Dingo
Test123
| Australian dingo | |
|---|---|

| |
| A male dingo | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Genus: | 'Canis' |
| Species: | 'C. lupus' |
| Subspecies: | ''C. l. dingo'' |
| Trinomial name | |
| Canis lupus dingo
(alternate: Canis dingo)[2] (Meyer, 1793)
| |

| |
| 2006 range | |
The dingo (Canis lupus dingo) is a free-ranging dog found mainly in Australia. Its exact ancestry is debated, but dingoes are generally believed to be descended from semi-domesticated dogs from East or South Asia, which returned to a wild lifestyle when introduced to Australia. As such, it is testingcurrently classified as a subspecies of the grey wolf, Canis lupus. The Australian name has therefore sometimes been applied to similar dogs in South-East Asia, believed to be close relations. As free-ranging animals, they are not considered tame, although tame dingoes and dingo-dog hybrids have been bred.
test 123
The dingo's habitat ranges from deserts to grasslands and the edges of forests. Dingoes will normally make their dens in deserted rabbit holes and hollow logs close to an essential supply of water.
The dingo is the biggest terrestrial predator in Australia, and plays an important role as an apex predator. However, the dingo is seen as a pest by livestock farmers due to attacks on animals. Conversely, their predation on rabbits, kangaroos and rats may be of benefit to graziers.
For many Australians, the dingo is a cultural icon. The dingo is seen by many as being responsible for thylacine extinction on the Australian mainland about two thousand years ago,[3] although a recent study challenges this view.[4] Dingoes have a prominent role in the culture of Aboriginal Australians as a feature of stories and ceremonies, and they are depicted on rock carvings and cave paintings.[5]
Despite being an efficient hunter, it is listed as vulnerable to extinction due to its proposed susceptibility to genetic pollution: a controversial concept according to which interbreeding with domestic dogs may dilute the dingo's unique adaptations to the Australian environment.
Nomenclature[edit]
The dingo has several names in both scientific and non-scientific literature, with "dingo" being the most commonly used. In Australia, the term "wild dog" is also widely used, but generally includes dingoes as well as dingo-hybrids and other feral dogs.[6]
Scientific name[edit]
Since its first official nomenclature in 1792 (Canis antarcticus), the scientific name of the dingo has changed several times.[7]
Current taxonomy classifies the Australian dingo, together with its closest relatives outside of Australia, as Canis lupus dingo, a subspecies of grey wolf separate from the familiar common dog, Canis lupus familiaris, while still united with familiaris as an intrataxonomic clade called "domestic dog".[7] An older taxonomy, used throughout most of the 20th century, applied the epithet Canis familiaris dingo. This taxonomy assumed that domestic dogs are a distinct species from the grey wolf, with the dingo classified as a subspecies of domestic dog. However, the term Canis dingo,[8][9] which classifies the dingo as a separate species from both dogs and wolves, has gained support in 2014 in a study that established a reference description of the dingo based on pre-20th century specimens that are unlikely to have been influenced by hybridisation.[10][11] The dingo differs from the domestic dog by relatively larger palatal width, relatively longer rostrum, relatively shorter skull height and relatively wider top ridge of skull.[10] A sample of 19th century dingo skins the study examined suggests that there was considerable variability in the colour of dingoes and included various combinations of yellow, white, ginger and darker variations from tan to black.[10] Although it remained difficult to provide consistent and clear diagnostic features, the study placed morphological limits on what can be considered a dingo.[10]
Colloquial and indigenous names[edit]
The most commonly used name is dingo, which has its origins in the early European colonisation in New South Wales and is most likely derived from the word tingo, used by the Aboriginal people of Port Jackson for their camp dogs.[12] Depending on where they live, local dingoes can be called "alpine dingoes," "desert dingoes," "northern dingoes," "Cape York dingoes," or "tropical dingoes". More recently, people have begun to call dingoes "Australian native dogs" or, by reasoning that they are a subspecies of Canis lupus, "Australian wolves".[13]
The dingo has been given different names in the Indigenous Australian languages, including joogong, mirigung, noggum, boolomo, papa-inura, wantibirri, maliki, kal, dwer-da, kurpany, aringka, palangamwari, repeti and warrigal.[6] Some languages have different names for the dingoes depending on where they live; the Yarralin, for instance, call the dingoes that live with them walaku and those in the wilderness ngurakin.[5]
Description[edit]

Domestic and pariah dogs in southern Asia share so many characteristics with Australian dingoes that they are now considered to be members of the same taxon Canis lupus dingo, a particular subspecies of Canis lupus. While the relationship with humans varies widely among these animals, they are all quite similar in terms of physical features.[6]

A dingo has a relatively broad head, a pointed muzzle and erect ears. Eye colour varies from yellow over orange to brown.[15] Compared to other similarly sized familiaris dogs, dingoes have longer muzzles, larger carnassials (large teeth found in many carnivorous mammals), longer canine teeth, and flatter skulls with larger nuchal lines.[12]
Size[edit]
The average Australian dingo is 52 to 60 cm (20 to 24 in) tall at the shoulders and measures 117 to 154 cm (46 to 61 in) from nose to tail tip. The average weight is 13 to 20 kg (29 to 44 lb); however, there are a few records of outsized dingoes weighing up to 27 to 35 kg (60 to 77 lb).[16][17] Males are typically larger and heavier than females of the same age. Dingoes from northern and northwestern Australia are larger than central and southern populations. Australian dingoes are invariably heavier than Asian ones.[6] The legs are about half the length of the body and the head put together. The hind feet make up a third of the hind legs and have no dewclaws.[6] Dingoes can have sabre-form tails (typically carried erect with a curve towards the back) or tails carried directly on the back.[15]
Fur[edit]

Fur of an adult dingo is short and soft, bushy on the tail, and varies in thickness and length depending on the climate. The fur colour is mostly sandy to reddish brown, but can include tan patterns and sometimes be black, light brown, or white. Completely black dingoes might have been more prevalent in Australia in the past, but have only been rarely sighted in recent times. They are now more common in Asia.[12]
Most dingoes are at least bi-coloured, with small, white markings on the chest, muzzle, tag, legs and paws being the most common feature. Pure Dingoes are also found in white or cream (not albinism) they are also found in black and tan colourations. In the case of reddish individuals, there can be small, distinctive, dark stripes on the shoulders.[6]
Origin and genetic status[edit]
Since dingoes were the largest wild placental mammals in Australia at the time of colonisation and looked similar to domestic dogs, their origin has always been questioned and much debated. Archaeological and morphological studies indicated a relatively late introduction and a close relationship to other domestic dogs. Their exact descent, place of origin and date of arrival in Australia were not identified, nor whether they had once been domesticated or half-domesticated and had gone feral, or whether they had already existed as truly wild animals.[18]
It is widely held that dingoes have evolved or were bred from the Indian wolf or Arabian wolf around 6,000 to 10,000 years ago, as was assumed for all domestic dogs.[19] This theory was based on the morphological similarities of dingo skulls and the skulls of these subspecies of wolves. However, genetic analyses indicated a much earlier domestication.
DNA analysis[edit]
Analyses of amino acid sequences of the haemoglobin from a "pure" dingo in the 1970s supported the theory that dingoes are more closely related to domestic dogs than they are to grey wolves or coyotes. As a result, it was assumed that dingoes and other similar Asian dogs belong to a group of domestic dogs that went feral at a very early time. DNA studies on Australian dingoes and domestic dogs were also undertaken in an effort to reliably differentiate between both populations and to try to determine the extent of interbreeding.
The first two examinations looked firstly at 14 loci (the specific locations of the DNA-sequence of a chromosome), with five of these being more closely examined. No genetic difference could be found. The analyses were then extended to cover 16 loci, comparing dingoes from Central Australia, dingoes from the Eastern Highlands, dingo-hybrids and domestic dogs of other origin. Again, no differences could be found, regardless of the type of examination used. It was reasoned that dingoes and domestic dogs must have a very similar gene pool. However, since only a few differences in the enzymes of different species of the genus Canis could be found, it was assumed that a lack of differences might not indicate a close taxonomic relationship. It was also reasoned that the degree of interbreeding in the wild would be hard to determine.[20]
During further analyses in the late 1990s, researchers examined 14 loci and detected a significantly lower genetic variability among Australian dingoes than among domestic dogs, leading to consideration of the possibility of a small founding population. There was one locus found that might have been suitable for differentiation, but not in the case of interbreeding of a dingo-hybrid with a "pure" dingo. Additionally, it was suspected that findings of other suitable loci might be used to determine whether there are clearly separate sub-populations of the "pure" dingoes.[21]
Mitochondrial DNA sequences[edit]
To determine the origin and time of arrival of Australian dingoes, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequences of 211 dingoes and 19 archaeological samples from pre-European Polynesia were compared with mtDNA samples of 676 domestic dogs and 38 grey wolves in 2004. The domestic dog samples came from China, Africa, Southwest Asia, India, Siberia, the arctic America, Europe, Mongolia, Korea, Japan, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, New Zealand, Hawaii and the highlands of New Guinea. The dingo samples came from zoos, wildlife parks, dingo conservation groups, dingo lovers and 192 wild living specimens from 27 areas in Australia, mainly located in the Pilbara region, New South Wales and northeastern Victoria. The wild specimens had been selected based on similarities of external appearance to exclude the influence of dingo-hybrids and domestic dogs as far as possible.
Compared to wolves and domestic dogs, the variation of mtDNA sequences was very limited. Among dingoes, only 20 mtDNA sequences differing in two point mutations at most could be found. In comparison, 114 mtDNA-sequences with a maximal difference of 16 point mutations between the DNA-types could be found among domestic dogs. Two of the dingo mtDNA-types were similar to that of domestic dogs (A9, A29), while the other 18 types were unique to dingoes.
In a phylogenetic tree of wolves and domestic dogs, dingoes were included in the main clade (A), which contained 70% of all domestic dog types. Within this clade, the dingo-types formed a group around the type A29, which was surrounded by 12 less frequent dingo-types, as well as a set of other domestic dog types. This mtDNA-type was found in 53% of the dingoes and was also found among some domestic dogs from East Asia, New Guinea and the American Arctic. Based on these findings, it was reasoned that all dingo-mtDNA-types originated in A29. A9 was only found in one individual, and it was regarded as possible that this type is the result of a parallel mutation.
Based on a mutation rate of mtDNA with A29 being the only founder type, it was considered that dingoes probably arrived in Australia between 4,600 and 5,400 years ago, which was consistent with archaeological findings. However, it was also considered that dingoes might have arrived from an even earlier date of up to 10,800 years ago in the event of the mtDNA-mutation rate being slower than assumed. It was further reasoned that these findings strongly indicate a descent of dingoes from East Asian domestic dogs and not from Indian domestic dogs or from wolves. In addition these findings indicated two possibilities of descent: all Australian dingoes are descended from a few domestic dogs, theoretically one pregnant female; and all Australian dingoes are descended from a group of domestic dogs, who radically lost their genetic diversity through one or several severe genetic bottlenecks on their way from the Asian continent over Southeast Asia.
Other types[edit]
Nonetheless, the existence of other mtDNA-types on the islands surrounding Australia indicate there have been other types apart from A29 and only one single founding event. These results also indicated that there hasn't been any significant introduction of other domestic dog on the Australian continent prior to the arrival of the Europeans. Also, a shared origin and some sort of genetic exchange between Australian dingoes and the New Guinea singing dogs was regarded as possible. The current state of the Australian dingoes was ascribed to the long wild existence of these dogs and assumed that they are an isolated example of early domestic dogs.
Despite accordant claims,[22][23] these findings did not show that only dingo females mate with non-dingo males and not vice versa. The findings would not allow such a conclusion, since the mating of a dingo female with a non-dingo male could not be detected via analyses of mtDNA. Furthermore the researchers made sure from the start that dingo-hybrids were excluded as far as possible.[18]
Communication[edit]
Like all domestic dogs, dingoes tend towards phonetic communication. However, in contrast to domestic dogs, dingoes howl and whimper more, and bark less. Eight sound classes with 19 sound types have been identified.[24]
Barking[edit]
Compared to most domestic dogs, the bark of a dingo is short and monosyllabic, and is rarely used. Barking was observed to make up only 5% of vocalisations. Dog barking has always been distinct from wolf barking.[25] Australian dingoes bark mainly in swooshing noises or in a mixture of atonal and tonal sounds. In addition, barking is almost exclusively used for giving warnings. Warn-barking in a homotypical sequence and a kind of "warn-howling" in a heterotypical sequence have also been observed. The bark-howling starts with several barks and then fades into a rising and ebbing howl and is probably (similar to coughing) used to warn the puppies and members of the pack. Additionally, dingoes emit a sort of "wailing" sound, which they mostly use when approaching a wateringhole, probably to warn already present dingoes.[6]
According to the present state of knowledge, it is not possible to get Australian dingoes to bark more frequently by putting them in contact with other domestic dogs. However, German zoologist Alfred Brehm reported a dingo that learned the more "typical" form of barking and how to use it, while its brother did not.[26] Whether dingoes bark or bark-howl less frequently in general is not certain.[24]
Howling[edit]

Dingoes have three basic forms of howling (moans, bark-howls and snuffs) with at least 10 variations. Usually, three kinds of howls are distinguished: long and persistent, rising and ebbing, and short and abrupt.
Observations have shown that each kind of howling has several variations, though their purpose is unknown. The frequency of howling varies with the season and time of day, and is also influenced by breeding, migration, lactation, social stability and dispersal behaviour. Howling can be more frequent in times of food shortage, because the dogs become more widely distributed within their home range.[6]
Additionally, howling seems to have a group function, and is sometimes an expression of joy (for example, greeting-howls). Overall howling was observed less frequently in dingoes than among grey wolves. It may happen that one dog will begin to howl, and several or all other dogs will howl back and bark from time to time. In the wilderness, dingoes howl over long distances to attract other members of the pack, to find other dogs, or to keep intruders at bay. Dingoes howl in chorus with significant pitches, and with increasing number of pack-members, the variability of pitches also increases.[27] Therefore, it is suspected that dingoes can measure the size of a pack without visual contact.[12] Moreover, it has been proposed that their highly variable chorus howls may generate a confounding effect in the receivers by making pack size appear larger.[28]
Other forms of communication[edit]
Growling, making up approximately 65% of the vocalisations, is used in an agonistic context for dominance, and as a defensive sound. Similar to many domestic dogs, a reactive usage of defensive growling is only rarely observed. Growling very often occurs in combination with other sounds, and has been observed almost exclusively in swooshing noises (similar to barking).[24]
During observations in Germany, dingoes were heard to produce a sound that observers have called Schrappen. It was only observed in an agonistic context, mostly as a defence against obtrusive cubs or for defending resources. It was described as a bite intention, during which the receiver is never touched or hurt. Only a clashing of the teeth could be heard.[24]
Aside from vocal communication, dingoes communicate, like all domestic dogs, via scent marking specific objects (for example, Spinifex) or places (such as waters, trails and hunting grounds) using chemical signals from their urine, feces and scent glands. Males scent-mark more frequently than females, especially during the mating season. They also scent-rub, whereby a dog rolls its neck, shoulders, or back on something that is usually associated with food or the scent markings of other dogs.[6]
Unlike wolves, dingoes can react to social cues and gestures from humans.[29]
Behaviour[edit]
Dingoes tend to be nocturnal in warmer regions, but less so in cooler areas. Their main period of activity is around dusk and dawn. The periods of activity are short (often less than one hour) with short times of resting. Dingoes have two kinds of movement: a searching movement (apparently associated with hunting) and an exploratory movement (probably for contact and communication with other dogs).[30][31]
In general, dingoes are shy towards humans. However, there are reports of dingoes that were agitated by the presence of humans, such as around camps in national parks, near streets or suburbs.[16][32] According to studies in Queensland, the wild dogs (dingo hybrids) there, move freely at night through urban areas and cross streets and seem to get along quite well.[33]
Dietary habits[edit]
About 170 species (from insects to buffalo) have been identified as part of the dingo's diet. In general, livestock seems to make up only a small proportion of their diet.[6] In continent-wide examinations, 80% of the diet of wild dogs consisted of 10 species: red kangaroo, swamp wallaby, cattle, dusky rat, magpie goose, common brushtail possum, long-haired rat, agile wallaby, European rabbit and the common wombat. This narrow range of major prey indicates these wild dogs are rather specialised,[12] but in the tropical rainforests of northeastern Australia, dingoes are supposed to be opportunistic hunters of a wide range of mammals.[34] In certain areas, they tend to specialise on the most common prey, with a preference for medium- to large-sized mammals. Their consumption of domestic cats has also been proven.[35] Non-mammalian prey is irregularly eaten and makes up only 10% of the dingo's diet. Big reptiles are only rarely captured, at least in eastern Australia, although they are widespread. It is possible that especially large monitor lizards are too defensive and well-armed, or they are simply able to flee fast enough into dens or climb trees.[12]

Dietary composition varies from region to region. In the gulf region of Queensland, feral pigs and agile wallabies are the dingo's main prey. In the rainforests of the north, the main prey consists of magpie geese, rodents and agile wallabies. In the southern regions of the Northern Territory, the dogs mainly eat European rabbits, rodents, lizards and red kangaroo; in arid Central Australia, rabbits, rodents, lizards, red kangaroo and cattle carcasses; and in the dry northwest, eastern wallaroos and red kangaroo. In the deserts of the southwest, they primarily eat rabbits, and in the eastern and southeastern highlands, they eat wallabies, possums and wombats.
To what extent the availability of rabbits influences the composition of the diet cannot be clarified. However, because rabbit haemorrhagic disease killed a large part of the Australian rabbit population at the end of the 20th century, it is suspected that the primary prey of the dogs has changed in the affected areas. Also, on Fraser Island, fish have been proven to be a part of the dingo diet. The main prey species, though, are bandicoots and several rodents. Dingoes also eat a lot of echidnas, crabs, small skinks, fruits and other plants, as well as insects (mostly beetles). During these observations, only 10% of the examined feces-samples contained human garbage (in earlier studies 50% were reported).[12]
When scavenging for food, wild dogs (presumably, all dogs free to roam, not just dingoes) primarily eat cattle and kangaroo carcasses. Dingoes in coastal regions regularly patrol the coast for dead fish, seals, penguins and other washed-up birds.[12]
Dingoes in general drink one litre of water a day in the summer and about half a litre a day in winter. During the winter in arid regions, dingoes could potentially live from the liquid in the bodies of their prey, as long as the number of prey is sufficient. Similarly, weaned cubs in Central Australia are able to draw their necessary requirements of liquid from their food. There, regurgitation of water by the females for the cubs was observed. During lactation, females have no higher need of water than usual, since they consume the urine and feces of the cubs and therefore recycle the water and keep the den clean.[12]
Hunting behaviour[edit]
Dingoes often kill by biting the throat, and they adjust their hunting strategies to suit circumstances. For larger prey, due to strength and potential danger, two or more individuals are needed to bring down the prey. Such group formations are unnecessary when hunting rabbits or other small prey.[12]
Kangaroo hunts are probably more successful in open areas than in places with high densities of vegetation, and juvenile kangaroos are killed more often than adults. Dingoes typically hunt large kangaroos by having lead dingoes chase the quarry toward their waiting packmates, which are skilled at cutting corners in chases. In one area of Central Australia, dingoes hunt kangaroos by chasing them toward a wire fence that hindered their escape.[27]
Birds can be captured when they do not fly or fail to take off fast enough. Dingoes also steal the prey of eagles and the coordinated attack of three dingoes for killing a large monitor lizard has been observed.[36]
Reports state that some dingoes live almost entirely on human food through stealing, scavenging, or begging. In fact, dingoes are well known for such behaviour in some parts of Australia. It is suspected that this might cause the loss of hunting strategies or a change in the social structures.[37]
During studies at the Fortescue River in the mid-1970s, observation showed that most of the studied dingoes learned to hunt and kill sheep very quickly, even without prior contact with sheep. Although the dingoes killed many sheep at that time, they still killed and ate kangaroos.
During the early 1990s, wild dogs were observed to have an extraordinarily high success rate when killing sheep, and did not have to hunt in a coordinated manner to achieve success. Often, a dog may chase and outrun a single sheep, only to turn away suddenly and chase another. Therefore, only a small proportion of the injured or killed sheep and goats are eaten, which seems to be the rule and not the exception. The dog probably falls into some kind of "killing spree," due to the rather panicked and uncontrolled flight behaviour of the sheep, which run in front of the dingoes time and again and, therefore, cause one attack after another. Dingoes often attack sheep from behind during the sheep's flight, which causes injuries to the sheep's hind legs. Rams are normally attacked from the side – probably in order to avoid the horns – or sometimes on the testicles. Inexperienced dingoes, or those that kill "for fun," sometimes cause significant damage to the sheep's hind legs, which often causes death.[38][39]
Nearly all dingo attacks on cattle and water buffalo are directed against calves. Hunting success depends on the health and condition of the adult bovines and on their ability to defend their calves. The defence behaviour of the mother can be sufficient to fend off an attack. Therefore, the basic dingo tactics of attack are distracting the mother, rousing the herd/group and waiting (sometimes for hours), and testing of the herd to find the weakest members.
While locating a cattle herd, dingoes have been observed to make several feint attacks, during which they concentrate on the calves at first then, later on, attack the mothers to distract them. Thereupon, the dingoes retreat and wait at a distance from the herd until the rest of the cows have gathered their calves and move on.
During another observed attack, "subgroups" of a dingo pack took turns in attacking and resting, until the mother was too tired to effectively defend her calf. Dingoes have been observed hunting a water buffalo with an estimated weight of 200 kg, and taking turns biting the buffalo's legs during the chase.[12][40]
Social behaviour[edit]
The dingo's social behaviour is about as flexible as that of a coyote or gray wolf, which is perhaps one of the reasons it was initially believed that the dingo was descended from the Indian wolf.[41] While young males are often solitary and nomadic in nature, breeding adults will often form a settled pack.[42] However, in areas of the dingo's habitat with a widely spaced population, breeding pairs remain together, apart from others.[42]
Where conditions are favourable among dingo packs, the pack is stable with a distinct territory and little overlap between neighbors.[43] The size of packs often appears to correspond to the size of prey that appears in the pack's territory.[43] Desert areas have smaller groups of dingoes with a more loose territorial behaviour and sharing of the water sites.[44] It has been noted that the average monthly pack size was between three and twelve members.[45]
Similar to other canids, a dingo pack largely consists of a mated pair, their current year's offspring, and occasionally a previous year's offspring.[43] There are dominance hierarchies both between and within males and females, with males usually being more dominant than females.[43] However, a few exceptions have been noted in captive packs.[43] During travel, while eating prey, or when approaching a water source for the first time, the breeding male will be seen as the leader, or alpha.[46] Subordinate dingoes will approach a more dominant dog in a slightly crouched posture, ears flat and tail down, to ensure peace in the pack.[43] Establishment of artificial packs in captive dingoes have failed.[43]
Reproduction[edit]

Dingoes breed once annually, depending on the estrus cycle of the females which, according to most sources, only come in heat once per year. Dingo females can come in heat twice per year, but can only be pregnant once a year, with the second time only seeming to be pregnant.[47][48]
Males are virile throughout the year in most regions, but have a lower sperm production during the summer in most cases. During studies on dingoes from the Eastern Highlands and Central Australia in captivity, no specific breeding cycle could be observed. All were potent throughout the year. The breeding was only regulated by the heat of the females. A rise in testosterone was observed in the males during the breeding season, but this was attributed to the heat of the females and copulation. In contrast to the captive dingoes, captured dingo males from Central Australia did show evidence of a male breeding cycle. Those dingoes showed no interest in females in heat (this time other domestic dogs) outside of the mating season (January to July) and did not breed with them.[49]
The mating season usually occurs in Australia between March and May (according to other sources between April and June). In Southeast Asia, mating occurs between August and September. During this time, dingoes may actively defend their territories using vocalisations, dominance behaviour, growling and barking.[12]
Most females in the wild start breeding at the age of two years. Within packs, the alpha female tends to go into heat before subordinates and actively suppresses mating attempts by other females. Males become sexually mature between the ages of one to three years. The precise start of breeding varies depending on age, social status, geographic range and seasonal conditions. Among dingoes in captivity, the pre-estrus was observed to last 10–12 days. However, it is suspected that the pre-estrus may last as long as 60 days in the wild.[6]

In general, the only dingoes in a pack that successfully breed are the alpha pair, and the other pack members help with raising the pups. Subordinates are actively prevented from breeding by the alpha pair and some subordinate females have a false pregnancy. Low-ranking or solitary dingoes can successfully breed if the pack structure breaks up.[50]
The gestation period lasts for 61–69 days and the size of the litter can range from one to 10 (usually five) cubs, with the number of males born tending to be higher than that of females. Pups of subordinate females usually get killed by the alpha female, which causes the population increase to be low even in good times. This behaviour possibly developed as an adaptation to the fluctuating environmental conditions in Australia. Pups are usually born between May and August (the winter period), but in tropical regions, breeding can occur at any time of the year.[6]
At the age of three weeks, the pups leave the den for the first time, and leave it completely at eight weeks. In Australia, dens are mostly underground. There are reports of dens in abandoned rabbit burrows, rock formations, under boulders in dry creeks, under large spinifex, in hollow logs, in augmented burrows of monitor lizards and wombat burrows. The pups usually stray around the den within a radius of 3 km, and are accompanied by older dogs during longer travels. The transition to consuming solid food is normally accompanied by all members of the pack during the age of 9 to 12 weeks. Apart from their own experiences, pups also learn through observation.[51] Young dingoes usually become independent at the age of three to six months or they disperse at the age of 10 months when the next mating season starts.
Migration[edit]
Dingoes usually remain in one area and do not undergo seasonal migrations. However, during times of famine, even in normally "safe" areas, dingoes travel into pastoral areas, where intensive, human-induced control measures are undertaken. It was noted in Western Australia in the 1970s that young dogs can travel for long distances when necessary. About 10% of the dogs captured—all younger than 12 months—were later recaptured far away from their first location. Among these, 10% of the travelled distance for males was 21.7 km and for females 11 km.[52] Therefore, travelling dingoes had lower chances of survival in foreign territories, and it was apparently unlikely that they would survive long migrations through occupied territories. The rarity of long migration routes seemed to confirm this. During investigations in the Nullarbor Plain, even longer migration routes were recorded. The longest recorded migration route of a radio-collared dingo was about 250 km.
Mortality and health[edit]
Documented evidence shows that dingoes in captivity have survived for up to 24 years.[15]
The main cause of death for dingoes is being killed by humans, crocodiles and dogs, including other dingoes. Other causes of death include starvation and dehydration during times of drought or after strong bush fires, infanticide, snake bites, killing of pups by wedge-tailed eagles, and injuries caused by cattle and buffalo.
Dingoes are susceptible to the same diseases as domestic dogs. At present, 38 species of parasites and pathogens have been detected in Australian dingoes. The bulk of these diseases have a minimal influence on their survival. The exceptions include canine distemper, hookworms and heart worms in North Australia and southeastern Queensland. Dingo pups can also be killed by lungworms, whipworms, hepatitis, coccidiosis, lice and ticks. Sarcoptic mange is a widespread parasitic disease among the dingoes of Australia, but is seldom debilitating. Free-roaming dogs are the primary host of Echinococcosis (tapeworms) and have an infection rate of 70 to 90%.
Distribution[edit]
It is only possible to give a crude description of the dingo's distribution area and the accordant population density. Giving an exact assessment of the distribution of dingoes and other domestic dogs is difficult since the exact extent of interbreeding between the two is not known. The following information on the distribution of the dingo applies to dogs classified as dingoes based on fur colour, body form and breeding cycle. Therefore, the maps illustrating their distribution might be conflicting.
Distribution in the past[edit]
Based on fossil, molecular and anthropogenic evidence, dingoes might have once had a widespread distribution. These early dingoes would have associated with nomadic hunter-gatherer societies and later with the rising agricultural centres. It is further assumed that they would have been tamed there and then transported to various places in the world. Findings of dingo habitation in Thailand and Vietnam, regarded as the oldest findings, have been estimated at 5,000 to 5,500 years old. The age of similar findings from the highlands of Indonesia vary from 2,500 to 5,000 years.

Originally, the dingo was suspected to have been introduced to Australia in the Pleistocene by Aborigines, which led to confusion concerning the dingo's nomenclature. Today, the most common theory is that the dingo arrived in Australia about 4,000 years ago. In 1979, an eroding dingo skeleton was excavated by Brown and Gollan (ANU) on the mid-coast of southern New South Wales,[54] dated to 6,000 years of age. More recent mitochondrial DNA research estimates the arrival of dingoes to be between 4,600 and 18,300 years.[55] Evidence of dingoes appears to be absent from Tasmania, which was separated from the main Australian landmass around 12,000 years ago due to a rise in sea level, which led to the theory that dingoes have not been in Australia longer than this time. To reach Australia from Asia, there would have been at least 50 km of open sea to be crossed, even at the lowest sea level. Since there are few, if any, cases of a large land animal making such a journey by itself (the Falkland Islands wolf being a possible exception), the ancestors of modern dingoes most likely were brought to Australia on boats by Asian seafarers.[18] A dance of the Aborigines in the coastal regions of the Kimberley, during which they depict dogs running excitedly up and down a boat and finally jumping into the water, is seen as further evidence for the introduction of dingoes by seafarers.[56] These dogs possibly were used as food or eventually guard dogs. Potentially, the dingo came to Australia and the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific during the course of expansion of the Austronesian culture.

The two main theories concerning the geographical origin and travel routes of the modern dingo's ancestors and their arrival in Australia are:[57]
- The dingoes originated in East Asia and took a travel route over the Southeast Asian islands due to their close proximity to Australia, and the relatively easy accessibility over the islands of the Southeast Asian archipelago. This theory is supported by examination of the mtDNA of Australian dingoes.[18]
- Sheepdogs were introduced from the Indus Valley in Asia, over Timor by Indian seafarers, based on similarities in skeletal anatomy of Indian pariah dogs and Iranian wolves. This theory implies that the oldest-known fossils are 4,000 years old and were found on Timor, where the dogs coexisted for a time with pigs and sheep. This theory would be supported by the assumption that the simultaneous appearance of certain stone tools was caused by Indian influence, but other authorities dispute this. Recent genetic research on aboriginal DNA seems to support this conclusion, that Indian seafarers brought their dogs and other tools with them to Australia 4,000 years ago.[58][59][60]
Whether there were several introductions of dingoes to Australia or just one is not yet known.
The first official report of a "wild dog" in Australia comes from Captain William Dampier in 1699.[61] At the time, dingoes were probably[citation needed] widespread over the main part of the continent and lived in the wild, as well as alongside the Aboriginals. They were mostly tolerated by the European settlers and sometimes kept as pets. The number of dingoes was probably[citation needed] low in those times and increased since then in some parts of Australia. Their numbers probably[citation needed] increased strongly around the 1880s due to the establishment of the pastoral economy and artesian watering places, and probably[citation needed] peaked in the 1930s and 1950s. Afterwards, the numbers remained high, but the percentage of dingo-hybrids has significantly increased since then[citation needed].
Present distribution[edit]
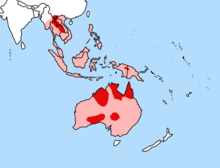
Today, dingoes live in many diverse habitats, including the snow-covered mountain forests of eastern Australia, the deserts of Central Australia, and Northern Australia's tropical forest wetlands. The absence of dingoes in many parts of the Australian grasslands is probably due to human persecution. Based on skull characteristics, size, fur colour and breeding cycles, distinct regional populations could be seen to exist between Australia and Asia, but not within Australia.[6][12]
The wild dog population of Australia now includes dingoes and a wide panoply of feral domestic dogs (mostly mixed-breeds and dingo-hybrids) having an enormous variety of colours. Due to the increased availability of water, native and introduced prey, livestock and human-provided food, this population is on the increase. Reports from some parts of Australia indicate that wild dogs now hunt in packs there, where they had previously been solitary hunters.[62] Dingo densities have been measured at up to 0.3 per square kilometre in both the Guy Fawkes River region of New South Wales and in South Australia at the height of a rabbit plague.[12]
"Pure"[63] dingoes are regarded as widespread in Northern, North West and Central Australia; rare in Southern and Northeast Australia; and possibly extinct in the Southeastern and Southwestern areas.

The establishment of agriculture caused a significant decrease in dingo numbers, and dingoes were practically expelled from the territories occupied by the sheep industry, primarily affecting large parts of southern Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia. This situation was maintained by the construction of the Dingo Fence. Although dingoes were eradicated from most areas south of the Dingo Fence, they still exist in an area of about 58,000 km2 in the dry northern areas north of the Dingo Fence and, therefore, on about 60% of the entire area.[clarification needed]
In Victoria, wild dog populations are currently concentrated on the densely forested areas of the Eastern Highlands, from the border to New South Wales, south to Healesville and Gembrook. They also exist in the large desert in the northwest of the state. Wild dog populations in New South Wales primarily exist along the Great Dividing Range and the hinterlands on the coast, as well as in the Sturt National Park in the northwest of the state.
In the rest of the continent, dingoes are regarded as widespread, with the exception of the arid eastern half of Western Australia. In the bordering areas of South Australia and the Northern Territory, they are regarded as naturally scarce. Wild dogs are widespread in the Northern Territory, with the exception of the Tanami and Simpson Deserts, where they are rare due to the lack of watering holes. However, local concentrations exist there near artificial water sources. According to DNA examinations from 2004, the dingoes of Fraser Island are "pure".[64] However, skull measurements from the mid-1990s had a different result.[65] A 2013 study showed that dingoes living in the Tanami Desert are among the "purest" in Australia.[66]
Outside Australia, dingoes were proven to exist in Thailand, based on comparisons between the skulls of Thai dogs and those of fossil and present-day dingoes. The population there probably has the largest proportion of "pure" dingoes. They are widespread in northern and central Thailand and rare in the southern regions. They may also exist in Burma (Myanmar), China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines and Vietnam, but if they exist there, their distribution is unknown. Dingoes are regarded as widespread in Sulawesi, but their distribution in the rest of Indonesia is unknown. They are regarded as rare in the Philippines and are probably extinct on many islands. In Korea, Japan and Oceania, a few local dog breeds with dingo-like features exist, but dingoes are considered extinct there.[6]
Ecological impact of the dingo after its arrival in mainland Australia[edit]
The dingo is suspected to have caused the extinction of the thylacine, the Tasmanian devil and the Tasmanian nativehen from mainland Australia, since a correlation in space and time is found between the arrival of the dingo and the extinctions of these species. Recent studies have questioned this theory, suggesting that climate change and increasing human populations may have been the cause.[67] Dingoes do not seem to have had the same ecological impact that the red fox had in later times. This might be connected to the dingo's way of hunting and the size of their favoured prey, as well as to the low number of dingoes in the time before European colonisation.[68]
The assumption that dingoes and thylacines were competitors for the same prey stems from their external similarities; the thylacine had a stronger and more efficient bite, but was probably dependent on relatively small prey, while the dingo's stronger skull and neck would have allowed it to bring down bigger prey.[69] The dingo was probably a superior hunter, as it hunted cooperatively in packs and could better defend resources, while the thylacine was probably more solitary. Also, wild dingo populations might have had demographic support from conspecific living with humans and may have introduced new diseases that affected the thylacine more severely.[citation needed]
The extinction of the thylacine on the continent around 2,000 years ago has also been linked to changes in climate and land use by the Aborigines. It is plausible to name the dingo as the cause of the extinction, but significant morphological differences between the two suggest that the ecological overlapping of both species might be exaggerated. The dingo has the dentition of a generalist, while the thylacine had the dentition of a specialist carnivore without any signs of consumption of carrion or bones. It is also argued that the thylacine was a flexible predator that should have withstood the competition by the dingo, but was instead wiped out due to human persecution.[citation needed]
This theory does not explain how the Tasmanian devil and the dingo coexisted on the same continent until about 430 years ago, when the dingo supposedly caused the Tasmanian devil's demise. The group dynamics of dingoes should have successfully kept devils away from carrion, and since dingoes are able to break bones, little would have been left for the devils to scavenge. Additionally, devils are successful hunters of small- to medium-sized prey, so there should have been an overlapping of the species in this area, too. Furthermore, the arguments that the dingo caused the extinction of the thylacine, the devil and the hen are in direct conflict with each other. If the dingo were really so similar to the thylacine and the Tasmanian devil in its ecological role and suppressed both, then coexisting with both for such an extended time is strange. Although this is a possible result of the dingo's introduction, critics regard the evidence for this as insubstantial.[70]
Impact[edit]
Reliable information about the exact ecological, cultural and economic impact of wild dogs does not yet exist. Furthermore, the impact of wild dogs depends on several factors, and a distinction between dingoes and other domestic dogs is not necessarily made.
The appearance of a wild dog is sometimes very important when it comes to the cultural and economical impact. Here, it is often desired that the wild dog's appearance complies to what is demanded, that it is a "pure" dingo or at least looks like one.[71] In the case of their economic impact, their appearance only seems to be important when "pure" dingoes are used as a tourist attraction. Where wild dogs are regarded as pests, their appearance is only of minor importance, if at all.
The impact wild dogs have in urban areas and whether they are a danger to humans (such as direct attacks or diseases) is currently unknown.
Ecological impact[edit]
The dingo is regarded as part of the native Australian fauna by many environmentalists and biologists, as these dogs existed on the continent before the arrival of the Europeans and a mutual adaption of the dingoes and their surrounding ecosystems had occurred. However, the contrary view has dingoes as just another introduced predator that are only native to Thailand.[72]
Much of the present place of wild dogs in the Australian ecosystem, especially in the urban areas, remains unknown. Although the ecological role of dingoes in Northern and Central Australia is well understood, the same does not apply to the role of wild dogs in the east of the continent. In contrast to some claims,[73] dingoes are assumed to have a positive impact on biodiversity in areas where feral foxes are present.[74]
Dingoes are regarded as apex predators and possibly perform an ecological key function. It is likely (with increasing evidence from scientific research) that they control the diversity of the ecosystem by limiting the number of prey and keeping the competition in check. Wild dogs hunt feral livestock such as goats and pigs, as well as native prey and introduced animals. The low number of feral goats in Northern Australia possibly is caused by the presence of the dingoes, but whether they control the goats' numbers or not is still disputable. Studies from 1995 in the northern wet forests of Australia found the dingoes there did not reduce the number of feral pigs, but their predation only has an impact on the pig population together with the presence of water buffalos (which hinder the pigs' access to food).[75]
Observations concerning the mutual impact of dingoes and red fox and cat populations suggest dingoes limit the access of foxes and cats to certain resources. As a result, it is assumed that a disappearance of the dingoes may cause an increase of red fox and feral cat numbers and, therefore, a higher pressure on native animals. These studies found the presence of dingoes is one of the factors that keep fox numbers in an area low, and therefore reduces pressure on native animals, which then do not disappear from the area. The countrywide numbers of red foxes are especially high where dingo numbers are low, but other factors might responsible for this, depending on the area.[35] Evidence was found for a competition between wild dogs and red foxes in the Blue Mountains of New South Wales, since there were many overlaps in the spectrum of preferred prey, but there was only evidence for local competition, not on a grand scale.[76]
It is also possible that dingoes can live with red foxes and feral cats without reducing their numbers in areas with sufficient food resources (for example, high rabbit numbers) and hiding places. Nearly nothing is known about the relationship of wild dogs and feral cats, except both mostly live in the same areas. Although wild dogs also eat cats, it is not known whether this has an impact on the cat populations.[35] At the moment, the Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre is investigating the exact effects of dingoes on the fox and cat populations to determine the benefits of keeping the dog in certain areas of Australia.[77] In many areas, wild dogs live together with the most species of quolls [citation needed], except for the eastern quoll, which is probably extinct on the mainland, so wild dogs are not regarded as a threat to them.
Additionally, the disappearance of dingoes might increase the prevalence of kangaroo, rabbit and turkey[clarification needed] numbers. In the areas outside the Dingo Fence, the number of dingoes and emus is lower than in the areas inside. However, the numbers changed depending on the habitat. Since the environment is the same on both sides of the fence, the dingo was assumed to be a strong factor for the regulation of these species.[clarification needed][78] Therefore, some people demand that dingo numbers should be allowed to increase or dingoes should be reintroduced in areas with low dingo populations to lower the pressure on endangered populations of native species and to reintroduce them in certain areas. In addition, the presence of the Australian brushturkey in Queensland increased significantly after dingo baiting was conducted.[79]
Cultural impact[edit]
Cultural opinions about the dingo are often based on its perceived "cunning", and the idea that it is an intermediate between civilisation and wildness.[80]
Some of the early European settlers looked on dingoes as domestic dogs, while others thought they were more like wolves. Over the years, dingoes began to attack sheep, and their relationship to the Europeans changed very quickly: they were regarded as devious and cowardly, since they did not fight bravely in the eyes of the Europeans, and vanished into the bush.[81] Dingoes were seen as predators that killed wantonly, rather than out of hunger (similar claims are made today concerning dingo-hybrids).[82] Additionally, they were seen as promiscuous or as devils with a venomous bite or saliva, and so they could be killed unreservedly. Over the years, dingo trappers gained some prestige for their work, especially when they managed to kill hard to catch dingoes. Dingoes were associated with thieves, vagabonds, bushrangers and parliamentary opponents. From the 1960s, politicians began calling their opponents "dingo," meaning they were cowardly and treacherous, and it has become a popular form of attack since then.[56] Today, the word "dingo" still stands for "coward" and "cheat," with verb and adjective forms used, as well.[80]
The image of the dingo now ranges from the romantic to the demonic.[83][84] While some Australians see the dingo as a wild dog, others see them as slightly tame wolves, and cultural biases about each of these animals affect general perceptions about dingoes. Some Australians believe the dingo which should be preserved (at least in its "pure" form), and its possible "extinction" is compared to that of the thylacine.[3]
Traditionally, dogs have a privileged position in the Aboriginal cultures of Australia[which?] (which the dingo may have adopted from the thylacine), and the dingo is a well-known part of rock carvings and cave paintings.[5] Ceremonies (like a keen at the Cape York Peninsula in the form of howling[51]) and dreamtime stories are connected to the dingo, which were passed down through the generations.
Similar to how Europeans acquired dingoes, the Aboriginal people of Australia acquired dogs from the immigrants very quickly. This process was so fast that Francis Barrallier (the first European to explore the Outback) discovered in 1802 that five dogs of European origin were there before him.[56] One theory holds that other domestic dogs will adopt the role of the "pure" dingo.[83] In fact, the majority of the myths about dingoes simply call them "dogs" (whether that role was adopted, or whether there was no difference for the storyteller, is unknown),[5] and other introduced animals, such as the water buffalo and the domestic cat, have been adopted into the indigenous Aboriginal culture in the forms of rituals, traditional paintings and dreamtime stories.[80]
The dingo is connected to holy places, totems, rituals and dreamtime characters. There are stories that dogs can see the supernatural, serve as guard dogs, and warn against evil powers. There is evidence that dogs have been buried with their owners to protect them against evil even after death.[85] Most of the published myths originate from the Western Desert and show a remarkable complexity. In some stories, dingoes are the central characters, while in others, they are only minor ones. One time, it is an ancestor from the dreamtime who created humans and dingoes or gave them their current shape. There are stories about creation, socially acceptable behaviour, and explanations why some things are the way they are. There are myths about shapeshifters (human to dingo or vice versa), "dingo-people," and the creation of certain landscapes or elements of those landscapes, like waterholes or mountains.
In other stories, the dingo is responsible for death. In some myths, advice and warnings are given to those who do not want to follow the social rules. Stories can show the borders of one's territory or the dingo in it might stand for certain members of the community; for example, rebellious dingoes stand for "wild" members of the tribe. The dingo has a wild and uncontrollable face in other stories, and there are many tales about dingoes that kill and eat humans (for example, the Mamu, which catches and devours the spirit of every child who roams too far from the campfire).[5] Other stories tell of a giant devil dingo, from which ordinary dingoes originate.
The dog is thereby depicted as a homicidal, malicious creature that—apart from the lack of a subtle mind—is similar to a trickster, since it plays the role of a mischievous adversary for other mythological beings. Many of them fall victim to blood-thirsty dogs or escape them. Here, individual beings have a significant meaning or sometimes become part of the landscape. The actions of these dogs result, for instance, in the creation of stones and trees from flying bones and meat or ochre from the spilled blood.[85]
Economic impact[edit]
Wild dogs are responsible for a wide range of negative and undesired impacts on the livestock industry of Australia, and they have been regarded as pests since the start of the European livestock industry. Sheep are the most frequent prey, followed by cattle and goats. Research on the real extent of the damage, though, and the reason for this problem, only started recently. Livestock can die from many causes and, when the carcass is found, it is often difficult to determine with certainty the cause of death. Since the outcome of an attack on livestock depends to a high degree on the behaviour and experience of the predator and the prey, only direct observation is certain to determine whether an attack was by dingoes or another domestic dog. Even the existence of remnants of the prey in the scat of wild dogs do not prove they are pests, since wild dogs also eat carrion. Exact numbers or reliable estimates of the damage caused by wild dogs are, therefore, hard to obtain and are seldom reliable. Even if livestock is not a big part of the dingo's diet, the extent of damage dingoes could potentially cause to the livestock industry could be much larger because of wanton killing.
The significance of dingoes as a pest is based primarily on the predation of sheep and, to a lesser extent, on cattle, and is not connected only to the direct loss of livestock. Sheep of every age are susceptible to dingo attacks, but in the case of cattle, only the calves are susceptible.[citation needed] Harassment of sheep can cause a less optimal use of grassland and miscarriages.
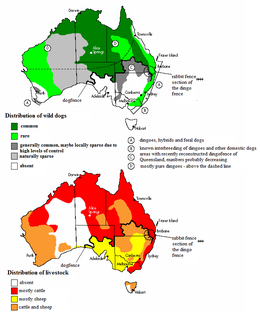
The cattle industry can tolerate low to moderate, and sometimes high, grades[clarification needed] of wild dogs (therefore dingoes are not so easily regarded as pests in these areas). In the case of sheep and goats, a zero-tolerance attitude is common. The biggest threats are dogs that live inside or near the paddock areas. The extent of sheep loss is hard to determine, due to the wide pasture lands in some parts of Australia. The numbers of cattle losses is much more variable and less well-documented. Although the loss of cattle can rise up to 30%,[50] the normal loss rate is about 0–10%.[86]
Therefore, factors such as availability of native prey, as well as the defending behaviour and health of the cattle, play an important role in the number of losses. A study in Central Australia in 2003 confirmed that dingoes only have a low impact on cattle numbers when a sufficient supply of other prey (such as kangaroos and rabbits) is available. In some parts of Australia, it is assumed that the loss of calves can be minimised if horned cattle are used instead of polled.[12] The precise economic impact is not known in this[which?] case, and it is unlikely that the rescue of some calves compensates for the necessary costs of control measures. Calves usually suffer less lethal wounds than sheep due to their size and the protection by the adult cattle, and therefore have a higher chance of surviving an attack. As a result, the evidence of a dog attack may only be discovered after the cattle have been herded back into the enclosure,[clarification needed] and signs such as bitten ears, tails and other wounds are discovered.
The opinions of cattle owners regarding dingoes are more variable than the those of sheep owners. Some cattle owners believe that it is better that the weakened mother loses her calf in times of drought so that she does not have to care for her calf, too. Therefore, these owners are more hesitant to kill dingoes.[51] The cattle industry may benefit from the predation of dingoes on rabbits, kangaroos and rats. Furthermore, the mortality rate of calves has many possible causes, and it is difficult to discriminate between them. The only reliable method to document the damage would be to document all pregnant cows, then observe their development and that of their calves.[50] The loss of calves in observed areas where dingoes were controlled was higher than in other areas. Loss of livestock is, therefore, not necessarily caused by the occurrence of dingoes and is independent from wild dogs.[87]
Domestic dogs are the only terrestrial predators in Australia that are big enough to kill fully-grown sheep, and only a few sheep manage to recover from the severe injuries. In the case of lambs, death can have many causes apart from attacks by predators, which are blamed for the deaths because they eat from the carcasses. Although attacks by red foxes are possible, such attacks are more rare than previously thought.[87] The fact that the sheep and goat industry is much more susceptible to damage caused by wild dogs than the cattle industry is mostly due to two factors: the flight behaviour of the sheep and their tendency to flock together in the face of danger, and the hunting methods of wild dogs, along with their efficient way of handling goat and sheep.
Therefore, the damage to the livestock industry does not correlate to the numbers of wild dogs in an area (except that there is no damage where no wild dogs occur[87]). Even if there are only a few wild dogs in an area, the damage to the sheep industry can be very high, since surplus killing can occur. Sometimes, extreme losses of livestock are reported (once reportedly 2,000 sheep in one night[72]) and are supposed[who?] to be increasing.
According to a report from the government of Queensland, wild dogs cost the state about $30 million annually due to livestock losses, the spread of diseases and control measures. Losses for the livestock industry alone were estimated to be as high as $18 million.[50] In Barcaldine, Queensland, up to one-fifth of all sheep are killed by dingoes annually, a situation which has been described as an "epidemic".[88] According to a survey among cattle owners in 1995, performed by the Park and Wildlife Service, owners estimated their annual losses due to wild dogs (depending on the district) to be from 1.6% to 7.1%.[89]
Despite the variety of estimates, there is little doubt that predation by dingoes can cause enormous economic damage, especially in times of drought when natural prey is sparse and the number of dingoes is still relatively high. Furthermore, wild dogs are involved in the spread of echinococcosis among cattle and sheep, as well as heartworms and parvoviruses among dogs under human care[citation needed]. An infection with echinococcosis can lead to confiscation of 90% of the intestines[clarification needed], which further leads to a value decrease of the meat and high economical damage. Furthermore, bitten livestock can only be sold for a lower price[citation needed].
Dogs are regarded as a delicacy in East Asia and Oceania, and are regularly killed for eating. In the northeast of Thailand, about 200 dingoes are killed per week to be sold on the meat market. Before the start of the 20th century, dingoes were eaten by indigenous Australians, but there are no recent reports about this practice.[6] Among the indigenous Australians, dingoes were also used as hunting aids, living hot water bottles and camp dogs. Their scalps were used as a kind of currency, their teeth were traditionally used for decorative purposes, and their fur for traditional costumes. In some parts of Australia, premiums are paid for dingo fur and scalps. The fur of dingoes generally has only a low value, and export of this fur is forbidden in states where they are protected. There is no widespread commercial catching and killing of dingoes for the purposes of obtaining their fur.
Sometimes "pure" dingoes are important for tourism, when they are used to attract visitors. However, this seems to be common only on Fraser Island, where the dingoes are extensively used as a symbol to enhance the attraction of the island. Tourists are drawn to the experience of personally interacting with dingoes. Pictures of dingoes appear on brochures, many websites and postcards advertising the island.[37] The use of dingo-urine as a repellent against dingoes and wallabies has been considered, but has not yet been economically implemented.[90]
Legal status[edit]
Until 2004, the dingo was categorised as of "least concern" on the Red List of Threatened Species. However, it has since been recategorised as "vulnerable," following the decline in numbers to around 30% of "pure" dingoes, due to crossbreeding with domestic dogs.[1] The dingo is regarded as a regulated, but not threatened, native species under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 in the Commonwealth of Nations and is, therefore, protected in the national parks of the Commonwealth, as well as in World Heritage Sites and other conservation areas. However, this law also allows that dingoes can be controlled in areas where they have a proven impact on the environment. The law forbids the export of dingoes or their body parts from Australia, except for cases where it is regulated by the law. The legal status of the dingo and other wild dogs varies across the Australian federal states and territories.[50]
- Northern Territory: The dingo is regarded as protected, not threatened, and native (due to its ecological impact) under the Territory Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act (2000). Dingoes in the Northern Territory are regarded as having an important conservational value, since interbreeding of dingoes and other domestic dogs is low in the area. However, dingoes can be legally killed when they are a danger to the livestock industry.
- Western Australia: Dingoes and their hybrids are regarded as declared animals under the Agriculture and Related Resources Protection Act (1976). Populations must be controlled, and dingoes can be kept as pets under certain conditions. Control measures are strictly confined to livestock areas, and other domestic dogs are controlled in general. Dingoes are also regarded as unprotected native fauna under the Western Australian Wildlife Conservation Act. Although not protected, dingoes are normally not hunted without permission in conservation areas.
- South Australia: Dingoes and their hybrids are considered pests in the sheep areas inside (south) of the Dingo Fence under the Animal and Plant Control Board (Agricultural Protection and Other Purposes) Act (1986). There, they must be controlled and can only be kept in captivity by authorised zoos and wildlife parks. Outside (north) of the Dingo Fence, dingoes are regarded as legitimate wildlife and, although not protected, control is not mandatory and certain control methods (such as aerial baiting) are not permitted. A 35 km wide buffer zone exists immediately outside (north) of the Dingo Fence, where dingo numbers are controlled to very low levels to reduce incursion through the fence.
- Queensland: Dingoes and their hybrids are regarded as pests under the Land Protection (Pest and Stock Route Management) Act 2002. All landowners are legally committed to reduce the number of all wild dogs on their lands. The dingo is regarded as wildlife and native wildlife under the Nature Conservation Act 1992 and is a natural resource (therefore protected) in conservation areas. Outside of these areas, dingoes are not regarded as native Australian and are not protected. Dingoes and their hybrids can only be kept in wildlife parks and zoos with ministerial agreement.
- New South Wales: The Rural Lands Protection Act (1998) allocates wild dogs the status of pests, and demands from landowners that dingoes shall be decimated or eradicated.[citation needed] Although dingoes are not regarded as protected under the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1974, they are granted full protection in national parks. The dingo is regarded as a native species under the Threatened Species Conservation Act (1995), since these dogs had established populations before the European colonisation. The Wild Dog Destruction Act (1921) includes dingoes in its definition of "wild dogs". This law only affects the western part of the state, where landowners are committed to control wild dogs. The law forbids the ownership of dingoes in that region, except with legal permission. In other parts of the federal state, dingoes can be kept as pets under the Companion Animals Act (1998).
- Australian Capital Territory: Dingoes are regarded as protected under the Nature Conservation Act (1980). On private land, the killing of wild dogs is allowed when with permission from the territory.
- Victoria: Wild dogs are regarded as established pests under the Catchment and Land Protection Act (1994), and landowners (except from the Commonwealth) have the legal duty to hinder the spreading of wild dogs on their lands and eradicate them as much as possible. The term "wild dogs" here includes all dingoes, feral domestic dogs, dogs who became wild and crossbreeds (except for recognised breeds such as the Australian Cattle Dog).[91] The Domestic (Feral and Nuisance) Animal Act (1994) requires every dog owner to have their dogs under control at all times. The dingoes are granted a certain protection in areas that are managed by the National Parks Act (1975). Since 1998, it is possible to own dingoes as pets.[56] There is the possibility that "pure" dingoes may become officially classified as a protected species, according to official statements, and would not stand in conflict with control measures against wild dogs.[92] Update: In 2008, Dingoes were officially declared a threatened species (in danger of extinction) and are now protected.
- Tasmania: The import of dingoes to Tasmania is forbidden under the National Parks and Wildlife Act (1970). The control of dogs that attack livestock is managed under the Dog Control Act (1987).
Control measures[edit]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2014) |
Dingo attacks on livestock led to widescale efforts to repel them from areas with intensive agricultural usage, and all states and territories have enacted laws for the control of dingoes.[12] In the early 20th century, fences were erected to keep dingoes away from areas frequented by sheep, and a tendency to routinely eradicate dingoes developed among some livestock owners. Established methods for the control of dingoes in sheep areas entailed the employment of specific workers on every property. The job of these people (who were nicknamed "doggers") was to reduce the number of dingoes by using steel traps, baits, firearms and other methods. The responsibility for the control of wild dogs lay solely in the hands of the landowners. At the same time, the government was forced to control the number of dingoes. As a result, a number of measures for the control of dingoes developed over time. It was also considered that dingoes travel over long distances to reach areas with richer prey populations, and the control methods were often concentrated along "paths" or "trails" and in areas that were far away from sheep areas. All dingoes were regarded as a potential danger and were hunted.
Apart from the introduction of 1080 (extensively used for 40 years and nicknamed "doggone"), the methods and strategies for controlling wild dogs have changed little over time. Information concerning cultural importance to indigenous people and the importance of dingoes and the impact of control measures on other species is also lacking in some areas. Historically, the attitudes and needs of indigenous people were not taken into account when dingoes were controlled. Other factors that might be taken into account are the genetic status (degree of interbreeding) of dingoes in these areas, ownership and land usage, as well as a reduction of killing measures to areas outside of the zones. However, most control measures and the appropriate studies are there to minimise the loss of livestock and not to protect dingoes.
Increasing pressure from environmentalists against the random killing of dingoes, as well as the impact on other animals, demanded that more information needed to be gathered to prove the necessity of control measures and to disprove the claim of unnecessary killings.Today, permanent population control is regarded as necessary to reduce the impact of all wild dogs and to ensure the survival of the "pure" dingo in the wild.[50]
Deterrence[edit]
One method that does not have any proven effect is to hang dead dogs along the borders of the property in the belief that this would repel wild dogs.[12]
Guardian animals[edit]
To protect livestock, livestock guardian dogs (for example, Maremmas), donkeys, alpacas and llamas are used.[93][94]
To keep wild dogs away from certain areas, efforts are taken to make these areas unattractive for them (for example, by getting rid of food waste) and therefore forcing them to move elsewhere. Control through deliberately spreading disease is normally not considered. Such attempts probably would not be successful, because typical dog diseases are already present in the population. Additionally, dogs under human care would also be susceptible. Other biological control methods are not regarded as achievable, since there would be a high risk of decimating dogs under human care.
Dingo Fence[edit]

In the 1920s, the Dingo Fence was erected on the basis of the Wild Dog Act (1921) and, until 1931, thousands of miles of Dingo Fences had been erected in several areas of South Australia. In the year 1946, these efforts were directed to a single goal, and the Dingo Fence was finally completed. The fence connected with other fences in New South Wales and Queensland. The main responsibilities in maintaining the Dingo Fence still lies with the landowners, whose properties border on the fence and receive financial support from the government.
Reward system[edit]
A reward system (local, as well from the government) was active from 1846 to the end of the 20th century, but there is no evidence that – despite the billions of dollars spent – it was ever an efficient control method. Therefore, its importance declined over time.[6]
Poisoning[edit]


Strychnine is still used in all parts of Australia.
Baits with the poison 1080 are regarded as the fastest as safest method for dog control, since they are extremely susceptible. Even small amounts of poison per dog are sufficient (0.3 mg per kg).[50] The application of aerial baiting is regulated in the Commonwealth by the Civil Aviation Regulations (1988). The assumption that the Tiger Quoll might be damaged by the poison led to the dwindling of areas where aerial baiting could be performed. In areas where aerial baiting is no longer possible, it is necessary to put down baits.
Over the last years, cyanide-ejectors and protection collars (filled with 1080 on certain spots) have been tested.[95][96]
The eradication of dingoes due to livestock damage decreased along with the importance of the sheep industry and the usage of strychnine (which beforehand had been used for 100 years) in the 1970s. The number of doggers also decreased and the frequency of government-approved aerial baiting increased. During this period, many farmers in Western Australia switched to the cattle industry, and findings in the area of biology led to a significant change in control measures and techniques in association with reduced costs and increased efficiency. At the same time, the importance of 1080 increased.
Spaying and neutering[edit]
Owners of dingoes and other domestic dogs are sometimes asked to spay or neuter their pets and keep them under observation to reduce the number of stray/feral dogs and prevent interbreeding with dingoes (for instance under the Territory Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act (2000)).[50]
Efficiency of measures[edit]
The efficiency of control measures was questioned in the past and is often questioned today, as well as whether they stand in a good cost-benefit ratio. The premium system proved to be susceptible to deception and to be useless on a large scale, and can therefore only be used for getting rid of "problem-dogs".[12][97] Animal traps are considered inhumane and inefficient on a large scale, due to the limited efficacy of baits. Based on studies, it is assumed that only young dogs that would have died anyway can be captured.[52] Furthermore, wild dogs are capable of learning and sometimes are able to detect and avoid traps quite efficiently. In one case, a dingo bitch followed a dogger and triggered his traps one after another by carefully pushing her paw through the sand that covered the trap.[81]
Poisonous baits can be very effective when they are of good meat quality; however, they do not last long[98] and are occasionally taken by red foxes, quolls, ants and birds. Aerial baiting can nearly eliminate whole dingo populations.[52] Livestock guardian dogs can effectively minimise livestock losses, but are less effective on wide open areas with widely distributed livestock. Furthermore, they can be a danger to the livestock or be killed by control measures themselves when they are not sufficiently supervised by their owners.[96] Fences are reliable in keeping wild dogs from entering certain areas, but they are expensive to build, need permanent maintenance, and only cause the problem to be relocated.
According to studies, control measures can eliminate 66% to 84% of a wild dog population, but the population can reach its old numbers very quickly over the course of a year, depending on the season, such as by immigration of young dogs from other areas. Only a cohesive coordinated control in all areas could be efficient in the long run, if at all.[71] Control measures mostly result in smaller packs and a disruption of pack structure. The measures seemTemplate:Which? to be rather detrimental to the livestock industry because the empty territories are taken over by young dogs and the predation then increases. Nonetheless, it is regarded as unlikely that the control measures could completely eradicate the dingo in Central Australia, and the elimination of all wild dogs is not considered a realistic option.
Conservation[edit]
Dingoes are reasonably abundant in large parts of Australia, but there is some argument that they are endangered due to interbreeding with other dogs in many parts of their range.[1] Dingoes are not a protected species, but they are regulated under federal law and, thus, their status varies in different states and territories. Dingoes receive varying levels of protection in conservation areas such as national parks and natural reserves in New South Wales, the Northern Territory and Victoria, Arnhem Land and other Aboriginal lands, UNESCO World Heritage Sites, and the whole of the Australian Capital Territory. In some states, dingoes are regarded as declared pests and landowners are allowed to control the local populations. Throughout Australia, all other wild dogs are considered pests.

The dingoes of Fraser Island are considered to be of significant conservational value. Due to their geographic and genetic isolation, they are considered to be the most similar to the original dingoes, and they are seen as the most pure dingo population. The dingoes there are not "threatened" by interbreeding with other domestic dogs. Because of their conservational value, outrage was sparked in January 2013 when two six-month-old dingo pups were found dead, believed to have been run over near Lake McKenzie.[99] The couple who found the dingoes were outraged at the reaction of the rangers, and Fraser Coast area manager Ross Belcher said that there will be serious penalties for those who kill or injure Fraser Island dingoes.[100]
In February 2013, a report on Fraser Island dingo management strategies was released, with options including ending the intimidation of dingoes, tagging practice changes and regular veterinarian checkups, as well as a permanent dingo sanctuary on the island.[101]
Groups that have devoted themselves to the conservation of the "pure" dingo by using breeding programs include the Australian Native Dog Conservation Society and the Australian Dingo Conservation Association. Presently, the efforts of the dingo conservation groups are considered to be ineffective because most of their dogs are untested or are known to be hybrids.[6]
Dingo conservation efforts focus primarily on preventing interbreeding between dingoes and other domestic dogs in order to conserve the population of pure dingoes. This is extremely difficult and costly. Conservation efforts are hampered by the fact that it is not known how many pure dingoes still exist in Australia. Steps to conserve the pure dingo can only be effective when the identification of dingoes and other domestic dogs is absolutely reliable, especially in the case of living specimens. Additionally, conservation efforts are in conflict with control measures.
Conservation of pure and survivable dingo populations is promising in remote areas, where contact with humans and other domestic dogs is rare. Under New South Wales state policy in parks, reserves and other areas not used by agriculture, these populations are only to be controlled when they pose a threat to the survival of other native species. The introduction of "dog-free" buffer zones around areas with pure dingoes is regarded as a realistic method to stop interbreeding. This is enforced in the way that all wild dogs can be killed outside of the conservation areas. However, studies from the year 2007 indicate that even an intensive control of core areas is probably not able to stop the process of interbreeding.[102]
There is presently no information regarding what opinions the public has regarding the conservation of dingoes. There is no unity on the definition of "pure" dingoes and to what extent they should be controlled.[103]
As a pet and working dog[edit]
This article contains weasel words: vague phrasing that often accompanies biased or unverifiable information. (May 2014) |
Opinion is divided about the keeping of dingoes as pets or as working dogs. Some consider the dingo unsuitable for domestication, while others see a domesticated dingo as no different from any other domesticated dog.[104] In this vein, dingoes would have the right to be recognised as a dog breed, and domestication would be the only reliable way of ensuring the survival of the "pure" dingo.[105] Some disagree that the dingo should be labeled a dog breed, as they believe "true" dingoes can be tamed but not truly domesticated.[106]

Dingoes can be very tame when they come in frequent contact with humans.[24] Furthermore, some dingoes live with humans (due to practical, as well as emotional reasons). Many indigenous Australians and early European settlers lived alongside dingoes. Indigenous Australians would take dingo pups from the den and tame them until sexual maturity and the dogs would leave.[106] Alfred Brehm reported cases where dingoes that were completely tame and, in some cases, behaved exactly like other domestic dogs (one was used for shepherding heavy livestock), as well as specimens that remained wild and shy. He also reported about dingoes that were aggressive and completely uncontrollable, but he was of the opinion that these reports "should not get more attention than they deserve," since the behaviour depends on how the dingo was raised since early puppyhood. He believed that these dogs could become very decent pets.[26]
According to Eberhard Trumler,[who?] dingoes are very smart and affectionate. To would-be owners, he recommended the provision of a large escape-proof enclosure and a partner of the opposite sex. During heat, dingoes are harder to manage than other domestic dogs which, combined with their attachment to their owners, can lead to problems, since they want to follow their owners and never miss the opportunity to feed. Dingoes are supposed[who?] to find every weak spot of an enclosure or residence, escape for a while and stray through towns and villages. Their intellectual ability is supposedly[who?] connected to an enormous ability to learn and a lightning perception. Dingoes have a reputation for not handling pressure, but this conflicts with their record as working dogs. They are suitable as shepherd dogs, appearing to see a purpose in it (keeping together a familiar group is in their nature) and, even today, some dingoes are employed as shepherd dogs. In addition, dingoes have strong toileting instincts and can be easily housebroken.
In 1976, the Australian Native Dog Training Society of NSW Ltd. was founded. Until this time, the ownership of dingoes was illegal.[citation needed] In mid-1994, the Australian National Kennel Council(ANKC) officially recognised the dingo as Australia's national dog breed, and a breed standard was published some years later. The dingo is listed in Group 4 (hound) of the ANKC.[107] However, it is still illegal in some states to own, breed or sell dingoes, as it is in some countries.[15]
In South Australia, dingoes can only be kept in specially licensed zoos, circuses and authorised research institutions. South Australia is a particularly sensitive region, due to extensive sheep farming conflicting with large populations of wild dingoes in the north of the state. Dingoes are bred by certain clubs and private individuals in Australia and the United States. The dingo is not regarded as a dog breed by the Fédération Cynologique Internationale. However, the American Rare Breed Association (ARBA) regards the dingo as a breed belonging to the Spitz and Primitive Group.
Goals[edit]
In 1998 in New South Wales, the dingo was reclassified as a pet in order to save the species from extinction. Breeding programs were introduced, which were considered to be the best option available for safeguarding the continuation of the species, with the goal of returning them to the wild at a later date.[104]
Dingoes have also been bred for sale or use as working dogs. The use of dingoes at customsTemplate:Huh? was first attempted in 1976 in Victoria. However, some peopleTemplate:Which? speculated that these dogs were cross-breeds of dingoes and shepherd dogs.[15]
Criticism[edit]
The ownership of dingoes as pets and their breeding is widely criticised. The main criticism is that the activities and the resulting consequences of the dingo conservation groups, "dingo farms" and legislation for legal ownership of dingoes for people in public, is seen to be an additional threat to the survival of the pure dingoes. This fear exists because the majority of these breeding activities effectively expedite the interbreeding of dingoes and other domestic dogs, when the identification of a pure dingo is not absolutely correct respectively when hybrids are sold as "pure" dingoes.[6][clarification needed]
Supporters of breeding programmes are only mildly optimistic about a successful outcome. Success in the form of a population viable for future re-wilding cannot be easily accomplished.[108] According to David Jenkins,[who?] the breeding and reintroduction of pure dingoes is no easy option and, at the time[when?], there were no studies that seriously dealt with this topic, especially in areas where dingo populations are already present.[109]
An additional threat is that breeders may unconsciously select tamer dingoes by breeding individuals who are easier to manage. Therefore it may happen that, over the years, the tame populations may become less suitable for living in the wild than their ancestors. In addition, a loss of genetic diversity (thus resulting in a higher susceptibility to diseases) might occur due to a small founding population, and negative changes could occur simply because the dogs were captive-bred. Furthermore, some features that are necessary for survival in the wild might "fade" under the conditions of domestication (for example, hunting techniques) because they are no longer needed.
Another criticism is that adult dingoes are viewed by some[who?] to be unsuitable as pets in the same ways as other domestic dogs. Dingoes are regarded[who?] as more independent-minded than other domestic dogs, making domestication reportedly[who?] difficult. As dingoes age, they succumb[clarification needed] to their natural instincts and become more likely to escape into the wild.[104] Furthermore, most people are unable to provide a dingo with what it needs, and dingoes may not react positively to domestication and training. Supposedly, only few dingoes and dingo-hybrids would reach an old age, since the owners would not know how to handle them. When a dingo is not socialised, it would be hard to control and develop behavioural problems from aspects of domestic life more easily tolerated by other dog breeds. To make dingoes more suitable as lapdogs, breeders would need to cross them with other domestic dogs.[110]
Interbreeding with domestic dogs[edit]

European domestic dogs first arrived in Australia during the European colonisation. These dogs reverted to the wild (both unintentionally and intentionally), produced feral populations and interbred with the existing dingoes. Hybrids of dingoes and domestic dogs exist today in all wild dog populations of Australia, with their numbers having increased to such a degree that any completely "pure" populations may no longer exist.[56] The degree of interbreeding is locally so high, for instance in urban and rural areas, that there are big populations consisting purely of hybrids. Estimates from the 1990s assumed a proportion of dingo-hybrids of about 78% in the wild.[111] It is not clear how large the current population of hybrids is today.
Dingo-like domestic dogs and dingo-hybrids can be generally distinguished from "pure" dingoes by their fur colour, since there is a wider range of colours and patterns among them than among dingoes. In addition, the more dog-typical kind of barking exists among the hybrids, and differences in the breeding cycle,[112] certain skull characteristics,[113] and genetic analyses[114] can be used for differentiation. Despite all the characteristics that can be used for distinguishing between dingoes and other domestic dogs, there are two problems that should not be underestimated. First, there is no real clarity regarding at what point a dog is regarded as a "pure" dingo,[103] and, secondly, no distinguishing feature is completely reliable—it is not known which characteristics permanently remain under the conditions of natural selection.
In science, there are two main opinions regarding this process of interbreeding. The first, and likely most common, position states that the "pure" dingo should be preserved via strong controls of the wild dog populations, and only "pure" or nearly "pure" dingoes should be protected.[115] The second position is relatively new and is of the opinion that people must accept that the dingo has changed and that it is impossible to bring the "pure" dingo back. Conservation of these dogs should therefore be based on where and how they live, as well as their cultural and ecological role, instead of concentrating on precise definitions or concerns about "genetic purity".[116] Both positions are controversially discussed.
There is a wider range of fur colours, skull shapes and body size in the modern-day wild dog population than in the time before the arrival of the Europeans. Over the course of the last 40 years, [when?] there has been an increase of about 20% in the average wild dog body size.[117] It is currently unknown whether, in the case of the disappearance of "pure" dingoes, remaining hybrids would alter the predation pressure on other animals. It is also unclear what kind of role these hybrids would play in the Australian ecosystems. However, it likely that the dynamics of the various ecosystems will not be disturbed by this process.[12]
Attacks on humans[edit]
Although dingoes are large enough to be dangerous, they generally avoid conflict with humans. Apart from the well-known case in which an infant was taken from a campsite (see below), there have been numerous confirmed dingo attacks, often involving people feeding wild dingoes, particularly on Fraser Island, a special center of dingo-related tourism (see main article). Most dingo attacks are minor in nature, but some can be major, and a few can be fatal. Many Australian national parks have signs advising visitors not to feed wildlife, partly because this practice is not healthy for the animals, and partly because it may encourage undesirable behaviour, such as snatching or biting by dingoes, goannas and some birds.
Azaria Chamberlain dingo attack[edit]
On 17 August 1980, a nine-week-old girl named Azaria Chamberlain was taken by a dingo near Uluru (then known as Ayers Rock) and killed.[32] Her mother, Lindy Chamberlain, was suspected and wrongly convicted of murder, and her father, Michael Chamberlain, with being an accessory after the fact, as the court did not believe that an animal generally shy of humans would be capable of such an act. After serving more than three years of her sentence, Lindy was released from prison when the jacket of the baby was found in a dingo den. The parents were thereafter found innocent, but the cause of death was not officially listed as a dingo attack until 12 June 2012.[118][119][120][121]
Fraser Island attacks[edit]
- In April 1998, a 3-year-old Norwegian girl was bitten and scratched by a dingo.[122]
- On 30 April 2001, nine-year-old Clinton Gage was attacked and killed by two dingoes near Waddy Point on Fraser Island. The incident and the resultant culling of 31 dingoes caused a large outcry among the residents. There were many protests and the suggestion was made to erect fences.[123][124]
- On 26 April 2011, a three-year-old girl was attacked on Fraser Island by two dingoes. She suffered serious puncture wounds to her leg.[125]
- In November 2012, a six-month-old dingo by the name[who?] of Inky was killed by rangers on Fraser Island after continued aggressive and dangerous behaviour towards people. The dangerous behaviour included "lunging" at a family, coming out of the bushland at high speed towards volleyball players, and grabbing two tourists on separate occasions with his mouth, not breaking the skin on either occasion.[126] Rangers attempted to trap the dangerous dingo for a month before they were successful. The captured animal was then euthanised.[127] One Dingo advocacy group argued that, as a juvenile, the dingo's aggressive behaviours would be considered normal for his young age.[126] Soon after, Inky's brother Byron was killed by rangers, although his documented incidents never reached the serious Code E level that his brother's had.[128]
Dingo conservation groups on Fraser Island have become frustrated with the killing of dingoes that attack humans.[citation needed] It has been proposed[who?] that problem dingoes be relocated to a wildlife sanctuary.[129] Queensland Environment Minister Andrew Powell said that the Fraser Island government should work to better educate people about dingoes to help stop attacks.[130]
Conclusions[edit]
Articles published about dingo attacks blame them on habituation, especially through the intentional and unintentional feeding of dingoes.[citation needed] The more frequently these animals are fed or allowed to scavenge on waste food, the more likely they are to react aggressively towards humans when they no longer receive or find food. It is further thought[who?] that dingoes might have started to regard the food sources found (garbage cans, leftovers and handouts) as part of their territory. Attacks then occur with humans seen as competition, and dingoes simply reacting to protect their food supply.
Even when habituation to humans seems to be the general cause for attacks, it is not absolutely clear, and therefore the overall threat towards people is not known for sure. Some attacks might result from the "play" of young cubs, especially with children. Attacks can also be caused by mistaken reactions of humans to aggressive and dominant behaviour of dingoes. That some dingoes might regard humans as prey is a possibility, as children or incapacitated adults could be theoretically overpowered.[37][124] Dr. Bradley Smith[who?] said that Fraser Island has a problem with humans and not with the dingoes, that dogs who were labelled "aggressive" were simply behaving naturally.[131]
The behaviour of humans might undermine efforts to guard against dingo attacks. Therefore, the change in human behaviour is at the centre of attention.[who?] Warning signs like "Beware of Dingoes" seem to have lost their effect on Fraser Island, despite the high number of such signs.[citation needed] Furthermore, some humans[which?] do not realise how adaptive and quick dingoes are. Therefore, humans do not remain attentive enough.[citation needed] They[who?] do not consider, for instance, that dingoes steal food like fruits and vegetables. In addition, some tourists seemed to be confused by the high number of rules in some parks, and they have been prompted in some cases to actively feed the wild animals.[37][50][123][124]
Problems in classification[edit]

There is no general agreement (scientific or otherwise) regarding what the dingo is, in a biological sense, since it has been called "wolf," "dingo," "dog," and "wild dog".[84] Even within the scientific community, the dingo is given several names. There is no consensus regarding whether the dingo is a feral or native animal, or what kinds of dogs should be classed as "dingoes". Thus, some people consider the New Guinea Singing Dog, the Basenji, the Carolina Dog[56] and certain other dog populations to be dingoes. Evidence indicates a discord concerning the status of these dogs, as well.
Dingoes have been variously considered to be wild dogs,[32] the progenitor of domestic dogs,[56] the ancestor of modern dog breeds, a separate species,[132] a link between wolf and domestic dog,[56] a primitive canine species[133] or primitive domestic dog,[6] a "dog-like" relative of wolves[134] or a subspecies of the domestic dog.[135] Others consider them to be native dogs of Asia,[136] a relatively unchanged form of early domestic dog,[12] part wolf and part dog,[137] or to have been selectively bred from wolves.[93] Then again, some do not consider dingoes feral any more but completely wild, since they have been living under natural selection for a very long time.[138] According to present scientific consensus and knowledge, dingoes are domestic dogs that arrived at their present distribution with humans, adapted to the respective conditions and are no more "primitive" or "primordial" than other domestic dogs.[139]

The Australian dingo has never been subject to the artificial selection that produced modern dog breeds,[83] and it may be an undomesticated descendant of an extinct Asian wolf.[140] However, compared to the European grey wolf, dingoes have an approximately 30% lower relative brain size,[141] reduced facial expressions,[142] reduced impressive behaviour,[24] curled tails that can be carried over the back, and generally a permanent fertility in males—features that all known domestic dogs share and are considered to be caused by domestication.[19][24] It might happen that one and the same source names the dingo as a subspecies of the grey wolf, but lists all other domestic dogs as separate species.[143] Likewise, the scientific name of the dingo might be Canis lupus dingo, but the dingo is regarded as a separate species, nonetheless.[144] Alfred Brehm originally considered the dingo to be a separate species but, after examining several different specimens, he came to the conclusion that they could only be domestic dogs.[26] In contrast, William Jardine considered the dingo to be an entirely separate species, while contemporary French naturalists regarded them as feral dogs.[145] Even among modern-day scientists, dingoes and other domestic dogs are sometimes considered two separate species, despite small genetic, morphological and behavioural differences.
The phenomenon of interbreeding between both is then attributed to the statement that all wolf-like species can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.[21] However, breeding experiments in Germany could only prove an unrestricted fertility in the offspring of domestic dogs and grey wolves. Hybrids between domestic dogs and coyotes, and domestic dogs and golden jackals, had communication problems[clarification needed] among each other, as well to the parent species. From the third hybrid generation on, a decrease in fertility and an increase in genetic damage[clarification needed] was observed among the coyote-hybrids and jackal-hybrids.[139] Observations of this kind have never been made for hybrids of dingoes and other domestic dogs, only that dingoes and other domestic dogs can freely interbreed with each other.[146]
The choice of classification can have a direct impact on the dingo. Dingoes officially cease to exist outside of national parks and become unprotected wild dogs.[84] The term "wild dog," itself, sometimes only includes dingoes and their hybrids[147] or respectively excludes dingoes.[148] Another view is that dingoes are "only" feral outside of national parks, with this term having a more negative meaning than the term "wild".
On the other hand, dingoes have been "rehabilitated" in some way, by changing their status from pests to "Australia's native dog" or, more subtly, from a subspecies of the domestic dog to that of the grey wolf. The undertone in the Australian press seemed to be that being a grey wolf or an Asian wolf means that the dingo is more "wild" and, therefore, more desirable than a companion animal (domestic dog). It is possible that the habit of calling the dingo only "dog" (not "wild dog") in colloquial language indicates a form of familiarity or debasing. In the last case, it might be morally easier to kill a dog when it causes problems because it would not have the "high status" of a wolf or dingo.[84] Sometimes, it is considered bad that dingoes are domestic dogs, that they are descended from them and not "directly" from the grey wolf.[149] In short, if the dingo is regarded as native, then it is worthy of protection. But if it is considered to be "just" a variant of the domestic dog, it is regarded as a pest and should be eradicated.[29][72]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Template:IUCN2012.2
- ^ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jzo.12134/abstract
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". DOGSLife, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "extinction" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". ESA Ecology, abgerufen am 9. September 2013.
- ^ a b c d e Rose, Deborah Bird (1992). Dingo makes us Human, life and land in an Aboriginal Australian culture. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-39269-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Corbett, Laurie (2004). "Dingo". In Claudio Sillero-Zubiri, Michael Hoffmann and David W. Macdonald (ed.). Canids: Foxes, Wolves, Jackals and Dogs (PDF). International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "canid" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b Template:MSW3 Wozencraft
- ^ Gaisler, J.; J. Zejda (1997). Enzyklopädie der Säugetiere (in German). Verlag Werner Dansien. ISBN 3-7684-2750-1.
- ^ Macdonald, David (2004). Die große Enzyklopädie der Säugetiere (in German). Könemann in der Tandem Verlag GmbH. ISBN 3-8331-1006-6.
- ^ a b c d Crowther, M. S.; M. Fillios; N. Colman; M. Letnic (27 March 2014). "An updated description of the Australian dingo (Canis dingo Meyer, 1793)". Journal of Zoology. doi:10.1111/jzo.12134. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "crowther" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Science
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Fleming, Peter; Laurie Corbett; Robert Harden; Peter Thomson (2001). Managing the Impacts of Dingoes and Other Wild Dogs. Commonwealth of Australia: Bureau of Rural Sciences. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "impact" defined multiple times with different content - ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Western Australian Dingo Association, archiviert vom Original am 2007-07-06; abgerufen am 17. Mai 2009.
- ^ Clutton-Brock, Juliat (1999). A natural history of domesticated mammals (2 ed.). Natural History Museum (London, England): Cambridge University Press. p. 238. ISBN 9780521634953.
- ^ a b c d e Trumler, Eberhard (1981). Meine wilden Freunde – Die Wildhundarten der Welt (in German). Muenich: R. Piper & Co. Verlag. ISBN 3-492-02483-1.
- ^ a b Allen, Ben: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Invasive Animals CRC, 2008, archiviert vom Original am 2009-04-24; abgerufen am 29. April 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "27kg" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Boitani, Luigi (1984) Simon & Schuster's Guide to Mammals. Simon & Schuster/Touchstone Books, ISBN 978-0-671-42805-1
- ^ a b c d Savolainen, Peter; Leitner, Thomas; Wilton, Alan N.; Matisoo-Smith, Elizabeth and Lundeberg, Joakim (2004). "A detailed picture of the origin of the Australian dingo, obtained from the study of mitochondrial DNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (33): 12387–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.0401814101. PMC 514485. PMID 15299143.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Zimen, Erik (1988). Der Hund: Abstammung – Verhalten – Mensch und Hund (in German) (1. ed.). München: Bertelsmann. ISBN 3-570-00507-0. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "zimen" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Henderson, Bruce; Coates, Michael; Brimhall, Bernadine; Thompson, Judith (1979). "THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF ?T-13 OF GLOBIN FROM A PURE BRED DINGO (CANIS FAMILIARIS DINGO)". Australian Journal of Experimental Biology and Medical Science. 57 (3): 261–3. doi:10.1038/icb.1979.28. PMID 533479.
- ^ a b Wilton, A. N.; Steward, DJ; Zafiris, K (1999). "Microsatellite variation in the Australian dingo". Journal of Heredity. 90 (1): 108–11. doi:10.1093/jhered/90.1.108. PMID 9987915. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "microsatellite" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". ECOS Magazine, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.Template:Cite book/Meldung
- ^ Young, Emma: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". NewScientist, 29. September 2003, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g Feddersen-Petersen, Dorit Urd (2008). Ausdrucksverhalten beim Hund (in German). Stuttgart: Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH & Co. KG. ISBN 978-3-440-09863-9.
- ^ Schassburger, R.M. (1987). "Wolf vocalization: An integrated model of structure, motivation, and ontogeny". In H. Frank (ed.). Man and Wolf. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Dr. W. Junk.
- ^ a b c Brehms Tierleben (in German). Leipzig, Wien: Bibliographisches Institut. 1900. pp. 82–85. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Brehm" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b Corbett, Laurie (1995). The Dingo in Australia & Asia. p. 106. ISBN 0-8014-8264-X. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Corbett" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Ortolani, A., Corbett, L.K., Feinstein, F.H., and R.P. Coppinger. 2001. "A comparative study of larynx anatomy and howling vocalizations in five canids," poster presented at Canid Biology and Conservation Conference, Oxford University, Oxford, UK.
- ^ a b Young, Emma (5 March 2010). "Dingoes skilled at Reading Human Gestures". Australian Geographic. Retrieved 13 January 2013.
- ^ Harden, RH (1985). "The Ecology of the Dingo in North-Eastern New South Wales I. Movements and Home Range". Wildlife Research. 12: 25–37. doi:10.1071/WR9850025.
- ^ Thomson, PC (1992). "The behavioural ecology of dingoes in north-western Australia. II. Activity patterns, breeding season and pup rearing". Wildlife Research. 19 (5): 519–29. doi:10.1071/WR9920519.
- ^ a b c Günther, Janine; Jens Mohr (2007). Das Northern Territory und weiterführende Routen (in German) (1 ed.). Gamehl: 360°. ISBN 978-3-9809763-2-9. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Northern1" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Department of Natural Resources and Water, September 2006, S. 6, abgerufen am 8. April 2009.
- ^ Vernes, Karl; Dennis, Andrew; Winter, John (2001). "Mammalian Diet and Broad Hunting Strategy of the Dingo (Canis familiaris dingo) in the Wet Tropical Rain Forests of Northeastern Australia". Biotropica. 33 (2): 339. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7429.2001.tb00185.x.
- ^ a b c Claridge, Andrew W.; Hunt, Rob (2008). "Evaluating the role of the dingo as a trophic regulator in Australian ecosystems". Ecological Management & Restoration. 9 (2): 116. doi:10.1111/j.1442-8903.2008.00402.x. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "regulator" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Webb, Jonathan K. (2006). "Observation of three Dingoes killing a large Lace Monitor (Varanus Varius)". Australian Mammalogy. l9 (1): 55–6.
- ^ a b c d Lawrance, Kate and Higginbottom, Karen: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Sustainable Tourism Cooperative Research Centre, 2002, abgerufen am 3. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Fraser1" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Thomson, PC (1992). "The behavioural ecology of dingoes in north-western Australia. III. Hunting and Feeding behaviour, and diet". Wildlife Research. 19 (5): 531–41. doi:10.1071/WR9920531.
- ^ Allen, L.R. and Fleming, P.J.S.: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] American Sheep Industry Association, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-29; abgerufen am 3. Mai 2009.
- ^ Thomson, Lee Allen Peter and Lisle, Alan: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Australian Government – Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry, archiviert vom Original am 2007-09-10; abgerufen am 3. Mai 2009.
- ^ Macdonald, David W, ed. (2006). "Other Dogs". The Princeton Encyclopedia of Mammals. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 619.
- ^ a b Burnie, David; Wilson, Don E, eds. (2001). Animal: The Definitive Visual Guide to the World's Wildlife. New York: DK Publishing. p. 185. ISBN 0-7894-7764-5. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "DK" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c d e f g Jackson, Stephen (2003). Australian Mammals: Biology and Captive Management. Collingwood, Victoria: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 0-643-06635-7. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "CSIRO" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Thomson, PC (1992). "The behavioural ecology of dingoes in north-western Australia. IV. Social and spatial organisation, and movements". Wildlife Research. 19 (5): 543–63. doi:10.1071/WR9920543.
- ^ Macpherson, Calum N. L.; et al., eds. (2000). Dogs, Zoonoses, and Public Health. Wallingford: CABI Publishing. p. 31. ISBN 0-85199-436-9.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|editor=(help) - ^ Miklósi, Ádám (2007). Dog Behaviour, Evolution, and Cognition. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 89. ISBN 978-0199545667.
- ^ Trummler, Eberhard; Dietmar Mundo (1984). Das Jahr des Hundes – Ein Jahr im Leben einer Hundefamilie (in German) (1 ed.). Nerdlen: Kynos Verlag. ISBN 3-924008-11-6.
- ^ Jones, E; Stevens, PL (1988). "Reproduction in Wild Canids, Canis-Familiaris, From the Eastern Highlands of Victoria". Wildlife Research. 15 (4): 385–97. doi:10.1071/WR9880385.
- ^ Catling, PC (1979). "Seasonal variation in plasma testosterone and the testis in captive male dingoes, Canis familiaries dingo". Australian Journal of Zoology. 27 (6): 939–44. doi:10.1071/ZO9790939.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Parks and Wildlife Service: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Department of Natural Resources, archiviert vom Original am 2008-09-13; abgerufen am 4. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Nord" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c Moffitt, Ian (1984). Der Australische Busch (in German) (5 ed.). Amsterdam: Time-Life Books. Template:Listed Invalid ISBN. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Ian" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c A.W. Hogstrom: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". University of Nebraska, 1986, abgerufen am 8. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "western" defined multiple times with different content - ^ The Voyage of Governor Phillip to Botany Bay: With an Account of the Establishment of the Colonies of Port Jackson & Norfolk Island By Arthur Phillip, John Marshall, John Stockdale, Henry Lidgbird Ball Published by Printed for J. Stockdale, 1790
- ^ Richard Barwick: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2013-04-20; abgerufen am 7. November 2012.
- ^ Oskarsson, M. C. R.; Klutsch, C. F. C.; Boonyaprakob, U.; Wilton, A.; Tanabe, Y.; Savolainen, P. (2011). "Mitochondrial DNA data indicate an introduction through Mainland Southeast Asia for Australian dingoes and Polynesian domestic dogs". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 279 (1730): 967. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.1395.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Williams, Robyn; Corbett, Laurie; Jenkins, David et al.: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] The Science Show, 23. Juni 2001, archiviert vom Original am 2002-02-12; abgerufen am 8. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "broadcast" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Downward, R. J. and Bromell, J. E.: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". University of Nebraska, 1990, abgerufen am 8. Mai 2009.
- ^ McRae, Alice. (17 April 2013) Aboriginal genetic study suggests Indian migration. Australian Geographic. Retrieved on 31 May 2013.
- ^ DNA study sheds light on aboriginal Australians' heritage – Los Angeles Times. Latimes.com (30 September 2000). Retrieved on 31 May 2013.
- ^ Charles Choi: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". NBC News, 14. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 16. Januar 2013.
- ^ Dampier, William: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Project Gutenberg, 1699, abgerufen am 8. Mai 2009.
- ^ Edmonds, Mike (22 October 2008). "Wild dog rampage in Victoria". heraldsun. Archived from the original on 24 October 2008. Retrieved 8 May 2009.
- ^ Since there is no unity on the definition of a pure dingo respectively it is not known whether the observed dogs were pure dingoes, the term itself is written with quotations in this article to reflect the unsure status of the term and the dogs.
- ^ Newby, Jonica: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". ABC, 31. März 2005, abgerufen am 8. Mai 2009.
- ^ Woodall, PF; Pavlov, P; Twyford, KL (1996). "Dingoes in Queensland, Australia: skull dimensions and the indenity of wild canids". Wildlife Research. 23 (5): 581–7. doi:10.1071/WR9960581.
- ^ Brown, Carmen (4 June 2013). "Tanami dingoes among purest in Australia". ABC Rural. Retrieved 6 June 2013.
- ^ Fiona MacDonald, AAP: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Nine MSN, 9. September 2013, abgerufen am 2. März 2014.
- ^ Short, J; Kinnear, J.E.; Robley, Alan (2002). "Surplus killing by introduced predators in Australia—evidence for ineffective anti-predator adaptations in native prey species?". Biological Conservation. 103 (3): 283–301. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(01)00139-2.
- ^ Wroe, S.; Clausen, P.; McHenry, C.; Moreno, K.; Cunningham, E. (2007). "Computer simulation of feeding behaviour in the thylacine and dingo as a novel test for convergence and niche overlap". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 274 (1627): 2819–28. doi:10.1098/rspb.2007.0906.
- ^ Johnson, C. N.; S. Wroe (2003). "Causes of extinction of vertebrates during the Holocene of mainland Australia: arrival of the dingo, or human impact?" (PDF). The Holocene. 13 (6): 1009–1016. doi:10.1191/0959683603hl682fa.
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 3. August 2008, archiviert vom Original am 2008-08-03; abgerufen am 1. April 2014. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "save" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c "Going to the dogs: DNA evidence is damning dingo's future". The Sydney Morning Herald. 31 August 2002. Retrieved 9 May 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Save Our Snowy, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ Letnic M,Baker L, Nesbitt B, 2013. "Ecologically functional landscapes and the role of dingoes as trophic regulators in south-eastern Australia and other habitats". Ecological Management and Restoration, Vol 14(2) 1-5.
- ^ Corbett, L (1995). "Does Dingo Predation or Buffalo Competition Regulate Feral Pig Populations in the Australian Wet-Dry Tropics? An Experimental Study". Wildlife Research. 22: 65–74. doi:10.1071/WR9950065.
- ^ Mitchell, Bruce D.; Banks, Peter B. (2005). "Do wild dogs exclude foxes? Evidence for competition from dietary and spatial overlaps". Austral Ecology. 30 (5): 581–91. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.2005.01473.x.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". heraldsun.com.au, 28. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 2. Februar 2013.
- ^ Pople, A. R.; Grigg, G. C.; Cairns, S. C.; Beard, L. A.; Alexander, P. (2000). Wildlife Research. 27 (3): 269–76. doi:10.1071/WR99030.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Williams, Brian (5 April 2013). "Stuff the turkeys, dingoes need a break". The Courier-Mail. Retrieved 5 April 2013.
- ^ a b c Trigger, D; Mulcock, J; Gaynor, A; Toussaint, Y (2008). "Ecological restoration, cultural preferences and the negotiation of 'nativeness' in Australia". Geoforum. 39 (3): 1273–83. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2007.05.010. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "heimisch" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b Parker, Merryl: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Animals & Society Institute, 2007, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "cunning" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Wild 'superdogs' may attack people, farmers warn Shanghai Star. Shanghai Star. 27 June 2002. Retrieved 9 May 2009.
- ^ a b c Merryl Ann Parker: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". UTAS ePrints, April 2006, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "bringing" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c d Howard, Peter: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Australian Digital Theses Program, 22. November 2006, archiviert vom Original am 2011-07-06; abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "beastwithin" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b Kolig, E. (1978). Aboriginal dogmatics: canines in theory, myth and dogma. Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde 134. Leiden. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Kolig" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". August 2005, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b c Allen, L.R. and Fleming, P.J.S. (2004). "Review of Canid Management in Australia for the Protection of Livestock and Wildlife – Potential Application to Coyote Management". Sheep & Goat Research Journal. 19: 97.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Invalid<ref>tag; name "ReviewCanid" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Miles, Aden (7 June 2013). "Dingo 'epidemic' on farm". Stuff. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Northern Territory Government, archiviert vom Original am 2009-03-09; abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ Rachel Nowak: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". New Scientist, 26. Juni 2008, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Department of Primary Industries, Dezember 2007, archiviert vom Original am 2008-07-26; abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". ABC News, 24. Oktober 2008, abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Queensland Government, September 2002, abgerufen am 13. Mai 2009.[dead link] Invalid
<ref>tag; name "wilddogs/dingo" defined multiple times with different content - ^ "Pest of the past, dingo's star in the ascendancy". The Age. Melbourne. 22 July 2007. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Department of Natural Resources and Mines, August 2003, archiviert vom Original am 2010-02-20; abgerufen am 13. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Department of Natural Resources and Mines, April 2004, archiviert vom Original am 2010-02-20; abgerufen am 13. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "beefy12" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Allen, L. R.; Sparkes, E. C. (2001). "The Effect of Dingo Control on Sheep and Beef Cattle in Queensland". Journal of Applied Ecology. 38 (1): 76–87. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2664.2001.00569.x. JSTOR 2655734.
- ^ Twigg, Laurie E.; Eldridge, Steve R.; Edwards, Glenn P.; Shakeshaft, Bernie J.; Depreu, Nicki D.; Adams, Neville (2000). "The longevity and efficacy of 1080 meat baits used for dingo control in central Australia". Wildlife Research. 27 (5): 473–81. doi:10.1071/WR99044.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". abc.net.au, 9. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 17. Januar 2013.
- ^ Carrie Walker: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Fraser Coast Chronicle, 8. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 17. Januar 2013.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". The New Zealand Herald, 27. Februar 2013, abgerufen am 27. Februar 2013.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". New South Wales Government, 29. August 2008, abgerufen am 13. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b Brad Purcell, Robert Mulley, Robert Close: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Invasive Animals CRC, 2008, S. 140, archiviert vom Original am 2009-04-24; abgerufen am 13. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "defpure" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c "Australia's dingo dogs face extinction". USA Today. 7 October 2003. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ^ Papalia, Nic: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". About.com, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b Coppinger, Raymond and Lorna (2001). Dogs: A Startling New Understanding of Canine Origin, Behavior, & Evolution. New York: Scribner. pp. 45, 67. ISBN 0-684-85530-5.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Breed standard Dingo. Ankc.org.au (31 August 2009). Retrieved on 31 May 2013.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 11. April 2009, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Beeby, Rosslyn: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] The Canberra Times, 7. Februar 2007, archiviert vom Original am 2009-04-15; abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". DOGSLife, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ Corbett, Lawrence K. (1995) The Dingo in Australia and Asia. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, ISBN 0-8014-8264-X.[page needed]
- ^ Catling, PC; Corbett, LK; Newsome, AE (1992). "Reproduction in captive and wild dingoes (Canis familiaris dingo) in temperate and arid environments of Australia". Wildlife Research. 19 (2): 195–209. doi:10.1071/WR9920195.
- ^ Newsome, AE; Corbett, LK; Carpenter, SM (1980). "The Identity of the Dingo I. Morphological Discriminants of Dingo and Dog Skulls". Australian Journal of Zoology. 28 (4): 615–25. doi:10.1071/ZO9800615.
- ^ Wilton, Alan: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] dingosanctuary, archiviert vom Original am 2004-02-19; abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Fraser Island Defenders Organization, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ Daniels, Mike J.; Corbett, Laurie (2003). "Redefining introgressed protected mammals: when is a wildcat a wild cat and a dingo a wild dog?". Wildlife Research. 30 (3): 213–8. doi:10.1071/WR02045.
- ^ Spencer, Ricky-John; Lapidge, Steven J.; Dall, David and Humphrys, Simon: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Inavisive Animals CRC, S. 149, archiviert vom Original am 2009-01-16; abgerufen am 10. April 2009.Template:Cite book/Meldung
- ^ "Mother jailed in dingo baby murder". BBC-News. 29 October 1982. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ^ "Little hope for baby girl taken by wild dog at Ayers Rock". The Sydney Morning Herald. 19 August 1980. Retrieved 14 May 2009.
- ^ "Coroner Rules That Dingo Snatched Baby". The Wall Street Journal. 12 June 2012. Retrieved 12 June 2012.
- ^ "Findings of Coroners Inquest 12 June 2012". NT Coroners Court. 12 June 2012. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ^ Jane Duckworth. Not Every Dog Has His Day: The Treatment of Dogs in Australia.
- ^ a b Beckmann, E. and Savage, Gillian: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Queensland Government, Juni 2003, abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "evaluationfraser" defined multiple times with different content - ^ a b c [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Environmental Protection Agency, Mai 2001, archiviert vom Original am 2011-04-13; abgerufen am 14. Mai 2009.
- ^ "Girl mauled by Fraser Island dingoes". ABC-News. 26 April 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ a b Walker, Carlie (28 January 2013). "What led to Fraser Island dingo Inky's death". Fraser Coast Chronicle. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ^ Walker, Carlie (15 November 2012). "Hunt continues for 'dangerous' dingo on Fraser". Fraser Coast Chronicle. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ^ Walker, Carlie (5 February 2013). "Seven dingoes culled and another 10 have died on Fraser". Fraser Coast Chronicle. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- ^ Bryant, Cheryl (15 June 2013). "Another dingo death on Fraser Island". Noose News. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ Edwards, Alyse (14 June 2013). "Fraser Island dingo attack prompts Environment Minister Andrew Powell's call for better education". ABC News. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ Carlie Walker: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Fraser Coast Chronicle, 5. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 2. Februar 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Lioncrusher's Domain, archiviert vom Original am 2005-03-07; abgerufen am 9. Mai 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Department of Primary Industries, now Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry (Queensland), abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Callinan, Rory (14 April 2008). "Free the Dingoes, Cage the Humans". TIME. Retrieved 15 May 2009.
- ^ Rudolph, Ellen K.: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Dr. Ellen K. Rudolph, 2003, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Invasive Animals RC, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009. [dead link]
- ^ Taylor, Rob: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Planet Ark, 3. Mai 2007, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Boitani, L. and Ciucci, P.: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Firenze University Press, 1995, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ a b Feddersen-Petersen, Dorit Urd (2004). Hundepsychologie (in German) (4. ed.). Stuttgart: Franck-Kosmos-Verlag & Co. KG. ISBN 978-3-440-09780-9. Invalid
<ref>tag; name "DoritPsychologie" defined multiple times with different content - ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Dingo Care Network, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Hemmer, Helmut (1983). Domestikation, Verarmung der Merkwelt (Domestication: the decline of environmental appreciation) (in German). Braunschweig: Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH. ISBN 3-528-08504-5.
- ^ Trumler, Eberhard (1982). Ein Hund wird geboren; Der Ratgeber für den Hundefreund (in German). Muenich: R. Piper GmbH & Co. KG. ISBN 3-492-02775-X.
- ^ Reed, J. Michael: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 20. Dezember 2004, abgerufen am 2. Mai 2009.
- ^ Wilton, Allan: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Wolfweb, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Jardine, William (1839) The Naturalist's Library. Lizards.
- ^ Hintze, Mary: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Animal Diversity Web, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Doherty, Megan: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] The Canberra Times, 18. Juli 2008, archiviert vom Original am 2008-07-20; abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Roach, John: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". National Geographic News, 10. Dezember 2004, abgerufen am 15. Mai 2009.
- ^ Dayton, L. (2003). "Modern human origins meeting. On the trail of the first dingo". Science. 302 (5645): 555–6. doi:10.1126/science.302.5645.555b. PMID 14576396.
Further reading[edit]
- J.S. Bacon: The Australian Dingo: The King of the Bush. McCarron Bird, Melbourne 1955.
- R. Breckwoldt: A Very Elegant Animal: the Dingo. Angus and Robertson, Australia 1988.
- Deborah Bird Rose: Dingo makes us Human, Life and Land in an Aboriginal Australian culture. Cambridge University Press, New York, Oakleigh 1992, ISBN 0-521-39269-1.
- Chris R. Dickman: A Symposium on the Dingo. Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales, Sydney 1999, ISBN 0-9586085-2-0.
- Erich Kolig: Aboriginal dogmatics: canines in theory, myth and dogma. In: Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde 134. Nr. 1, Leiden 1978, Seite 84–115.
- Peter Fleming, Laurie Corbett, Robert Harden, Peter Thomson: Managing the Impacts of Dingoes and Other Wild Dogs. Bureau of Rural Sciences, Commonwealth of Australia, 2001.
- Western Australian Wild Dog Management Strategy 2005. August 2005.
- Georgette Leah Burns, Peter Howard: When wildlife tourism goes wrong: a case study of stakeholder and management issues regarding dingoes on Fraser Island. Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Griffith University.
External links[edit]
- "Dingo found to be one of the world's oldest dog breeds." From Times Online 18 March 2010. [1]
- BBC story on dingo mitochondrial DNA study
- Pages with reference errors
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 German-language sources (de)
- CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list
- CS1 errors: explicit use of et al.
- CS1 errors: missing title
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from January 2014
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- CS1 errors: access-date without URL
- Articles with dead external links from September 2012
- Wikipedia articles needing page number citations from March 2011
- Articles with dead external links from September 2010
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Wikipedia pages with incorrect protection templates
- Use dmy dates from May 2013
- Use Australian English from February 2012
- All Wikipedia articles written in Australian English
- IUCN Red List vulnerable species
- Articles with 'species' microformats
- Taxoboxes with the error color
- Taxoboxes with the incertae sedis color
- Taxobox articles possibly missing a taxonbar
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from July 2014
- Wikipedia articles needing clarification from May 2014
- Articles with unsourced statements from November 2011
- Articles with unsourced statements from May 2014
- NPOV disputes from October 2014
- All NPOV disputes
- Articles using small message boxes
- All articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases
- Articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases from October 2014
- Articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases from May 2014
- Wikipedia articles needing clarification from July 2014
- Articles with unsourced statements from August 2011
- Articles needing additional references from October 2014
- All articles needing additional references
- Articles with weasel words from May 2014
- All articles with vague or ambiguous time
- Vague or ambiguous time from May 2014
- Articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases from June 2014
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2014
- Wikipedia articles needing clarification from December 2011
- Dogs articles needing expert attention
- Fauna naturalised in Australia
- Vulnerable fauna of Australia
- Mammals of the Northern Territory
- Mammals of Queensland
- Mammals of South Australia
- Mammals of Western Australia
- Megafauna of Australia
- Feral dogs
- Animals described in 1793
- Subspecies of Canis lupus
- Dog landraces


