19th century. Today Danish photographers such as Astrid Kruse Jensen and Jacob Aue Sobol are active both at home and abroad, participating in key exhibitions around the world.[250]
Cuisine
[edit]
The traditional cuisine of Denmark, like that of the other Nordic countries and of Northern Germany, consists mainly of meat, fish and potatoes. Danish dishes are highly seasonal, stemming from the country's agricultural past, its geography, and its climate of long, cold winters.
The open sandwiches on rye bread, known as smørrebrød, which in their basic form are the usual fare for lunch, can be considered a national speciality when prepared and decorated with a variety of fine ingredients. Hot meals traditionally consist of ground meats, such as frikadeller (meat balls of veal and pork) and hakkebøf (minced beef patties), or of more substantial meat and fish dishes such as flæskesteg (roast pork with crackling) and kogt torsk (poached cod) with mustard sauce and trimmings. Denmark is known for its Carlsberg and Tuborg beers and for its akvavit and bitters.
Since around 1970, chefs and restaurants across Denmark have introduced gourmet cooking, largely influenced by French cuisine. Also inspired by continental practices, Danish chefs have recently developed a new innovative cuisine and a series of gourmet dishes based on high-quality local produce known as New Danish cuisine.[251] As a result of these developments, Denmark now has a considerable number of internationally acclaimed restaurants of which several have been awarded Michelin stars. This includes Geranium and Noma in Copenhagen.
Sports
[edit]
Sports are popular in Denmark, and its citizens participate in and watch a wide variety. The national sport is football, with over 320,000 players in more than 1600 clubs.[252] Denmark qualified six times consecutively for the European Championships between 1984 and 2004, and were crowned European champions in 1992; other significant achievements include winning the Confederations Cup in 1995 and reaching the quarter-final of the 1998 World Cup. Notable Danish footballers include Allan Simonsen, named the best player in Europe in 1977, Peter Schmeichel, named the "World's Best Goalkeeper" in 1992 and 1993, and Michael Laudrup, named the best Danish player of all time by the Danish Football Union.[253]
There is much focus on handball, too. The women's national team celebrated great successes during the 1990s and has won a total of 13 medals – seven gold (in 1994, 1996 (2), 1997, 2000, 2002 and 2004), four silver (in 1962, 1993, 1998 and 2004) and two bronze (in 1995 and 2013). On the men's side, Denmark has won 12 medals—four gold (in 2008, 2012, 2016 and 2019), four silver (in 1967, 2011, 2013 and 2014) and four bronze (in 2002, 2004, 2006 and 2007)—the most that have been won by any team in European Handball Championship history.[254] In 2019, the Danish men's national handball team won their first World Championship title in the tournament that was co-hosted between Germany and Denmark.[citation needed]
In recent years, Denmark has made a mark as a strong cycling nation, with Michael Rasmussen reaching King of the Mountains status in the Tour de France in 2005 and 2006. Other popular sports include golf—which is mostly popular among those in the older demographic;[255] tennis—in which Denmark is successful on a professional level; basketball—Denmark joined the international governing body FIBA in 1951;[256] rugby—the Danish Rugby Union dates back to 1950;[257] ice hockey— often competing in the top division in the Men's World Championships; rowing—Denmark specialise in lightweight rowing and are particularly known for their lightweight coxless four, having won six gold and two silver World Championship medals and three gold and two bronze Olympic medals; and several indoor sports—especially badminton, table tennis and gymnastics, in each of which Denmark holds World Championships and Olympic medals. Denmark's numerous beaches and resorts are popular locations for fishing, canoeing, kayaking, and many other water-themed sports.
See also
[edit]- [[Archivo:
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:Iconos|20px|Ver el portal sobre Denmark]] Portal:Denmark. Contenido relacionado con Faroe Islands.
Explanatory notes
[edit]- ^ Danish: [Kongeriget Danmark] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), Template:IPA-da.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Kingdom of Denmark's territory in continental Europe is referred to as "metropolitan Denmark",[40] "Denmark proper" (Danish: [egentlig Danmark] Error: [undefined] Error: {{Lang}}: no text (help): text has italic markup (help)), or simply "Denmark". In this article, usage of "Denmark" excludes the Faroe Islands and Greenland.
- ^ The island of Bornholm is offset to the east of the rest of the country, in the Baltic Sea.
- ^ Denmark has a codified constitution. Changes to it require an absolute majority in two consecutive parliamentary terms and the approval of at least 40% of the electorate through a referendum.[69]
- ^ The Constitution refers to "the King" (Danish: [kongen] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), rather than the gender-neutral term "monarch". In light of the restriction of powers of the monarchy, this is best interpreted as referring to the government Cabinet.
- ^ The Economist Intelligence Unit, while acknowledging that democracy is difficult to measure, listed Denmark 5th on its index of democracy.[75]
- ^ The Faroese declined membership in 1973; Greenland chose to leave the EEC in 1985, following a referendum.
- ^ As measured in official development assistance (ODA). Denmark, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom exceeded the United Nations' ODA target of 0.7% of GNI.
- ^ This data is for Denmark proper only. For data relevant to Greenland and the Faroe Islands see their respective articles.
- ^ The Church of Denmark is the established church (or state religion) in Denmark and Greenland; the Church of the Faroe Islands became an independent body in 2007.
Citations
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b *Benedikter, Thomas (19 June 2006). "The working autonomies in Europe". Society for Threatened Peoples. Archived from the original on 9 March 2008. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
Denmark has established very specific territorial autonomies with its two island territories
- Ackrén, Maria (November 2017). "Greenland". Autonomy Arrangements in the World. Archived from the original on 30 August 2019. Retrieved 30 August 2019.
Faroese and Greenlandic are seen as official regional languages in the self-governing territories belonging to Denmark.
- "Greenland". International Cooperation and Development. European Commission. 3 June 2013. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
Greenland [...] is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark
- Ackrén, Maria (November 2017). "Greenland". Autonomy Arrangements in the World. Archived from the original on 30 August 2019. Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- ^ About Denmark
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Area". Statistics Denmark. Archived from the original on 14 April 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Denmark in numbers 2010" (PDF). Statistics Denmark. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 April 2013. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- ^ "Statistikbanken". statistikbanken.dk.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Population at the first day of the quarter by municipality, sex, age, marital status, ancestry, country of origin and citizenship". Statistics Denmark. Retrieved 2 October 2020.
January 2020
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stone et al. (2008), p. 31.
- ^ Kristian Andersen Nyrup, Middelalderstudier Bog IX. Kong Gorms Saga Archived 9 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Indvandrerne i Danmarks historie, Bent Østergaard, Syddansk Universitetsforlag 2007, ISBN 978-87-7674-204-1, pp. 19–24
- ^ Jump up to: a b J. de Vries, Altnordisches etymologisches Wörterbuch, 1962, 73; N. Å. Nielsen, Dansk etymologisk ordbog, 1989, 85–96.
- ^ Navneforskning, Københavns Universitet"Udvalgte stednavnes betydning". Archived from the original on 16 July 2006. Retrieved 27 January 2008.
- ^ O'Donoghue, Heather (2008). Old Norse-Icelandic Literature: A Short Introduction. John Wiley & Sons. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-470-77683-4. Archived from the original on 12 April 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ Michaelsen (2002), p. 19.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Nielsen, Poul Otto (May 2003). "Denmark: History, Prehistory". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Archived from the original on 22 November 2005. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- ^ Busck (2002), p. 20.
- ^ Busck (2002), p. 19.
- ^ Jordanes (22 April 1997). "The Origin and Deeds of the Goths, chapter III". Translated by Charles C. Mierow. Archived from the original on 24 April 2006. Retrieved 1 May 2006.
- ^ Michaelsen (2002), pp. 122–123.
- ^ Jump up to: a b *Lund, Niels (May 2003). "Denmark – History – The Viking Age". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Archived from the original on 10 May 2006. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- ^ Berend, Nora (22 November 2007). Christianization and the Rise of Christian Monarchy: Scandinavia, Central Europe and Rus' c.900–1200. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-46836-7 – via Google Books.
- ^ Stone et al. (2008), p. 33.
- ^ Lauring, Palle (1960) A History of the Kingdom of Denmark, Host & Son Co.: Copenhagen, p. 108.
- ^ "Kalmarkriget 1611–1613". Svenskt Militärhistoriskt Bibliotek. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 4 May 2007.
- ^ Rawlinson, Kevin (5 November 2018). "Prince Charles says Britain's role in slave trade was an atrocity". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 5 November 2018. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- ^ Olson, James Stuart; Shadle, Robert, eds. (1991). Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-26257-9. Retrieved 15 May 2014.
- ^ Parker (1984), p. 78.
- ^ Parker (1984), p. 79.
- ^ Isacson (2002), p. 229.
- ^ Englund (2000), p. 610.
- ^ Stone et al. (2008), p. 35.
- ^ Frost (2000), pp. 180–183.
- ^ Ekman, Ernst (1957). "The Danish Royal Law of 1665". The Journal of Modern History. 29 (2): 102–107. doi:10.1086/237987. ISSN 0022-2801. S2CID 145652129.
- ^ "League of Armed Neutrality". Oxford Reference. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 28 August 2015.
- ^ Jenssen-Tusch, Georg Friedrich (1852). Zur Regierungsgeschichte Friedrich VI. Königs von Dänemark, Herzogs von Schleswig, Holstein und Lauenburg (in German). Verlag Schröder. p. 166.
- ^ Dörr, Oliver (2004). Kompendium völkerrechtlicher Rechtsprechung : eine Auswahl für Studium und Praxis. Tübingen: Mohr Siebeck. p. 101. ISBN 978-3-16-148311-0.
- ^ Tellier, Luc-Normand (2009). Urban world history an economic and geographical perspective. Québec: Presses de l'Université du Québec. p. 457. ISBN 978-2-7605-2209-1. Archived from the original on 12 April 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ "Lost in translation: Epic goes to Denmark". Politico. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ Rugg, Andy. "Traitor Danes: most soldiers return heroes, but this lot came home total zeroes". Copenhagen Post. Archived from the original on 29 January 2013. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- ^ "Finland: Now, the Seven and a Half". Time. 7 April 1961. Archived from the original on 4 November 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2009.
- ^ Administrative divisions – Denmark The World Factbook. Access date: 16 September 2021
- ^ "Facts and Figures Archived 30 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine", Danish Defence, Defence Command Denmark. Retrieved 11 June 2010.
- ^ "Nature & Environment". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Archived from the original on 3 April 2007. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ^ Nationalencyklopedin, (1990)
- ^ "Nyt højeste punkt i Danmark" (in Danish). Danish Geodata Agency. Archived from the original on 28 May 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Climate Normals for Denmark". Danish Meteorological Institute. Archived from the original on 3 January 2015. Retrieved 2 January 2015. Figures, labelled in Danish: First plot is the whole country; Nedbør=Precipitation, Nedbørdage=Precipitation days (>1 mm), (Dag/Middel/Nat)temp.=(Daytime/Average/Nighttime) temperature, Solskinstimer=Hours of sunshine.
- ^ "Vejrekstremer i Danmark [Weather extremes in Denmark]" (in Danish). Danish Meteorological Institute (DMI). 6 October 2016. Archived from the original on 19 October 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ "The weather cross – the four corners of autumn weather". Danish Meteorological Institute. Archived from the original on 21 September 2015. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ^ "Copenhagen, Denmark – Sunrise, sunset, dawn and dusk times for the whole year". Gaisma. Archived from the original on 2 July 2012. Retrieved 24 June 2012.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; Olson, David; Joshi, Anup; Vynne, Carly; Burgess, Neil D.; Wikramanayake, Eric; Hahn, Nathan; Palminteri, Suzanne; Hedao, Prashant; Noss, Reed; Hansen, Matt; Locke, Harvey; Ellis, Erle C.; Jones, Benjamin; Barber, Charles Victor; Hayes, Randy; Kormos, Cyril; Martin, Vance; Crist, Eileen; Sechrest, Wes; Price, Lori; Baillie, Jonathan E. M.; Weeden, Don; Suckling, Kierán; Davis, Crystal; Sizer, Nigel; Moore, Rebecca; Thau, David; Birch, Tanya; Potapov, Peter; Turubanova, Svetlana; Tyukavina, Alexandra; de Souza, Nadia; Pintea, Lilian; Brito, José C.; Llewellyn, Othman A.; Miller, Anthony G.; Patzelt, Annette; Ghazanfar, Shahina A.; Timberlake, Jonathan; Klöser, Heinz; Shennan-Farpón, Yara; Kindt, Roeland; Lillesø, Jens-Peter Barnekow; van Breugel, Paulo; Graudal, Lars; Voge, Maianna; Al-Shammari, Khalaf F.; Saleem, Muhammad (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Hogan, C. Michael. "Ecoregions of Denmark". Encyclopedia of Earth. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jensen, Christian Lundmark. "Forests and forestry in Denmark – Thousands of years of interaction between man and nature" (PDF). Danish Ministry of the Environment Nature Agency. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 July 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Forest area (% of land area)". worldbank.org. The World Bank. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity – Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ "Animals in Denmark". listofcountriesoftheworld.com. 2012. Archived from the original on 1 June 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Bird list of Denmark". Netfugl.dk. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
It involves all category A, B and C birds recorded in Denmark (according to SU/BOURC/AERC standard).
- ^ Byskov, Søren. "Theme: Herring, cod and other fish – 1001 Stories of Denmark". The Heritage Agency of Denmark. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ^ Farand, Chloé (4 December 2020). "Denmark to phase out oil and gas production by 2050 in "watershed" decision". Climate Home News. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
- ^ The law of environmental damage: liability and reparation. Marie-Louise Larsson.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Denmark". The World Factbook. CIA. 19 January 2012. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- ^ "Ecological Footprint Atlas 2010". Global Footprint Network. 2010. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ WWF (2014): Living Planet Report.
- ^ AMI (2012); preliminary data for 2011
- ^ Burck, Jan; Marten, Franziska; Bals, Christoph. "The Climate Change Performance Index: Results 2015" (PDF). Germanwatch. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 December 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ^ "2020 EPI Results". Environmental Performance Index. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- ^ "Climate change: Whisper it cautiously... there's been progress in run up to COP26". BBC. 25 September 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ "Almost Saving Whales: The Ambiguity of Success at the International Whaling Commission [Full Text] – Ethics & International Affairs". Ethics & International Affairs. 29 March 2012. Archived from the original on 27 December 2017. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ^ "Hundreds of whales slaughtered in Faroe Island's annual killing". The Independent. 20 June 2017. Archived from the original on 28 December 2017. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ^ "Greenland quotas for big whales". Government of Greenland. 5 January 2013. Archived from the original on 5 November 2018. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- ^ Tschentscher, Axel. "The Constitution of Denmark – Section 88". Servat.unibe.ch. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "The executive power is vested in the King." The Constitution of Denmark – Section 3. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The body of Ministers shall form the Council of State, in which the Successor to the Throne shall have a seat when he is of age. The Council of State shall be presided over by the King ..." The Constitution of Denmark – Section 17. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ The Monarchy today Archived 15 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine – The Danish Monarchy (kongehuset.dk). Access date: 16 June 2012
- ^ "The King shall not be answerable for his actions; his person shall be sacrosanct." The Constitution of Denmark – Section 13. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "A Bill passed by the Parliament shall become law if it receives the Royal Assent not later than thirty days after it was finally passed." The Constitution of Denmark – Section 22. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Democracy Index 2014" (PDF). The Economist/Economist Intelligence Unit. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ^ "ICL – Denmark – Constitution – Section 31. Elections". unibe.ch. Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ Template:Harvnb
- ^ "A Minister shall not remain in office after the Parliament has passed a vote of no confidence in him." The Constitution of Denmark – Section 15. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Radikale ved historisk skillevej". Berlingske Tidende. 17 June 2007. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2007.
- ^ "Danish election: Opposition bloc wins". BBC News. 19 June 2015.
- ^ "Denmark's New Centre-Right Government Takes Power". NDTV.com.
- ^ "Danish PM invites support parties into government". The Local Denmark. 21 November 2016.
- ^ "Denmark's new leader joins Nordic swing to left". BBC News. 27 June 2019. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ "Frederiksen prepares to take over as new Danish prime minister". The Local Denmark. 27 June 2019.
- ^ "Denmark: Mette Frederiksen's Social Democrats win the best result in 20 years". The Progressive Post. 8 November 2022.
- ^ "Denmark election: Centre-left bloc comes out on top". BBC News. 2 November 2022.
- ^ "Danish PM picks right-leaning rivals as key ministers in new government". Reuters. 15 December 2022.
- ^ Orfield, Lester Bernhardt Orfield (2002). The Growth of Scandinavian Law. Union, N.J.: Lawbook Exchange. p. 14. ISBN 978-1-58477-180-7.
- ^ "The administration of justice shall always remain independent of the executive power. Rules to this effect shall be laid down by Statute ..." The Constitution of Denmark – Sections/Articles 62 and 64. Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Template:Harvnb
- ^ The working autonomies in Europe Archived 9 March 2008 at the Wayback Machine – Gesellschaft für bedrohte Völker (GFBV). Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c The unity of the Realm Archived 20 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine – Statsministeriet – stm.dk. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- ^ "Act on the Faroese authorities acquisition of affairs and fields" [Lov om de færøske myndigheders overtagelse af sager og sagsområder]. retsinformation.dk (in Danish). 24 June 2005. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2014.
- ^ Lov om Grønlands Selvstyre Archived 6 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine Template:In lang. Retsinformation.dk. "I erkendelse af, at det grønlandske folk er et folk i henhold til folkeretten med ret til selvbestemmelse, bygger loven på et ønske om at fremme ligeværdighed og gensidig respekt i partnerskabet mellem Danmark og Grønland."
- ^ "Faroe Islands Population". Hagstova Føroya. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ "2020 Population". Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Michael Kjær, Jonas (15 November 2006). "Christiansø betaler ikke sundhedsbidrag". dr.dk (in Danish). Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2007.
- ^ Denmark: Regions, Municipalities, Cities & Major Urban Areas Archived 8 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine – Statistics and Maps on City Population.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Danish Regions – in Brief (3rd revised ed.). Copenhagen: Danske Regioner. 2007. ISBN 978-87-7723-471-2.
- ^ "Regional Tasks in Denmark". Danske Regioner. Archived from the original on 10 May 2014. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Danish Tax System". Aarhus University. Archived from the original on 21 August 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ^ Behringer, Ronald M. (September 2005). "Middle Power Leadership on the Human Security Agenda". Cooperation and Conflict. 40 (3): 305–342. doi:10.1177/0010836705055068. S2CID 144129970. Archived from the original on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- ^ "Danish Presidency of the European Union 2012". European Union. Archived from the original on 3 January 2012. Retrieved 25 May 2014.
- ^ Government of the United States. "US Department of State: Denmark". Retrieved 25 May 2014.
- ^ "2015 Preliminary ODA Figures" (PDF). Paris: OECD. 13 April 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 May 2016. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- ^ "Hjemmeværnet » Se Karrieremuligheder, Job & Løn". Forsvaret (in Danish). Retrieved 18 October 2022.
- ^ Olesen, Gunnar (7 September 2011). "Denmark as a warring nation: A bracket that should be closed" (in Danish). The council for international conflict resolution (RIKO). Archived from the original on 15 February 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ Lavrsen, Lasse (19 June 2010). "Danmark er en krisnation" (in Danish). Information. Archived from the original on 25 February 2016. Retrieved 1 January 2016.
- ^ "Forsvarsministerens Verdenskort". Ministry of Defense of Denmark. 27 December 2007. Archived from the original on 27 December 2007. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
- ^ Clark, A.L. (1996). Bosnia: What Every American Should Know. New York: Berkley Books.
- ^ Phillips, R. Cody. Bosnia-Hertsegovinia: The U.S. Army's Role in Peace Enforcement Operations 1995–2004. Washington, D.C.: United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 70-97-1. Archived from the original on 9 December 2013.
- ^ "Denmark follows UK Iraq pullout". Al Jazeera English. 21 February 2007. Archived from the original on 11 December 2012. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
- ^ "Danmarks Radio – Danmark mister flest soldater i Afghanistan". Dr.dk. 15 February 2009. Archived from the original on 19 February 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- ^ Country and Lending Groups. Archived 2 July 2014 at the Wayback Machine World Bank. Accessed on 14 March 2016.
- ^ "Gross national income per capita 2017, Atlas method and PPP. World Development Indicators database, World Bank, 21 September 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 September 2014. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ "Country Ratings" Archived 16 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine, 2012 Index of Economic Freedom. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ^ "Economic Freedom of the World: 2011 Annual Report Complete Publication (2.7 MB)" (PDF). freetheworld.com. Fraser Institute. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
- ^ "Global Competitiveness Report 2018". World Economic Forum. Archived from the original on 8 December 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ UNESCO 2009 Global Education Digest Archived 28 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Shared fourth with Finland at a 30.3% ratio. Graph on p28, table on p194.
- ^ Kevin Short (28 May 2014). The Worst Places On The Planet To Be A Worker Archived 28 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine. The Huffington Post. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- ^ Joumard, Isabelle; Pisu, Mauro; Bloch, Debbie (2012). "Tackling income inequality. The role of taxes and transfers" (PDF). OECD. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 December 2014. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ Neamtu, Ioana; Westergaard-Nielsen, Niels (March 2013). "Sources and impact of rising inequality in Denmark" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2015. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey. Eurostat, last data update 20 November 2018, retrieved 6 December 2018". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2010 Edition". IMF. 6 October 2010. Archived from the original on 22 February 2011. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ Liz Alderman and Steven Greenhouse (27 October 2014). Living Wages, Rarity for U.S. Fast-Food Workers, Served Up in Denmark Archived 28 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times. Retrieved 28 October 2014.
- ^ On Sweden and Denmark, see Anders Kjellberg and Christian Lyhne Ibsen "Attacks on union organizing: Reversible and irreversible changes to the Ghent-systems in Sweden and Denmark" Archived 9 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine in Trine Pernille Larsen and Anna Ilsøe (eds.)(2016) Den Danske Model set udefra (The Danish Model Inside Out) – komparative perspektiver på dansk arbejdsmarkedsregulering, Copenhagen: Jurist- og Økonomforbundets Forlag (pp.292)
- ^ "StatBank Denmark, Table NABP10: 1-2.1.1 Production and generation of income (10a3-grouping) by transaction, industry and price unit. Retrieved on December 6, 2018". Archived from the original on 17 November 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Denmark". The World Factbook. CIA. 3 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "Eurostat: Net international investment position – quarterly data, % of GDP. Last update 24 October 2018, retrieved December 6 2018". Archived from the original on 26 November 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ Mathias, Peter and Polard, Sidney (eds.) (1989) The Cambridge Economic History of Europe. Cambridge University Press. p. 22.
- ^ Baten, Jörg (2016). A History of the Global Economy. From 1500 to the Present. Cambridge University Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-107-50718-0.
- ^ Template:In lang Danskerne og LO elsker globalisering. Newspaper article 17 November 2016 on finans.dk. Retrieved 6 December 2018. Archived 6 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Denmark and the euro". Danmarks Nationalbank. 17 November 2006. Archived from the original on 16 November 2006. Retrieved 3 February 2007.
- ^ "Standard Eurobarometer 89, Spring 2018. The key indicators. Publication date June 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018". Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "The largest companies by turnover in Denmark". largestcompanies.com. Nordic Netproducts AB. Archived from the original on 6 November 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "Denmark mulls higher taxes for energy traders". 4 May 2023.
- ^ Business Environment Archived 21 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, Invest in Denmark
- ^ "StatBank Denmark, SKTRYK: Tax level by national account groups. Retrieved December 6 2018". Archived from the original on 25 November 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ^ "OECD Revenue Statistics 2018 – Denmark. Retrieved 18 December 2018" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 September 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Society at a Glance 2014 Highlights: DENMARK OECD Social Indicators" (PDF). OECD. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 23 August 2015.
- ^ "The surprising ingredients of Swedish success – free markets and social cohesion" (PDF). Institute of Economic Affairs. 25 June 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ "Tax and Benefit Systems: OECD Indicators. Benefit generosity. Data retrieved 18 December 2018". Archived from the original on 27 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "The world's best business environment". Investindk.com. Archived from the original on 1 July 2012. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- ^ "10 Good Reasons to Invest in Denmark". Investindk.com. Archived from the original on 16 February 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "LFS by sex and age – indicators. OECD Statistics, data retrieved 18 December 2018". Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "Eurostat Employment and Unemployment Database, Table une_rt_a. Unemployment by sex and age – annual average. Last update 31 October 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018". Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "The Danish Government: Denmark's Convergence Programme 2018, p. 8. Publication date April 2018, retrieved 18 December 2018" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ "Ny undersøgelse: I dag er statens udgifter til dagpenge tre gange mindre end i 1995 | Information". Archived from the original on 27 December 2018.
- ^ "Denmark Confirms Participation in E-ELT". ESO Announmentes. Archived from the original on 16 April 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2013.
- ^ WIPO (2022). Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition. Global Innovation Index. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ "Release of the Global Innovation Index 2020: Who Will Finance Innovation?". World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2019". World Intellectual Property Organization. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Novozymes, the world's leading provider of enzymes to the biofuels industry". Canadian Biomass Magazine. Archived from the original on 10 October 2014. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ "EIA – International Energy Data and Analysis for Denmark". Tonto.eia.doe.gov. 15 May 2009. Archived from the original on 4 March 2010. Retrieved 29 May 2009.
- ^ Denmark Crude Oil Production and Consumption by Year (Thousand Barrels per Day) Archived 4 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine – indexmundi.
- ^ Wind energy in Denmark breaking world records Archived 19 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine The Copenhagen Post, Retrieved 17. January 2016.
- ^ Denmark Invests the Most in Clean Energy per GDP Archived 16 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine – yourolivebranch.org. Retrieved 3 January 2012
- ^ "Plug-in and Electrical Vehicles". EnergyMap.dk. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ^ "Global support for International Renewable Energy Agency growing fast". IRENA. 10 September 2014. Archived from the original on 24 September 2014. Retrieved 10 September 2014.
- ^ "Energi og emissioner". www.dst.dk (in Danish). Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Group Annual Report 2014" (PDF). cph.dk. Copenhagen Airports A/S. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2015. Retrieved 19 August 2015.
- ^ Menteth, Thames (13 May 2022). "Construction of Fehmarnbelt tunnel portal begins in Denmark". Ground Engineering (GE). Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ "Ring 3 summary report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 April 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- ^ "Cykelruter og regioner" (in Danish). Visitdenmark.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012.
- ^ "Vi cykler til arbejde 2011" (in Danish). Dansk Cyklist Forbund. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 16 August 2011.
- ^ "Tyske miljøzoner sender gamle biler til Danmark". Politiken.dk (in Danish). 9 January 2009. Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2010.
- ^ "Transport" (PDF). Statistical Yearbook 2012. dst.dk. Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ^ "World Factbook EUROPE : DENMARK", The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ Helliwell, John; Layard, Richard; Sachs, Jeffrey (eds.). "World Happiness Report 2016" (PDF). Sustainable Development Solutions Network. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 March 2016. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ^ Helliwell, John; Layard, Richard; Sachs, Jeffrey World Happiness Report Archived 2 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine. The Earth Institute at Columbia University, p. 8. See also: World Happiness Report 2013 Archived 4 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine, p. 23.; Denmark Is Considered The Happiest Country. You'll Never Guess Why. Archived 23 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine Huffington Post. 22 October 2013.
- ^ Stokes, Buce (8 June 2011). The Happiest Countries in the World Archived 25 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine. The Atlantic. Retrieved 20 September 2013
- ^ Taylor, Jerome (1 August 2006). "Denmark is the world's happiest country – official – Europe, World". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income (source: SILC)". Eurostat Data Explorer. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2015.
- ^ Thomas, Alastair H. (2016). Historical Dictionary of Denmark. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-4422-6465-6.
- ^ "VAN8A: Immigrations (year) by citizenship, sex and residence permit". Statistics Denmark. Archived from the original on 12 October 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ For comparisons and developments see: "Denmark – Migration Profiles" (PDF). UNICEF. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ Statistics on migration only includes people changing citizenship and does not always provide a realistic picture of migration pressure. In Denmark, 5% of the population were non-citizens in 2005, which is a relatively high figure. See Counting Immigrant and Expatriates in OECD Countries: A New Perspective (PDF) (Report). OECD. 21 October 2005. pp. 119–120. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 April 2016. Retrieved 5 January 2016. for example.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Lewis, M. Paul, ed. (2009). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (16th ed.). Dallas, Texas: SIL International. ISBN 978-1-55671-216-6. Archived from the original on 27 December 2007. Retrieved 27 August 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Language". The Nordic Council. Archived from the original on 21 July 2014. Retrieved 7 June 2014.
- ^ "Europeans and their Languages" (PDF). Eurobarometer. European Commission. February 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2014.
- ^ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs named:1 - ^ Denmark – Constitution Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine – Part I – Section 4 [State Church]: "The Evangelical Lutheran Church shall be the Established Church of Denmark, and, as such, it shall be supported by the State."
- ^ Thomsen Højsgaard, Morten (21 February 2018). "Derfor mister kirken mere af folket". Kristeligt Dagblad (in Danish). Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ "Denmark – Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor". International Religious Freedom Report 2009. U.S. Department of State. 2009. Retrieved 23 August 2012.
- ^ Manchin, Robert (21 September 2004). "Religion in Europe: Trust Not Filling the Pews". Gallup Poll. Gallup. Archived from the original on 20 January 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2012.
- ^ Crabtree, Steve (31 August 2010). "Religiosity Highest in World's Poorest Nations". Gallup. Archived from the original on 23 August 2017. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ^ Denmark – Constitution Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine – Part II – Section 6 .
- ^ Denmark – Constitution Archived 10 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine – Part VII – Section 70: "No person shall for reasons of his creed or descent be deprived of access to complete enjoyment of his civic and political rights, nor shall he for such reasons evade compliance with any common civic duty."
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Freedom of religion and religious communities in Denmark Archived 5 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine – The Ministry of Ecclesiastical Affairs – May 2006
- ^ "Hvor mange muslimer er der i Danmark?". tjekdet.dk (in Danish). Retrieved 14 November 2020.
- ^ "Hvor mange muslimer bor der i Danmark?". religion.dk (in Danish). Archived from the original on 9 December 2018. Retrieved 8 February 2018.
- ^ "Religion in Denmark". Archived from the original on 8 February 2006. Retrieved 8 February 2006. – From the Danish Foreign Ministry. Archive retrieved on 3 January 2012.
- ^ Biotechnology (PDF) (Report). Eurobarometer 73.1. October 2010 [Fieldwork: Jan–Feb 2010]. p. 204. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2010.
- ^ Tobias Stern Johansen (23 December 2009). "Hver fjerde dansker tror på Jesus" [One in four Danes believe in Jesus]. Kristeligt Dagblad (in Danish). Archived from the original on 25 December 2009.
Poll performed in December 2009 among 1114 Danes between ages 18 and 74
- ^ "Overview of the Danish Education System". Danish Ministry for Children, Education and Gender Equality. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ^ "Education Policy Outlook: Denmark" (PDF). OECD. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ^ Rick Noack (4 February 2015). Why Danish students are paid to go to college Archived 24 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine. The Washington Post. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Study in Denmark, official government website on international higher education in Denmark". Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ "Om hospitalet". www.rigshospitalet.dk. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ^ "Life expectancy". World Health Organization. 6 July 2016. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brønnum-Hansen, Knud Juel, Jan Sørensen, Henrik (2007). Risk factors and public health in Denmark – Summary report (PDF). København: National Institute of Public Health, University of Southern Denmark. ISBN 978-87-7899-123-2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2014. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Obesity – Adult prevalence". CIA Factbook. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- ^ "Why is Denmark the cancer capital of the world?". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ "Data for cancer frequency by country". WCRF. 2012. Archived from the original on 30 December 2015. Retrieved 4 January 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "International Profiles of Health Care Systems" (PDF). The Commonwealth Fund. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2013. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ "Country Comparison :: Life Expectancy at Birth". The World Factbook. CIA. Archived from the original on 20 January 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Nielson, Emil Gjerding. "In Danish 'ghettos', immigrants feel stigmatized and shut out". U.S. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "In Denmark's Plan To Rid Country Of 'Ghettos,' Some Immigrants Hear 'Go Home'". NPR.org. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Barry, Ellen; Sorensen, Martin Selsoe (2 July 2018). "In Denmark, Harsh New Laws for Immigrant 'Ghettos'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Danes to double penalty for ghetto crime". BBC News. 27 February 2018. Archived from the original on 18 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Denmark to school 'ghetto' kids in democracy and Christmas". Reuters Editorial. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ "Here's what we know about Denmark's 'ghetto plan'". 28 February 2018. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ "What to Know About Denmark's Plan to End Immigrant "Ghettos"". Time. Archived from the original on 5 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ ""No ghettos in 2030": Denmark's controversial plan to get rid of immigrant neighborhoods". Vox. Archived from the original on 4 July 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
- ^ "Her er den nye liste over parallelsamfund - TV 2". nyheder.tv2.dk (in Danish). 1 December 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ^ "Denmark – An Overview". Royal Danish Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 22 September 2007. Archived from the original on 22 January 2008. Retrieved 22 September 2007.
- ^ Sheila Rule: "Rights for Gay Couples in Denmark" Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine – The New York Times. Published: 2 October 1989. Retrieved 7 June 2012
- ^ "Same-Sex Marriage FAQ". Marriage.about.com. 17 June 2003. Archived from the original on 12 February 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ "Denmark approves same-sex marriage and church weddings". BBC News. 7 June 2012. Archived from the original on 16 January 2019. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ^ "Denmark passes bill allowing gays to marry in church". AFP. 7 June 2012. Archived from the original on 10 June 2012. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ Denmark – Language, Culture, Customs and Etiquette. From Kwintessential Archived 10 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 4 December 2008.
- ^ Chopik, William J.; O'Brien, Ed; Konrath, Sara H. (2017). "Differences in Empathic Concern and Perspective Taking Across 63 Countries". Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. 48 (1). Supplementary Table 1. doi:10.1177/0022022116673910. hdl:1805/14139. ISSN 0022-0221. S2CID 149314942.
- ^ "New exhibition: The Danish Golden Age just got longer". SMK – National Gallery of Denmark in Copenhagen (Statens Museum for Kunst). 13 June 2019. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- ^ "Denmark: Properties inscribed on the World Heritage List (8)". UNESCO. Archived from the original on 13 July 2012. Retrieved 19 July 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Human rights in Denmark". The Danish Institute for Human Rights. The Danish Institute for Human Rights. Archived from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ^ "THE CONSTITUTIONAL ACT OF DENMARK". Folketinget.dk. Retrieved 21 October 2020.
- ^ "Four Countries, One People: Inuit Strengthen Arctic Co-operation | Inuit Circumpolar Council Canada". 24 November 2016.
- ^ Template:Cite thesis
- ^ [1] Archived 23 October 2020 at the Wayback Machine Report published by the Greenland Reconciliation Commission
- ^ The Copenhagen Post, 7 June 2012: Gay marriage legalised Archived 16 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 19 September 2012
- ^ "Vedtaget af Folketinget ved 3. behandling den 19. januar 2016 Forslag til Lov om ændring af myndighedsloven for Grønland, lov om ikrafttræden for Grønland af lov om ægteskabets retsvirkninger, retsplejelov for Grønland og kriminallov for Grønland" (PDF) (in Danish). Folketinget. 19 January 2016. Retrieved 28 January 2016.
- ^ "Denmark approves same-sex marriage in the Faroe Islands". Pink News. 19 June 2017. Retrieved 23 December 2017.
- ^ Williams, Steve (20 May 2016). "Denmark to the WHO: Trans Identity Is Not a Mental Illness". Care2 Causes. Archived from the original on 27 March 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^ Simon, Caroline (20 June 2018). "Being transgender no longer classified as mental illness. Here's why". USA TODAY. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kenneth E. Olson, The history makers: The press of Europe from its beginnings through 1965 (LSU Press, 1966) pp 50 – 64, 433
- ^ "Carl Dreyer:Day of Wrath, Ordet, Gertrud". Bright Lights Film Journal. July 2000. Archived from the original on 7 March 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
- ^ Ebert, Robert (16 February 1997). "The Passion of Joan of Arc". Chicago Sun Times. Archived from the original on 10 June 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2013.
Carl Theodor Dreyer (1889–1968), the Dane who was one of the greatest early directors.
- ^ TNS-Gallup meter Archived 19 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine; Television station viewer statistics, figures for July 2012 (week 28). Retrieved 20 July 2012.
- ^ "Commercial radio". Danish Agency for Culture. Archived from the original on 15 May 2014. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ "The Royal Danish Orchestra". The Royal Danish Theatre. Archived from the original on 7 May 2014. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ Festivalguide Gaffa Template:In lang
- ^ Musikfestivaler i Danmark Archived 3 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine VisitDenmark Template:In lang
- ^ "Danish Architecture: An Overview". Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 19 July 2011., Visit Denmark. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- ^ "Architecture". Archived from the original on 6 February 2010. Retrieved 6 February 2010., Embassy of Denmark, Hanoi. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ^ "Danish by Design", DDC. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
- ^ Wall Paintings in Danish Churches from Panoramas.dk Archived 28 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 12 August 2009. Adopting the Biblia pauperum approach, they present many of the most popular stories from the Old and New Testaments.
- ^ Art Encyclopedia: Skagen. Archived 1 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 9 December 2008.
- ^ "The Funish Art Colony" Archived 18 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine, Johannes Larsen Museet. Retrieved 12 August 2011.
- ^ The Bornholm School from the Rough Guide to Denmark. Archived 20 January 2013 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- ^ Contemporary Danish Photography. From Photography-Now Archived 7 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved 28 January 2010.
- ^ "new nordic recipes". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
- ^ "DIF specialforbunds medlems" (in Danish). Danmarks Idrætsforbund. 2013. Archived from the original on 26 May 2014. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ^ "Michael Laudrup bedste spiller gennem tiderne". DBU. 13 November 2006. Archived from the original on 17 May 2011. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
- ^ "National Team rankings". European Handball Federation. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 13 May 2014.
- ^ "Om DIF – Medlemstal". Archived from the original on 16 July 2007. Retrieved 16 July 2007. Template:In lang, The National Olympic Committee and Sports Confederation of Denmark
- ^ Profile | Denmark Archived 14 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine, Fiba.com. Retrieved 24 September 2015.
- ^ Bath, Richard (ed.) The Complete Book of Rugby (Seven Oaks Ltd, 1997 ISBN 978-1-86200-013-1) p66. Archived from July 2007 and Retrieved June 2012.
General and cited sources
[edit]- Stone, Andrew; Bain, Carolyn; Booth, Michael; Parnell, Fran (2008). Denmark (5th ed.). Footscray, Victoria: Lonely Planet. p. 31. ISBN 978-1-74104-669-4.
- Busck, Steen (2002). Poulsen, Henning (ed.). "Danmarks historie – i grundtræk" (in Danish). Aarhus Universitetsforlag. ISBN 978-87-7288-941-2.
- Englund, Peter (2000). Den oövervinnerlige (in Swedish). Stockholm: Atlantis. ISBN 978-91-7486-999-6.
- Frost, Robert I. (2000). The Northern Wars (1558–1721). Pearson Education. ISBN 978-0-582-06429-4.
- Gammelgaard, Frederik; Sørensen, Niels (1998). Danmark – en demokratisk stat (in Danish). Alinea. ISBN 978-87-23-00280-8.
- Isacson, Claes-Göran (2002). Karl X Gustavs krig (in Swedish). Lund: Historiska Media. ISBN 978-91-85057-25-2.
- Jørgensen, Gitte (1995). Sådan styres Danmark (in Danish). Flachs. ISBN 978-87-7826-031-4.
- Michaelsen, Karsten Kjer (2002). "Politikens bog om Danmarks oldtid". Politikens Forlag (1. bogklubudgave) (in Danish). ISBN 978-87-00-69328-9.
- Template:In lang Nationalencyklopedin, vol. 4, Bokförlaget Bra Böcker, 2000, ISBN 978-91-7024-619-7.
- Parker, Geoffrey (1984). The Thirty Years' War. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-02534-6.
External links
[edit]- Denmark.dk Archived 11 December 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Denmark. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Denmark entry at Britannica.com.
- Template:Cite EB9
 Gosse, Edmund William (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). pp. 23–44.
Gosse, Edmund William (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). pp. 23–44. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|HIDE_PARAMETER15=,|HIDE_PARAMETER13=,|HIDE_PARAMETER14c=,|HIDE_PARAMETER9=,|HIDE_PARAMETER3=,|separator=,|HIDE_PARAMETER4=,|HIDE_PARAMETER2=,|HIDE_PARAMETER14bb=,|HIDE_PARAMETER20=,|HIDE_PARAMETER14b=,|HIDE_PARAMETER14cb=,|HIDE_PARAMETER14a=,|HIDE_PARAMETER10=,|HIDE_PARAMETER7=,|HIDE_PARAMETER6=,|HIDE_PARAMETER8=,|HIDE_PARAMETER11=, and|HIDE_PARAMETER12=(help)- Template:Cite EB1922
- Denmark at Curlie
- Denmark profile from the BBC News.
- Key Development Forecasts for Denmark from International Futures.
- Lang and lang-xx template errors
- Pages using the JsonConfig extension
- Webarchive template wayback links
- CS1 German-language sources (de)
- CS1 Danish-language sources (da)
- CS1 errors: periodical ignored
- CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list
- Articles with short description
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Wikipedia pages with incorrect protection templates
- Coordinates not on Wikidata
- Use British English from January 2022
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Use dmy dates from February 2023
- Articles containing German-language text
- Articles containing Danish-language text
- Articles containing Old Norse-language text
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from December 2020
- Pages using multiple image with auto scaled images
- Articles containing Faroese-language text
- Articles containing Greenlandic-language text
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2021
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2017
- All articles containing potentially dated statements
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2014
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2011
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2015
- Articles containing potentially dated statements from 2012
- All articles lacking reliable references
- Articles lacking reliable references from April 2023
- Articles with unsourced statements from February 2019
- CS1 Swedish-language sources (sv)
- Pages using Sister project links with default search
- CS1 errors: empty unknown parameters
- Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the 1911 Encyclopaedia Britannica with Wikisource reference
- Articles with Curlie links
- Denmark
- Barbarian kingdoms
- Christian states
- Countries in Europe
- Danish-speaking countries and territories
- Danish monarchy
- Member states of NATO
- Member states of the European Union
- Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean
- Member states of the United Nations
- Members of the Nordic Council
- Metropolitan or continental parts of states
- NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union
- Northwestern European countries
- Scandinavian countries
- Member states of the Council of Europe
- States and territories established in the 8th century
- OECD members